Table of Contents
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has discovered a distant galaxy called “Firefly Sparkle.
Key Findings of James Webb Space Telescope (JWST)
Rate of Expansion: Data from the Webb telescope indicates that the universe’s expansion rate is approximately 8% faster than what is predicted based on current astrophysical models. This phenomenon is known as the Hubble Tension.
| Hubble’s Law |
| It is also known as the Hubble Constant, it says that the universe is expanding at a rate of 67-68 kilometers per second per megaparsec (a megaparsec is 3.26 million light-years). |
- Validation of Hubble’s Findings: The findings corroborate earlier measurements obtained from the Hubble Space Telescope, suggesting that the discrepancies are not due to instrument errors in Hubble.
Understanding Dark Matter and Dark Energy
- Dark Matter: Comprising about 27% of the universe, dark matter is an invisible form of matter inferred from its gravitational effects on visible matter.
- Dark Energy: Believed to constitute approximately 69% of the universe, dark energy is a hypothesized form of energy that drives the accelerated expansion of the universe.
Key Features of Firefly Sparkle
- Formation:
- The galaxy was formed 100–400 million years after the Big Bang.
- Its current observed state shows it as an infant galaxy, still in the process of assembling.
- Size and Structure:
- Mass: About 10 million stars, equivalent to the size of the Sun.
- Neighboring Galaxies: Two smaller neighboring galaxies named Firefly-Best Friend and Firefly-New Best Friend.
- Comparison with the Milky Way: At this stage, Firefly Sparkle is 10,000 times less massive than the present-day Milky Way.
Significance of the Discovery
- Insights into Galactic Formation: Firefly Sparkle provides a direct look at how galaxies like the Milky Way might have looked like in their infancy. Its mass and structure align with theoretical models of early Milky Way-like galaxies.
- Understanding Evolution: Firefly Sparkle represents the early formation phase in the evolutionary process of galaxies.
Gravitational Lensing
- Gravitational lensing is a phenomenon that occurs when a massive celestial body bends and warps space, causing light to bend and magnify.
- This effect allows astronomers to observe objects that would otherwise be too faint or distant to detect.
- Einstein’s General Theory of Relativity describes gravity not as a force between masses, but as the curvature of spacetime caused by mass and energy.
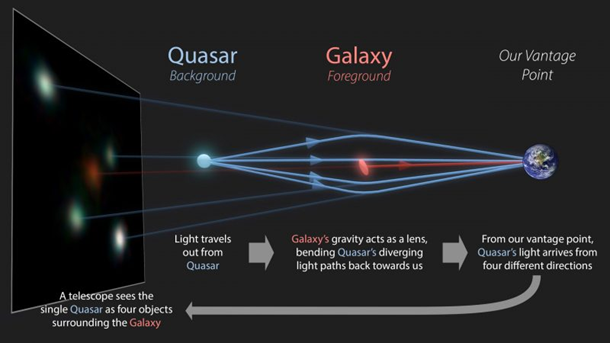
- Gravitational Lenses: The massive objects causing the bending of light are referred to as gravitational lenses. These can be individual stars, galaxies or clusters of galaxies.
- Without this effect, even the advanced JWST would not have been able to observe Firefly Sparkle due to its small size and distance.


 Akashteer System, Purpose, Benefits, Sig...
Akashteer System, Purpose, Benefits, Sig...
 Ozempic Drug Could Reverse Liver Disease...
Ozempic Drug Could Reverse Liver Disease...
 India secures Hawkeye 360 Technology dea...
India secures Hawkeye 360 Technology dea...





















