Table of Contents
Context: A 2021 report by the U.S.- India Strategic Partnership Forum states that the third-gen web will be crucial for India to realize its $1.1 trillion digital asset opportunity by 2032.
What is Web 3?
Web3 is an upcoming Internet development where programs and websites perceive and process information intelligently like humans.
- Web 3 introduces the concept of decentralization in everything it does.
- It is the concept that believes that content and data must be owned and controlled by decentralized autonomous bodies, thus reducing the censorship and centralized control exercised by the Big Tech companies.
- Payments in Web 3 use token-based authentication, thus personal data does not need to be shared with third-party intermediaries
Evolution from Web 1.0 to Web 3.0: The World Wide Web has evolved through different phases since its inception.
- Web 3.0 is the potential next phase of the internet wherein the internet will be decentralised and run on blockchain technology.
- Of the earlier versions, Web 1.0 was mostly static where users would go to a website and read and interact with static information; the differentiating characteristic of Web 2.0 compared to Web1.0 is that users can create content. They can interact and contribute in the form of comments, registering likes, sharing and uploading their photos or videos and perform other such activities.

Need for Web3
- It grants you ownership, it allows you to take control of your digital assets in a unique way.
- Web3 aims to provide solutions to the existing problems of Web 2.0. surrounding breach of security and privacy, and the inability to have control over data are to be addressed in Web3 by assuring the sense of ownership and control.
- It is a trustless, permission-less, and decentralized internet that leverages blockchain technology.
Difference between Web 3.0 and Web3
Web3 and Web 3.0, also known as the decentralized web and semantic web respectively, have different focuses and technologies.
- Web3 emphasizes security and user empowerment by returning control of data and identity to users through blockchain technology, while Web 3.0 focuses on efficiency and intelligence by reusing and linking data across websites using data interchange technologies.
- Data in Web3 is difficult to modify or delete as it is scattered across multiple nodes, while in Web 3.0, data can be changed easily.
- Web3 and Web 3.0 are distinct but overlap and use similar technologies such as AI, Big Data, and Blockchain. The Metaverse is an example of how they interact, with Web3 being a significant contributor to the advancements of Web 3.0.
Key Features: Web 3 is built on four main pillars that will transform the internet as we know it. These are:
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Web 3 will use Natural Language Processing (NLP) to understand spoken and written language. This will enable the internet to analyze and derive the meaning of words, which will be used to improve search results, spell check, spam filtering, and auto-complete.
- Decentralization and blockchain: Web 3 will use blockchain technology, which is a chain of blocks that contains data of previous blocks. This technology will be used to create decentralized systems that run on peer-to-peer (P2P) protocols, reducing the dependency on Big Tech that exists with Web 2.0.
- Ubiquity/ Omnipresence: Web 3 envisions that systems are available anywhere and everywhere, using decentralized servers. This will reduce reliance on centralized servers of big tech companies and make the internet more accessible.
- 3D graphics and spatial web: Web 3 will see the merging of reality with virtual worlds, using sensors, smart glasses, and AR/VR technologies. This will create 3D systems that use NLP and machine learning to enhance user experience.
| Web 3 Strengths: | Web 3 Weaknesses: |
| Web 3.0 offers benefits such as an open network with transparent development, elimination of middlemen, greater user control of data, and decentralized monetization which can benefit professional content creators. | Web3 technology requires a comprehensive overhaul of the current internet architecture, including backend solutions, peer-to-peer communications, and handling blockchain-based business rules. |
| Since information can be accessed from all ends of the web spectrum, it makes data interoperable across different platforms and IoT devices. | Since Web 3.0 is a technology of the future, not all gadgets will be able to operate with it. Newcomers might find it difficult to comprehend. |
| Use of permissionless blockchains thus reducing limitations that exist due to wealth, geographic location, gender, or other demographics. | Regulatory challenges include the potential for new types of cybercrime, hate speech, and misinformation, as well as a lack of accountability for data breaches and content moderation. |
| Removal of a central authority leading to self-governance and distributed ownership. | Since security and ownership are decentralized, it might require a lot of law changes. |
| Improved security because of the distribution, decentralization, and use of blockchain technologies. | There is also concern over the lack of a grievance redressal mechanism and potential difficulty in removing inappropriate content. |
| Reduced dependence on the Big Tech companies. No need to share personal information with third parties when making payments | Since Web 3.0 is a neural network, accessing one’s personal and political data becomes easier. |
Web 3 and India’s Potential Benefits
1: Protecting Handcraft Industry Innovations
- India’s handcraft industry is renowned for design-related innovations, many of which are not protected by Intellectual Property rights. Digital tokens minted by Web 3 platforms can enable handcraft enterprises to secure their innovations.
- Web 3-based instruction tools can enable rapid dissemination of grassroots innovations from master artisans to fellow members.
- This would improve the economic fortunes of craftsmen and artisan communities in north-east, western and peninsular India.
2: Deploying Web 3.0 in Rural Areas
- India’s major digital public infrastructure push and the large-scale deployment of IoT in rural development projects offer major possibilities for deploying Web 3 in rural areas.
- Web 3.0’s (decentralised) analytics systems can overcome the limitation of data analytics capabilities at the community level.
- Web 3.0 can yield insights from large volumes of community data, generated by IoT-enabled development programmes such as the Jal Jeevan Mission.
- Web 3.0 can facilitate ‘analytics at the edge,’ providing considerable scope for mapping the water use habits of communities.
- Early warning systems for floods will improve with Web 3.0 due to data analytics facilities being obtained at the sub-basin level. Web 3.0 will have a transformative role in regionally disadvantaged areas.
3: Drawing upon India’s Talent Pool
- One constraint today is the inability of data analytics capabilities to catch up with the pace of data generation in rural areas. India has a rapidly expanding pool of data analytics and web design talent.
- By providing incentives for decentralised analytics and tokenising them (as envisaged in Web 3), it is possible to draw upon the talent pool for the benefit of rural communities.
4: Crafting a Third-gen Web Strategy
- India’s National Blockchain Strategy 2021 proposes to explore tokenisation and apply blockchain solutions for development programmes.
- It will be a natural progression for India to craft a third-gen web strategy that optimises public interest. Such a strategy should seek to combine the welcome features of Web3 and Web 3.0.

 Pakistan-Occupied Kashmir (PoK): History...
Pakistan-Occupied Kashmir (PoK): History...
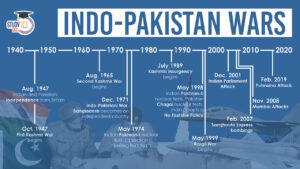 List of Indo-Pakistan Wars and Conflicts...
List of Indo-Pakistan Wars and Conflicts...
 Daily Quiz 24 April 2025
Daily Quiz 24 April 2025






















