Table of Contents
As of March 2025, India has designated 58 protected areas as tiger reserves, covering approximately 82,836.44 square kilometres. These reserves play a crucial role in conserving the country’s tiger population, which, as of 2023, stands at around 3,682 individuals—nearly 75% of the global wild tiger population. Read this article to get the complete details about the List of Tiger Reserves in India.
Tiger Reserves in India
Project Tiger, managed by the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) looks at 58 tiger reserves in India. India is home to 80% of the world’s tigers. According to the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972, the state government must declare an area a Tiger Reserve if the NTCA recommends it. The state must accept this recommendation.
The boundaries of a tiger reserve cannot be changed without approval from the National Board for Wildlife and the NTCA. A state government cannot remove the status of a tiger reserve unless it is in the public interest and approved by both the National Board for Wildlife and the NTCA.
Critical Tiger Habitats (CTH), also called the core areas of tiger reserves, are protected under the Wildlife Protection Act. These areas must be kept safe for tigers while respecting the rights of local tribes and forest dwellers. The state government decides these areas after consulting experts.
| Project Tiger |
|
National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA)
The National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) is a statutory body under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change, Government of India. It was set up in 2005 to protect tigers and their habitats in India. The NTCA is responsible for:
- Formulating and implementing the National Tiger Conservation Strategy and Action Plan (NTCS&AP)
- Overseeing the management of tiger reserves
- Researching tigers and their habitat
- Raising awareness about tiger conservation
List of Tiger Reserves in India 2025
Here is the List of Tiger Reserves in India with states and other relevant information:
| S No. | Name of Tiger Reserves in India | Location | Relevant Info |
| 1 | Bandipur Tiger Reserve | Western Ghats, Karnataka |
|
| 2 | Corbett Tiger Reserve | Himalayan Foothills, Uttarakhand |
|
| 3 | Kanha Tiger Reserve | Central India, Madhya Pradesh |
|
| 4 | Manas Tiger Reserve | Eastern Himalayas, Assam |
|
| 5 | Melghat Tiger Reserve | Satpura Range, Maharashtra |
|
| 6 | Palamu Tiger Reserve | Chota Nagpur Plateau, Jharkhand |
|
| 7 | Ranthambore Tiger Reserve | Aravalli Range, Rajasthan |
|
| 8 | Simlipal Tiger Reserve | Eastern Ghats, Odisha |
|
| 9 | Sunderban Tiger Reserve | Sundarbans, West Bengal |
|
| 10 | Periyar Tiger Reserve | Western Ghats, Kerala |
|
| 11 | Sariska Tiger Reserve | Aravalli Range, Rajasthan |
|
| 12 | Buxa Tiger Reserve
|
Eastern Himalayas, West Bengal |
|
| 13 | Indravati Tiger Reserve | Bastar Plateau, Chhattisgarh |
|
| 14 | Namdapha Tiger Reserve | Eastern Himalayas, Arunachal Pradesh |
|
| 15 | Nagarjunsagar-Srisailam Tiger Reserve | Andhra Pradesh and Telangana |
|
| 16 | Dudhwa Tiger Reserve | Uttar Pradesh |
|
| 17 | Kalakad-Mundanthurai Tiger Reserve | Tamil Nadu |
|
| 18 | Valmiki Tiger Reserve | Bihar |
|
| 19 | Pench Tiger Reserve | Madhya Pradesh |
|
| 20 | Tadoba Andhari Tiger Reserve | Maharashtra |
|
| 21 | Bandhavgarh Tiger Reserve | Madhya Pradesh |
|
| 22 | Panna Tiger Reserve | Madhya Pradesh |
|
| 23 | Dampa Tiger Reserve | Mizoram |
|
| 24 | Bhadra Tiger Reserve | Western Ghats, Karnataka |
|
| 25 | Pench Tiger Reserve | Satpura Range, Maharashtra |
|
| 26 | Pakke Tiger Reserve | Eastern Himalayas, Arunachal Pradesh |
