Table of Contents
The Earth’s geography is marked by several lines of latitude that help define climatic and environmental patterns. Among these, the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn are particularly significant as they demarcate the boundaries of the tropical zone. Understanding these lines provides insights into various climatic phenomena and their impact on ecosystems around the world. Know all about the Tropic of Cancer and Capricorn in this article.
Tropic of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn
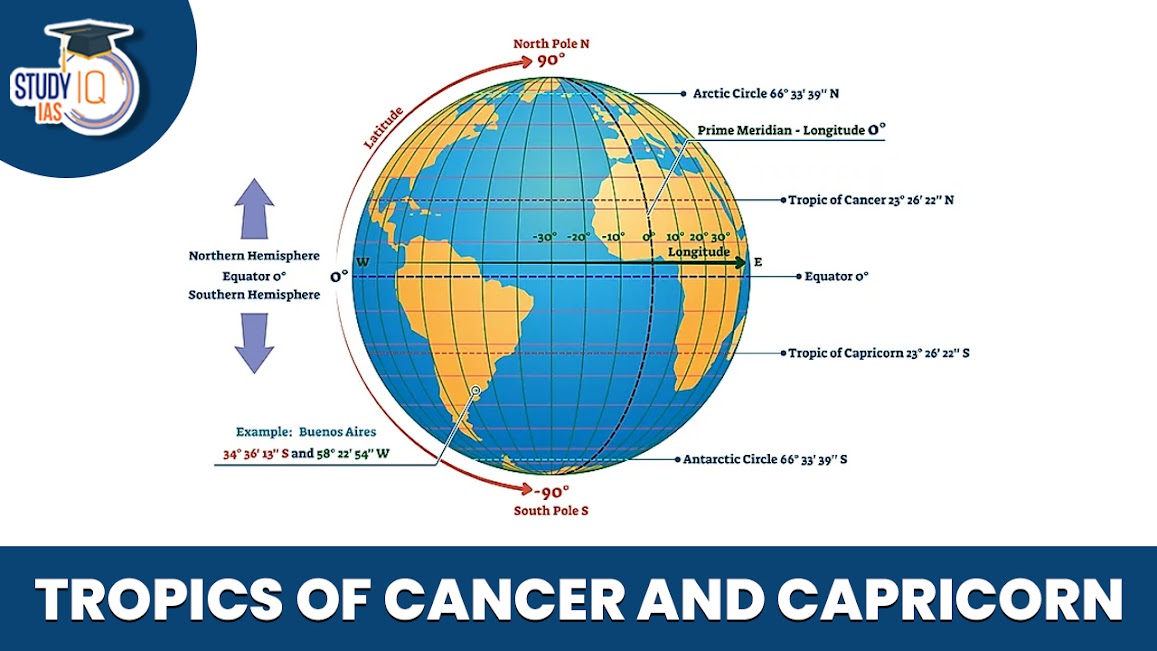
The Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn are significant latitudes located at 23.5 degrees north and south of the equator, respectively. These latitudes mark the boundaries of the tropical climate zone on Earth. Understanding their characteristics, locations, and importance helps in comprehending various natural phenomena and the distribution of life on our planet.
| Aspect | Tropic of Cancer | Tropic of Capricorn |
|---|---|---|
| Location | 23.5 degrees North of the Equator | 23.5 degrees South of the Equator |
| Hemisphere | Northern Hemisphere | Southern Hemisphere |
| Sun’s Position | Sun can be directly overhead at noon twice a year | Sun can be directly overhead at noon twice a year |
| Seasons | Experiences summer solstice in June and winter solstice in December | Experiences summer solstice in December and winter solstice in June |
| Temperatures | Generally warmer temperatures due to its proximity to the equator | Generally cooler temperatures due to its distance from the equator |
Tropic of Cancer
- Location: Situated at 23.5 degrees north of the equator, the Tropic of Cancer passes through 16 nations across three continents and six water bodies, including Mexico, Egypt, India, and the Gulf of Mexico.
- Sun’s Position: During the summer solstice, typically on June 21st, the sun is directly overhead at noon at the Tropic of Cancer, making it the northernmost point where this phenomenon occurs.
- Seasons: Experiences summer solstice in June and winter solstice in December, affecting the seasonal variations in temperature and climate in the northern hemisphere.
- Temperature: Generally warmer temperatures prevail due to the proximity to the equator, contributing to the tropical climate zone.
Tropic of Capricorn
- Location: Positioned at 23.5 degrees south of the equator, the Tropic of Capricorn traverses across ten countries, three continents, and three water bodies, including Brazil, Australia, and the Indian Ocean.
- Sun’s Position: During the summer solstice, which occurs around December 21st in the southern hemisphere, the sun is directly overhead at noon at the Tropic of Capricorn.
- Seasons: Experiences summer solstice in December and winter solstice in June, influencing the seasonal patterns and climate conditions in the southern hemisphere.
- Temperature: Generally cooler temperatures compared to the Tropic of Cancer due to the greater distance from the equator and the tilt of the Earth’s axis.
Importance of Tropic of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn
The Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn hold significant importance due to several reasons:
Importance of the Tropic of Cancer
- Boundary of Tropical Climate Zone: The Tropic of Cancer marks the northern boundary of the tropical climate zone. This area receives the most direct sunlight, leading to warm temperatures and distinct ecosystems.
- Seasonal Variation: The Tropic of Cancer plays a crucial role in seasonal changes, especially in the Northern Hemisphere. It marks the location where the sun is directly overhead during the summer solstice, influencing weather patterns and agricultural cycles.
- Cultural Significance: Throughout history, civilizations have observed celestial events associated with the Tropic of Cancer. The summer solstice, when the sun reaches its highest point in the sky, has been celebrated in various cultures as a symbol of renewal and abundance.
- Biodiversity: Regions near the Tropic of Cancer, such as tropical rainforests and deserts, host diverse flora and fauna adapted to the warm climate. Protecting these ecosystems is essential for preserving global biodiversity.
Importance of the Tropic of Capricorn
- Boundary of Tropical Climate Zone: Similar to the Tropic of Cancer, the Tropic of Capricorn marks the southern boundary of the tropical climate zone. It experiences direct sunlight during the summer solstice in the Southern Hemisphere.
- Seasonal Variation: The Tropic of Capricorn influences seasonal changes in the Southern Hemisphere, experiencing summer solstice during December and affecting weather patterns and agricultural cycles in regions south of the equator.
- Ecological Diversity: The areas surrounding the Tropic of Capricorn, such as the Amazon Rainforest and the Australian Outback, harbor unique ecosystems with species adapted to the warm and diverse climates. Protecting these ecosystems is crucial for global biodiversity conservation.
- Cultural Heritage: Indigenous cultures and ancient civilizations residing near the Tropic of Capricorn have developed traditions and ceremonies based on celestial events and seasonal changes. These cultural practices often reflect a deep connection to the natural world.
Tropic of Cancer and Capricorn UPSC
The Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn are latitudes located 23.5 degrees north and south of the equator, respectively. They mark the boundaries of the tropical climate zones, where the sun is directly overhead at least once a year. These regions play crucial roles in influencing seasonal variations, biodiversity, and cultural traditions across the globe, making them significant for understanding Earth’s climate and ecosystems.

 UPSC CDS 2 Result 2025 Declared at upsc....
UPSC CDS 2 Result 2025 Declared at upsc....
 UPSC to Release Provisional Answer Key A...
UPSC to Release Provisional Answer Key A...
 UPSC NDA 2 Result 2025 OUT – Download ...
UPSC NDA 2 Result 2025 OUT – Download ...




















