Table of Contents
Context: International observers have expressed concerns about rising tensions in the Arctic, cautioning that if not addressed, they could potentially lead to conflict in the region.
Current Scenario in the Arctic
- The Arctic is witnessing rising geopolitical tensions as climate change accelerates ice melting, unlocking new opportunities for resource extraction, trade routes, and military expansion.
- Nations such as Russia, the U.S., Canada, Denmark, and China are asserting their claims and strategic interests, leading to growing concerns over potential conflict.
- NATO and Russia are increasing military posture in the region, with Russia maintaining a strong icebreaker fleet and military bases, while NATO allies, including Sweden and Finland, are expanding their Arctic presence.
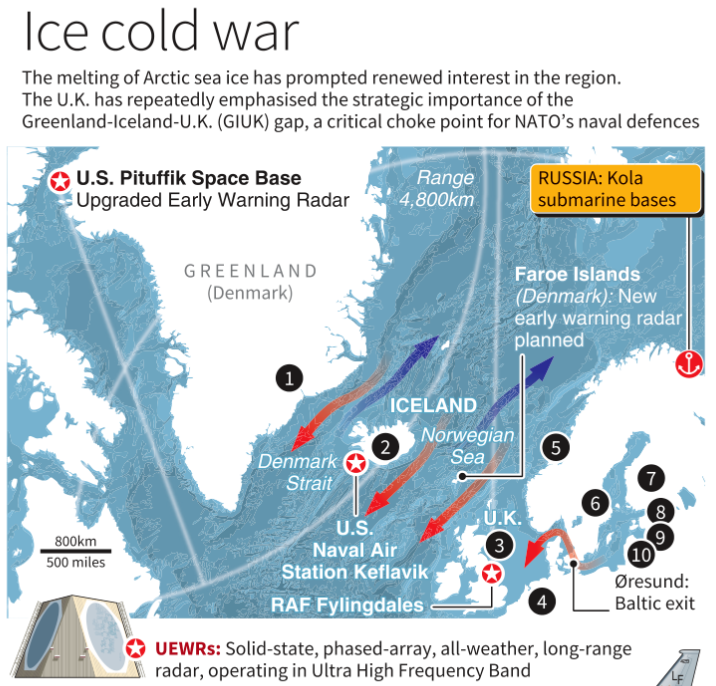
| How Has Russia Made Its Presence Known in the Arctic? |
|
Why is the Arctic Crucial?
- Resource Reserves: The Arctic is estimated to hold 13% of the world’s undiscovered oil and 30% of its untapped natural gas reserves, along with rare earth elements, phosphates, and copper, making it a key battleground for energy security.
- New Trade Routes: Melting ice is opening up strategic shipping routes like the Northeast Passage (along Russia’s coast) and the Northwest Passage (through Canada), potentially reducing maritime travel distances between Asia and Europe.
- Strategic Significance: The Arctic has become an area of military interest, particularly for NATO and Russia. The Greenland-Iceland-U.K. (GIUK) gap is a key naval choke point.
How is the Arctic Controlled?
| Arctic Council |
|
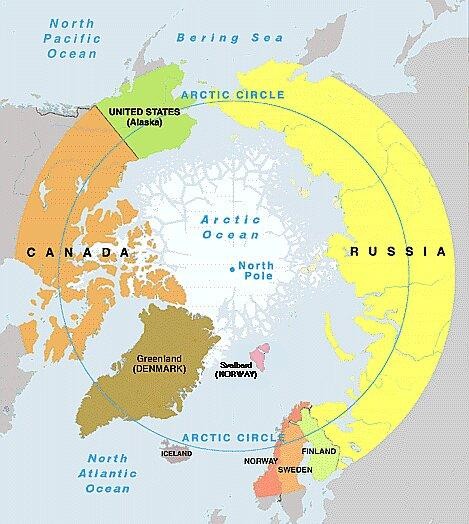
- Sovereign Territories: Eight Arctic nations (Permanent members of the Arctic Council) control land and resources within their Exclusive Economic Zones (EEZs).
- UNCLOS Regulations: Nations can extend claims beyond their 200-nautical-mile EEZ if they prove the seabed is a natural extension of their continental shelf. Overlapping claims by Russia, Canada, and Denmark remain unresolved.
What Lies Ahead?
- Geopolitical Rivalries Intensifying: U.S.-Canada disputes over the Northwest Passage, Russia’s military buildup and China’s growing Arctic ambitions are expected to fuel tensions.
- Increased Militarization: Russia and NATO are conducting military drills in the Arctic, while China is developing nuclear-powered icebreakers to expand its presence.
- Expanded Commercial Interests: As Arctic sea routes become more viable, countries will compete for economic benefits, particularly in resource extraction and shipping.
- Environmental and Legal Challenges: Rising global temperatures and the absence of a comprehensive Arctic treaty (like the Antarctic Treaty) may lead to uncontrolled exploitation, further straining international relations.


 Indus Water Treaty 1960 Suspended by Ind...
Indus Water Treaty 1960 Suspended by Ind...
 Places in News for UPSC 2025 for Prelims...
Places in News for UPSC 2025 for Prelims...
 Tobacco Cultivation in India: Relief to ...
Tobacco Cultivation in India: Relief to ...





















