Table of Contents
Wave Energy
Wave energy is the movement of waves in the ocean which is in the form of kinetic energy. Waves are created by winds blowing over the ocean’s surface. This energy can be used to run turbines. There are many places where strong winds create continuous waves, providing a lot of energy. Wave energy is captured just below the surface of the waves or from changes in pressure below the surface. This energy can drive a turbine as the wave rises in a chamber, the water’s power pushes air out of the chamber, and this moving air drives the turbine, which then powers a generator.
According to estimates, the world’s total wave resource could contain up to 2 terawatts (TW) of energy, which is equal to all the power used worldwide. Over 40% of the world’s energy needs or the output of over 800 nuclear power plants may be met by wave energy if it is adequately exploited. You will learn about Wave Energy in this article, which will aid you while you study the Environment Syllabus for the UPSC Civil Service exam.
Read about: Nuclear Power Plants in India
What is Wave Energy?
Wave energy is the energy from ocean waves. This energy can be used to make electricity, clean water, and pump water. Wave energy is the biggest ocean energy resource and is renewable. When the wind blows over the ocean, it gives energy to the waves. These waves are very powerful. The energy from waves is measured by their height, speed, length, and the water’s density. Stronger waves can produce more electricity. However, there aren’t many wave power plants because they are hard to build and use.
Read about: Major Ports in India
Wave Energy Presence
Wave energy is most common in Asia and Australia. It is also found in South and North America. Western and Northern Europe have a lot of wave energy. Central America, the Mediterranean Sea, and the Atlantic Archipelagos have less wave energy because of their location. Other renewable energy sources from ocean water movement include tidal energy, ocean current energy, salinity gradient energy, and ocean thermal gradient energy. All of these can be used to produce electricity.
Read about: Hydropower Plants in India
How is Wave Energy Converted into Electricity?
- Wave energy hitting the coast is turned into electricity by a wave energy converter (WEC), which works like a power plant.
- Strong sea waves enter and exit a sealed compartment through a hole at the bottom.
- As the water level rises and falls with the waves, air is pushed through turbines at the top of the chamber.
- Both compressed and uncompressed air can power the turbines.
- The air moves the turbine in the same direction, back and forth.
- The moving turbine turns a shaft connected to a generator, producing electricity.
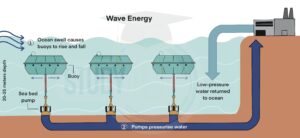
Power is produced by the generator and then distributed to electrical grids, demand centres, and distribution lines that link individual residences and commercial establishments. The benefit of this wave energy converter is that it can generate airflow from even the smallest wave motions, which will keep the turbine spinning and produce energy.
Read about: Manganese Ore
India’s Potential for Wave Energy
India’s 7517 kilometer coastline, with its estuaries and gulfs is ideal for marine energy projects. Wave energy potential in India is between 40 and 60 GW. Ocean energy technologies like wave and tidal are still developing in India. A study by IIT Madras and CRISIL found the western coast has more wind potential than the eastern coast.
Potential wave power areas on India’s west coast include Maharashtra, Goa, Karnataka, and Kerala. Kanyakumari, near the southern tip, has the most power due to refraction and strong winds.
Read about: Minerals
Wave Energy Advantages
1. Highly Predictable
Waves come in a predictable pattern. They store more energy than wind and sun, and they come day and night.
2. Renewable Energy
Wave energy is a renewable resource, so it is always available. It does not need help from people to exist. Humans can use it forever. This makes wave energy a reliable and efficient energy source.
3. Environmentally Friendly
Since wave energy does not release any damaging greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, it is a completely clean energy source.
4. Employment Generation
Wave power can reach places without regular electricity. It can create many eco-friendly jobs for people in both remote and city areas.
5. Beneficial for Remote Areas
Wave energy can be collected and sent to distant places. This can help new industries and businesses grow quickly. Rural areas will see big economic growth in the future.
6. Reliable
Building a strong wave energy system can reduce a country’s reliance on fossil fuels and make its energy supply more secure. Wave energy is cheap, reliable, and efficient, making it a great way to solve energy problems.
7. Unharmed
Offshore wave energy plants can be built, avoiding problems like soil pollution from onshore plants. The land stays natural, unlike fossil fuel extraction, which needs a lot of digging and harms the environment.
Read about: Cobalt Ore
Wave Energy Disadvantages
The disadvantages associated with wave energy are as follows:
1. High Initial Capital Expenses
Building wave energy plants need a lot of money. Issues like maintenance, connecting to the grid, wave resources, and how long the technology lasts make wave energy expensive. It is also hard to know the exact cost because wave energy is still new.
2. Deficiency of the Equipment
The size of ocean waves is very unpredictable. Sometimes, big waves can hit hard and damage the turbines that produce wave energy. Fixing this equipment can be costly and would also stop the electricity supply.
3. Impact on Aquatic Ecosystem
Shallow oceans are key for marine life to rest and breed. Building wave plants can harm the marine ecosystem. Leaks or spills from these plants can contaminate water and kill marine life
4. Locational Problems
Wave energy is limited by location. It benefits people near oceans and seas but can not power everyone. Towns, cities, and countries far from water will not get its advantages.
5. Noise Pollution
Wave energy is clean, but plant generators can be noisy and affect the ocean’s beauty. However, wave noise usually balances out the generator noise.
Read about: Minerals
Wave Energy UPSC
The fact that most wave energy systems are small and insufficient to power large buildings or structures is one of the biggest obstacles to wave energy. Another problem with wave energy is that the amount of energy that may be produced depends on the magnitude of the waves at any given time, just like with solar or wind energy. Wave height, wave speed, wavelength, and wave density are some of the unpredictable factors that have an impact on wave energy. As technology develops, experts are exploring novel ways to generate more electricity from ocean waves.
However, when weighing the advantages and disadvantages of wave energy, the advantages clearly exceed the disadvantages, particularly in this day and age when everyone is focusing on renewable energy sources.
Read about: Cobalt Ore


 Jallianwala Bagh Massacre, Date, History...
Jallianwala Bagh Massacre, Date, History...
 Important Lakes of India, State wise and...
Important Lakes of India, State wise and...
 Buddhism History, Origin, Sect, Councils...
Buddhism History, Origin, Sect, Councils...





