|
| 27 | Nameri Tiger Reserve | Eastern Himalayas, Assam |
|
| 28 | Satpura Tiger Reserve | Central India, Madhya Pradesh |
|
| 29 | Anamalai Tiger Reserve | Western Ghats, Tamil Nadu |
|
| 30 | Udanti-Sitanadi Tiger Reserve | Maikal Hills, Chhattisgarh |
|
| 31 | Satkosia Tiger Reserve | Eastern Ghats, Odisha |
|
| 32 | Kaziranga Tiger Reserve | Assam |
|
| 33 | Achanakmar Tiger Reserve | Maikal Hills, Chhattisgarh |
|
| 34 | Kali Tiger Reserve | Western Ghats, Karnataka |
|
| 35 | Sanjay-Dubri Tiger Reserve | Central India, Madhya Pradesh |
|
| 36 | Mudumalai Tiger Reserve | Western Ghats, Tamil Nadu |
|
| 37 | Nagarhole Tiger Reserve | Western Ghats, Karnataka |
|
| 38 | Parambikulam Tiger Reserve | Western Ghats, Kerala |
|
| 39 | Sahyadri Tiger Reserve | Western Ghats, Maharashtra |
|
| 40 | Biligiri Ranganatha Temple Tiger Reserve | Western Ghats, Karnataka |
|
| 41 | Kawal Tiger Reserve | Deccan Plateau, Telangana |
|
| 42 | Sathyamangalam Tiger Reserve | Western Ghats, Tamil Nadu |
|
| 43 | Mukundara Tiger | Aravalli Range, Rajasthan |
|
| 44 | Nawegaon Nagzira Tiger Reserve | Central India, Maharashtra |
|
| 45 | Amrabad Tiger Reserve | Deccan Plateau, Telangana |
|
| 46 | Pilibhit Tiger Reserve | Terai, Uttar Pradesh |
|
| 47 | Bor Tiger Reserve | Central India, Maharashtra |
|
| 48 | Rajaji Tiger Reserve | Shivalik Range, Uttarakhand |
|
| 49 | Orang Tiger Reserve | Eastern Himalayas, Assam |
|
| 50 | Kamlang Tiger Reserve | Eastern Himalayas, Arunachal Pradesh |
|
| 51 | Srivilliputhur Megamalai Tiger Reserve | Western Ghats, Tamil Nadu |
|
| 52 | Ramgarh Tiger Reserve | Aravalli Range, Rajasthan |
|
| 53 | Ranipur Tiger Reserve | Chitrakoot district, Uttar Pradesh |
|
| 54 | Veerangana Durgavati | Central India, Madhya Pradesh |
|
| 55 | Dholpur-Karauli Tiger Reserve | Aravalli Range, Rajasthan |
|
| 56 | Guru Ghasidas-Tamor Pingla Tiger Reserve | Baghelkhand plateau, Chhattisgarh |
|
| 57 | Ratapani Tiger Reserve | Madhya Pradesh |
|
| 58 | Madhav National Park | Shivpuri district of Madhya Pradesh |
|
Tiger Census 2022
In the 2022 tiger census, India’s tiger population increased to 3682 from 2967 in 2018. The Wildlife Institute of India reports that the upper limit of the tiger population is 3925, with an average of 3682 tigers, showing a 6.1% annual growth rate.
| Tiger Census 2022 |
|
Top 10 Largest Tiger Reserves in India
Check out the top 10 Largest Tiger reserves in India:
| Top 10 Largest Tiger Reserves in India | |||
| S.No | Tiger Reserves | Area | State |
| 1 | Nagarjunsagar Srisailam | 3296.31 sq. km. | Andhra Pradesh |
| 2 | Manas National Park | 3150.92 sq. km | Assam |
| 3 | Melghat Tiger Reserve | 2768.52 sq. km | Maharashtra |
| 4 | Similipal National Park | 2750 sq. km | Odisha |
| 5 | Amrabad Tiger Reserve | 2611.39 sq. km | Telangana |
| 6 | Sunderbans Tiger Reserve | 2584.89 sq. km | West Bengal |
| 7 | Dudhwa Tiger Reserve | 2201.7748 sq. km | Uttar Pradesh |
| 8 | Satpura Tiger Reserve | 2133.30 sq. km | Madhya Pradesh |
| 9 | Namdapha Tiger Reserve | 2052.82 sq. km | Arunachal Pradesh |
| 10 | Kanha Tiger Reserve | 2051.79 Sq.km | Madhya Pradesh |
Tiger Reserves of India Map
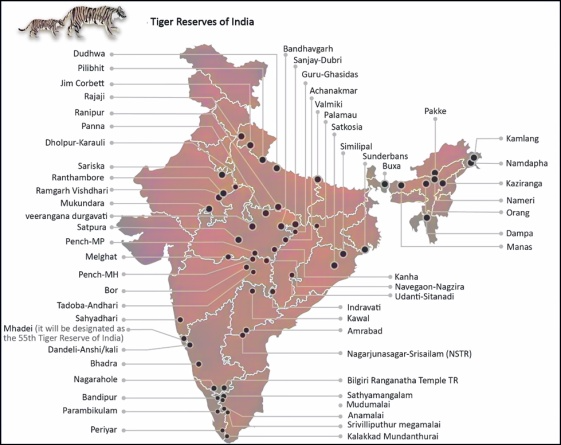
Significance of Tiger Reserves in India
Since the early 1900s, the number of tigers has been decreasing. Tigers have lost 93% of their original habitat. India is home to over 70% of the world’s tigers. Tigers are very important in Indian culture. As the top predators, they help keep ecosystems healthy and diverse. Protecting tiger habitats also helps preserve rivers, reduce soil erosion, and improve services like pollination and water retention.
