Table of Contents
What is a X-band Radar?
- X-band radar operates in the 8-12 GHz range (2-4 cm wavelength).
- Its shorter wavelengths make it effective for detecting smaller particles, such as raindrops, fog and fine particulate matter.
- Usage in Wayanad: The radar will monitor particle movement, such as soil shifts, providing real-time data to issue landslide warnings.
Other Radar’s
- Doppler Radar: It is a common weather radar, it tracks movement and speed using the Doppler effect. The radar emits pulses of radiation, which are reflected back by clouds or other particles. The frequency of the reflected waves changes with motion, revealing speed and direction.
- Pulse-Doppler Radar: It measures rainfall intensity by emitting pulses of radiation and measuring how often they are reflected back.
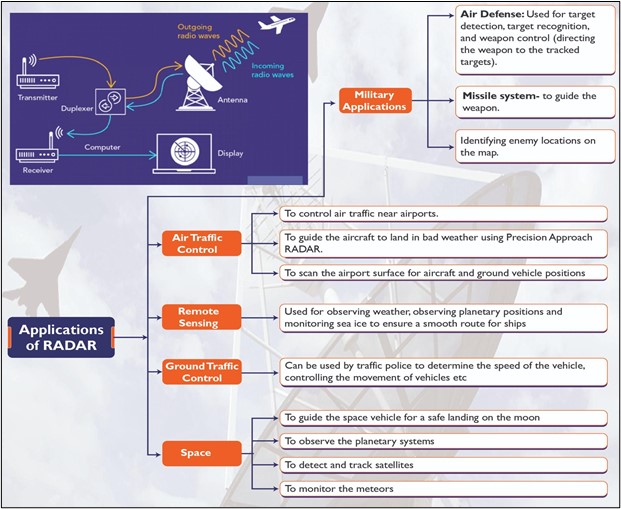
About Radars (Radio Detection and Ranging System)
- It is an electromagnetic system used to notice, track, locate and identify different objects which are at certain distances.
- Working of RADAR’s:
- It transmits electromagnetic energy in the direction of targets to observe the echoes and returns from them.
- Targets can be ships, aircraft, astronomical bodies, automotive vehicles, spacecraft, rain, birds, insects, etc.


 Lok Adalats in India: Meaning, Types, Ca...
Lok Adalats in India: Meaning, Types, Ca...
 New Insurance Bill, 2025: Key Provisions...
New Insurance Bill, 2025: Key Provisions...
 United Nations Environment Assembly (UNE...
United Nations Environment Assembly (UNE...

























