Table of Contents
Context: The recent announcement of President Trump related to reciprocal tariff could be a chance for India to transition from protectionism to a productivity-driven agri-export strategy.
Challenges for India in Trade with the USA
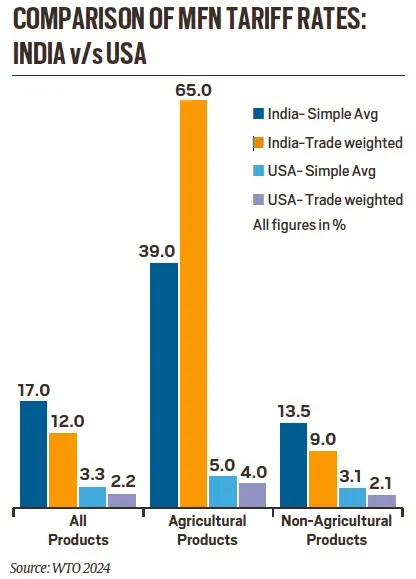
High Tariff Disparities
- India imposes an average tariff of 17% on all goods compared to 3% in the US.
- Agriculture tariffs are especially high in India (39% simple average, 65% trade-weighted) compared to the US (5% and 4%, respectively).
- The US may introduce reciprocal tariffs that could hurt India’s exports, especially shrimp, basmati rice, processed foods, and honey.
Agricultural Trade Imbalance
- India enjoys a trade surplus of $3.46 billion in agricultural trade with the US.
- US exports to India include almonds, cotton, ethanol, and soybean oil, but high tariffs (100-150%) on whiskey, walnuts, chicken legs, and skimmed milk powder are major points of contention.
Genetically Modified (GM) Crop Restrictions
- India bans GM soy and maize, despite rising demand for animal feed and ethanol.
- The US, a global leader in GM crops, wants India to ease restrictions.
Non-Tariff Barriers
- Stringent quality standards, lengthy approval processes, and bureaucratic hurdles impact trade.
- Limited market access for Indian agri-exports in the US due to high import duties on certain products (butter, bovine meat cuts, fruits & vegetables).
Weak Agricultural Infrastructure
- India lacks cold storage, efficient logistics, and export-focused processing units.
- Quality certification and traceability issues hinder global competitiveness.
What Needs to Be Done?
Strategic Trade Negotiations
- Leverage negotiations under Mission 500 (targeting $500 billion bilateral trade by 2030).
- Seek lower duties for high-value agri-exports (bananas, okra, mango pulp).
- Offer phased tariff reductions on walnuts, cranberries, cheese, and skimmed milk powder to facilitate trade.
R&D Investments for Agri-Competitiveness
- Increase agri-R&D spending from <0.5% to at least 1% of agri-GDP.
- Encourage high-yielding crops, sustainable farming practices, and export-driven varieties.
Modernize Agricultural Value Chains
- Expand cold storage, logistics, and supply chain infrastructure.
- Improve quality certification and food safety standards for easier global market access.
- Develop agri-export hubs in key production clusters.
Selective Trade Concessions
- Reduce tariffs on low-impact imports like walnuts and blueberries.
- Gradual tariff reductions on poultry, dairy, and ethanol to balance trade interests.
Policy Shift from Protectionism to Productivity
- Move away from subsidy-heavy agriculture (fertilizers, free power) towards efficiency-driven growth.
- Focus on export-oriented policies rather than heavy tariff barriers.


 Global Pandemic Treaty, Objectives and K...
Global Pandemic Treaty, Objectives and K...
 Shimla Agreement 1972 to 2025: From Peac...
Shimla Agreement 1972 to 2025: From Peac...
 China's Salami Slicing Tactics
China's Salami Slicing Tactics





















