Table of Contents
Context
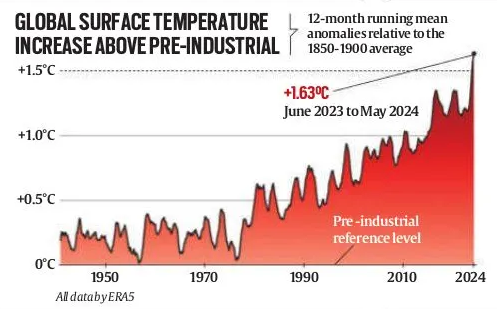
- Over the past year, each month has consecutively set a new record for being the warmest of that specific month, according to Europe’s Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S).
- The 12-month period from June 2023 to May 2024 averaged 1.63 degrees Celsius above the same baseline.
The 1.5°C Threshold/ Paris Agreement
- The 2015 Paris Agreement aims to keep global temperatures “well below” 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels by 2100, with a preference for staying within a 1.5-degree Celsius limit.
- The 1850-1900 period is generally used as the baseline for these measurements due to its reliable, near-global climate data.
- Significance of 1.5°C Threshold: Exceeding 1.5°C for extended periods could lead to irreversible and catastrophic climate change impacts.
- When will it be breached?: The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) projects an 80% chance that at least one year between 2024 and 2028 will exceed a 1.5-degree Celsius increase over pre-industrial levels, marking a historical first.
- What happens if it’s breached?: Increased sea-level rise, intense floods, droughts, wildfires, and other devastating consequences.
- Evidence of Climate Change Impacts:
- Extreme Heat Waves: The severe heatwave in North and Central India in May 2024, with temperatures near 50°C, was about 1.5°C warmer than previous heatwaves and caused hundreds of deaths.
- Coral Bleaching: The fourth global mass coral bleaching event was triggered by exceptionally high ocean temperatures, threatening marine life and livelihoods.
- Climate Tipping Points: Five major climate tipping points, critical thresholds that lead to irreversible changes, are at risk due to global warming. These include:
- Cryosphere: Melting of the Greenland ice sheet.
- Ocean-Atmosphere: Changes in water temperature.
- Biosphere: Death of coral reefs.
El Niño and Global Warming
- The year 2023 was the warmest calendar year on record, partly exacerbated by an El Niño event, known for causing widespread warming of ocean surface temperatures.
- The ongoing El Niño is expected to transition to La Niña, potentially moderating temperatures, but the 1.5-degree Celsius threshold is still likely to be breached temporarily in the next five years.
Required Global Actions
- GHG Emissions: Immediate and substantial reductions in greenhouse gas emissions, particularly from burning fossil fuels, are necessary to stay within the 1.5-degree limit.
- Example: Carbon dioxide levels in 2023 saw one of the highest annual increases in the past 65 years.
- Global Responsibility: As emphasised by UN Secretary-General António Guterres, urgent global action is required to divert from the current trajectory towards severe and irreversible climate impacts.


 National Maritime Day 2025, Theme, Histo...
National Maritime Day 2025, Theme, Histo...
 International Day for Mine Awareness and...
International Day for Mine Awareness and...
 List of Military Exercises of India 2024...
List of Military Exercises of India 2024...





















