Table of Contents
About Tungsten (or Wolfram)
- Symbol: W
- Atomic Number: 74
- Appearance: A shiny, silvery-white metal.
- Ores: Scheelite and Wolframite.
- Unique Properties:
- High Melting Point: Highest melting point of all metals at 3,422°C (6,192°F).
- High Density: Density of 3 g/cm³, comparable to gold.
- Hardness: Very hard, especially when alloyed with other metals (measured as 5 on the Mohs scale).
- Excellent Thermal and Electrical Conductivity: High resistance to thermal expansion.
- Corrosion Resistance: Resistant to oxidation and most acids.
- High Tensile Strength: Retains strength at high temperatures.
- Low Vapor Pressure: Does not vaporize easily, even at high temperatures.
| Do you Know? |
|
Real-world Applications of Tungsten
- Electronics and Electrical Industry:
- Filaments in incandescent and halogen bulbs due to its high melting point.
- Electrodes in gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW) due to its high conductivity.
- Semiconductors and X-ray tubes because of its ability to withstand heat.
- Aerospace and Defense:
- Used in high-speed aircraft, missiles, and rocket engine nozzles for its heat resistance.
- Armor-piercing projectiles and radiation shielding due to its high density.
- Manufacturing and Machining: Tungsten carbide (WC), an incredibly hard compound, is used in:
- Cutting tools, drills, and milling instruments.
- Mining tools, wear-resistant parts, and abrasives.
- Medical Sector:
- Radiation shielding in medical imaging (X-rays, CT scans).
- Medical electrodes in surgical instruments.
- Jewelry: Tungsten carbide rings and accessories due to their scratch resistance and durability.
- Automotive:
- High-performance engines and braking systems.
- Counterweights for balancing vehicles.
- Chemical Industry: Catalysts in chemical reactions and petroleum refining.
- Sports and Recreation: Fishing weights, darts, and golf club heads due to its density and durability.
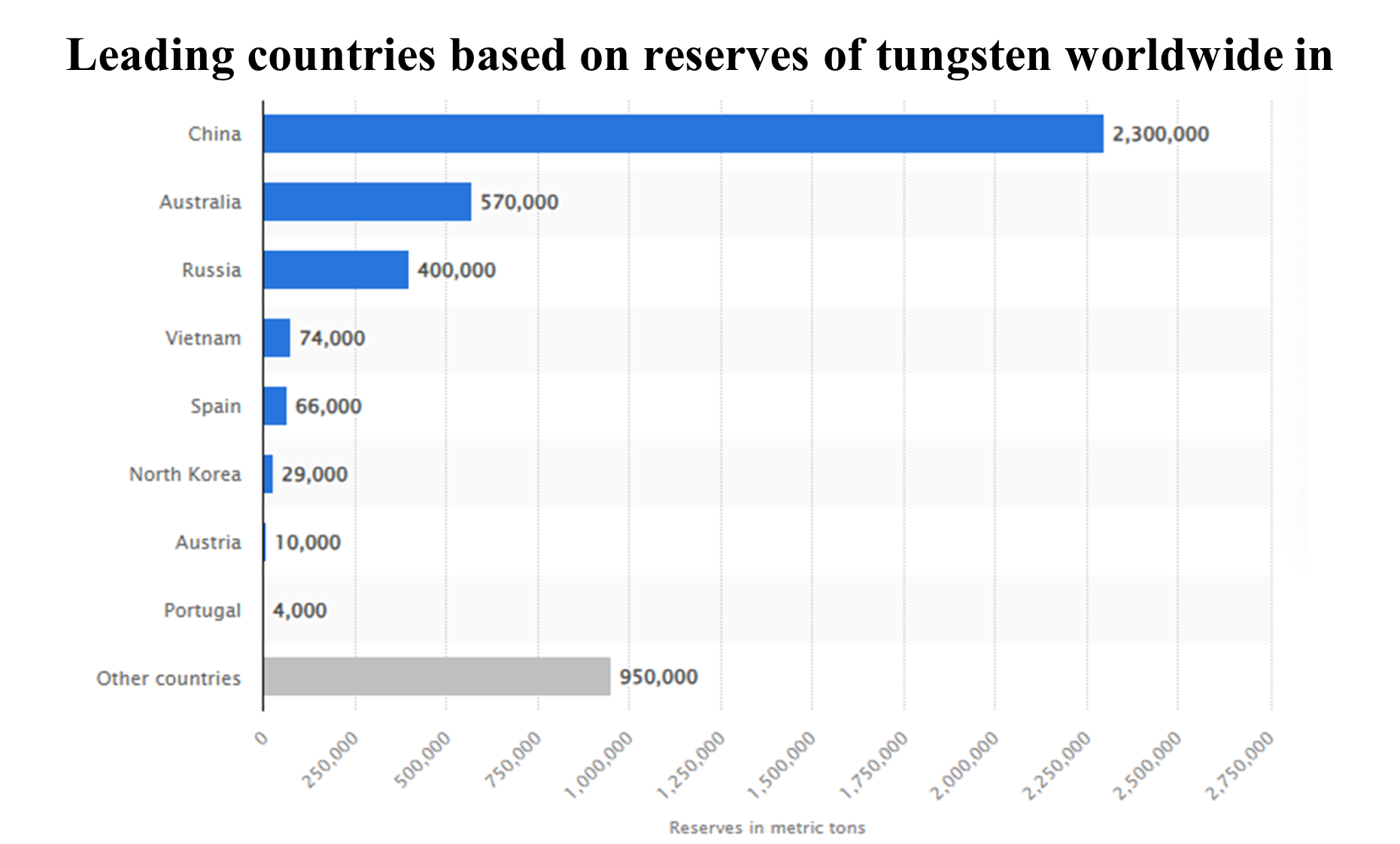
| Fact |
|
| UPSC PYQ |
Q. Consider the following minerals: (2020)
In India, which of the above is/are officially designated as major minerals? a) 1 and 2 only b) 4 only c) 1 and 3 only d) 2, 3 and 4 only Ans: D |


 World Veterinary Day 2025: Theme, Histor...
World Veterinary Day 2025: Theme, Histor...
 Pahalgam Terror Attack: All Eyes on Paha...
Pahalgam Terror Attack: All Eyes on Paha...
 Serious Fraud Investigation Office (SFIO...
Serious Fraud Investigation Office (SFIO...





