Threats to Tiger Reserves in India
One of the biggest problems in saving tigers is poaching. Many people hunt tigers because they are sold out with a lot of money. Climate change and global warming are making it hotter forcing tigers and other animals to move to cooler places. Natural disasters like big forest fires are also a big danger. People are taking over tiger habitats for farming, building roads, and grazing cattle. This is a serious threat to where tigers live.
Tiger Reserves in India Conservation Plan
According to the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972’s section 38. v.(3) For the proper management of each area referred to in subsection (1), the State Government shall develop a Tiger Conservation Plan, including a staff development and deployment plan. This will ensure:
- Protection of the Tiger Reserve and provision of habitat inputs specific to the tiger reserve for maintaining a viable population of tigers, co-predators, and prey animals.
- Ecologically friendly land uses that provide dispersing habitat and corridors in tiger reserves and areas connecting one Protected Area (PA) with another PA or tiger reserve.
- The forestry needs of tiger protection are not incompatible with the activities of conventional forest divisions or divisions next to tiger reserves.
- Of the 50 tiger reserves, the TCPs of the following 35 have received NTCA approval, while the other reserves are undergoing preparation or review.
Tiger Conservation Foundation (TCF)
Tiger conservation is a shared duty between the federal government and the states that call for coordinated, creative, and time-bound efforts. Along with updating the ongoing Project Tiger Scheme with increased funding to support the tiger States, the Government of India has launched several ground-breaking efforts in this area. At this level, appropriate institutional adjustments have also been made.
According to section 38X of the Wildlife (Protection) Act of 1972, the State Government must create a Tiger Conservation Foundation (TCF) for tiger reserves located within the State to facilitate and support the management of tiger reserves for the conservation of tigers and associated biodiversity as well as for taking eco-development initiatives through community involvement in the development process.
The Foundation’s goal is to assist and support the management of tiger reserves for the conservation of tigers and biodiversity, through multi-stakeholder participation by approved management plans, and to support related initiatives in neighbouring landscapes by national and state laws.
Schemes for Tiger Reserves in India
There are some schemes launched by the Government of India to protect the Tiger Reserves in India such as:
|
Schemes |
Objectives |
|
Project Tiger |
On April 1st, 1973, Project Tiger was established to support the preservation of tigers in India. It is a fully federally funded program that gives money to the “tiger range States” in order to support in-situ tiger conservation in the selected tiger reserves. The National Tiger Conservation Authority oversees Project Tiger. |
|
Tiger Census |
The National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) and the Wildlife Institute of India (WII), with assistance from several state forest agencies and conservation NGOs, have been leading the government of India’s four-year-old Tiger Census since 2006. |
|
M-STrIPES |
In 2010, a software-based monitoring system called Monitoring System for Tigers – Intensive Protection and Ecological Status was introduced throughout Indian tiger reserves. Its goal is to increase patrolling and oversight of the critically endangered Bengal tiger. |
| St. Petersburg Declaration on Tiger Conservation | In 2010, during the Petersburg Tiger Summit, the leaders of 13 nations that are home to tigers, including India, committed to taking all necessary steps to protect tigers worldwide and to doubling their population in the wild. TX2 was chosen as the initiative’s motto. |
| Related Articles | |
| Mangrove Forests in India | Biosphere Reserves in India |
| Wildlife Sanctuaries of India | Wetlands in India |
| National Parks in India | Rivers of India |


 Antibiotic Pollution in Rivers, Reasons ...
Antibiotic Pollution in Rivers, Reasons ...
 National Environmental Engineering Resea...
National Environmental Engineering Resea...
 Tiger Reserves in Madhya Pradesh List an...
Tiger Reserves in Madhya Pradesh List an...





















