Table of Contents
Context: Recently, NITI Aayog released its 4th evaluation report on India’s progress on the 16 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) adopted by the United Nations in 2015.
India’s SDG Progress: Key Data from The Report
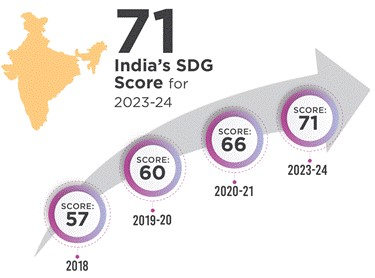
Overall India Score
- 2023-24: 71 points out of 100
- 2020-21: 66 points out of 100
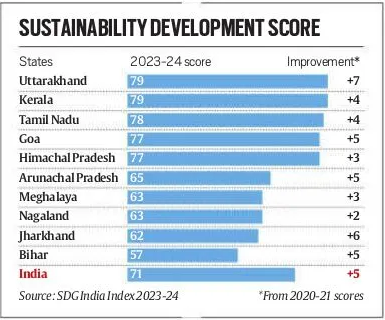
- Top Performing States
- Kerala: 79 points out of 100
- Uttarakhand: 79 points
- Lowest Performing States
- Bihar: 57 points
- Jharkhand: 62 points
- States with Highest Increase in Scores (compared to 2020-21)
- Punjab: Increased by 8 points to 76
- Manipur: Increased by 8 points to 72
- West Bengal: Increased by 8 points to 70
- Assam: Increased by 8 points to 65
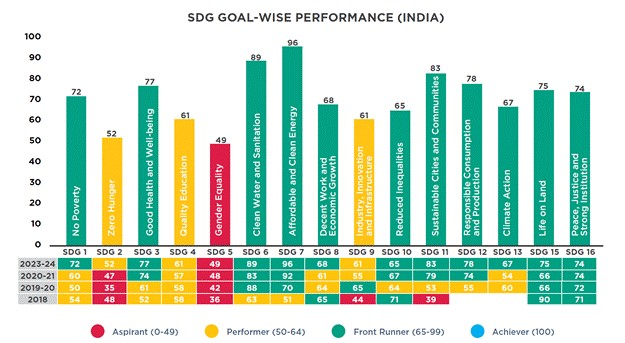
- Goals with Highest Increase in Points
- No Poverty
- Decent Work and Economic Growth
- Life on Land
- Goals with the Smallest Increase in Points
- Gender Equality
- Peace, Justice, and Strong Institutions
- Goals with Decrease in Points:
- Reduced Inequalities: Decreased from 67 points in 2020-21 to 65 points in 2022-23
- Specific Goal Scores
- Gender Equality: Lowest score of 49 points, increased by 1 point from 2020-21
- Zero Poverty: Increased by 8 points to 72
- Zero Hunger: Increased by 5 points to 52
- Quality of Education: Increased by 4 points to 61.
Related information:
- The report noted a slight drop in the ratio of women’s earnings compared to men, from 0.75 in 2020-21 to 0.73.
Read this article below to learn all about the Sustainable Development Goals that were adopted by the United Nations in 2015. SDGs) are a significant topic for the UPSC Syllabus. The UPSC Mock Test can help candidates prepare for the exam with more precision.
Sustainable Development Goals
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), commonly referred to as the Global Goals, are a collection of 17 interconnected objectives that serve as a shared framework for world peace and prosperity both now and in the future.
A method called sustainable development tries to meet human development goals while letting natural systems meet human demands for vital ecosystem functions and natural resources. The term “sustainable development” was originally used in the 1987 report Our Common Future by the Brundtland Commission. Sustainable development (SD) refers to a coordinated Endeavour to build an equitable, sustainable, and resilient future for people and the earth.
Agenda of Sustainable Development Goals
The Sustainable Development Goals are the blueprints for attaining a better, more sustainable future for everyone. In other words, the Sustainable Development Goals are a set of 17 pointers that all UN members have agreed to work towards to better the future of their respective nations. In the film “Future We Want,” which was shown at the Rio+20 conferences, a post-2015 development agenda was suggested.
As the post-2015 development agenda, the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are an intergovernmental agreement that takes the role of the Millennium Development Goals. The United Nations General Assembly’s Open Working Group on Sustainable Development Objectives established 17 goals with 169 targets and 304 indicators that must be achieved by 2030.
The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, often known as “Transforming Our World,” was formed during the United Nations Sustainable Development Summit. The SDGs, which are non-binding documents, were developed by the Rio+20 summits in Rio de Janeiro in 2012.
17 Sustainable Development Goals List
The United Nations created the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), a list of 17 objectives, as part of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development in 2015. By 2030, the SDGs seek to eradicate poverty, safeguard the environment, and promote prosperity for all. The 17 goals are:
| S. No. | Name of SDG |
| 1. | No Poverty |
| 2. | Zero Hunger |
| 3. | Good Health and Well-being |
| 4. | Quality Education |
| 5. | Gender Equality |
| 6. | Clean Water and Sanitation |
| 7. | Affordable and Clean Energy |
| 8. | Decent Work and Economic Growth |
| 9. | Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure |
| 10. | Reduced Inequalities |
| 11. | Sustainable Cities and Communities |
| 12. | Responsible Consumption and Production |
| 13. | Climate Action |
| 14. | Life Below Water |
| 15. | Life On Land |
| 16. | Peace, Justice and Strong Institutions |
| 17. | Partnerships for the Goals |
The SDGs are interconnected and are intended to address some of the most important issues facing the globe today, including violence, poverty, inequality, climate change, and environmental degradation. Collaboration and engagement between governments, civic society, the private sector, and individuals are necessary to achieve the SDGs.
Sustainable Development Goal Explanations
- No Poverty: Put an end to poverty in all its manifestations worldwide.
- Zero Hunger: End hunger, achieve greater nutrition and food security, and advance sustainable agriculture.
- Good Health & well-being: Ensure healthy lifestyles and encourage well-being for everyone of all ages.
- Quality Education: Make sure all students have access to high-quality, inclusive education, and encourage possibilities for lifelong learning.
- Gender Equality: Obtain gender parity and give all women and girls more power.
- Clean Water and Sanitation: Make sure that everyone has access to water and is managed sustainably.
- Affordable and Clean Energy: Ensure that everyone has access to modern, sustainable, cheap energy.
- Decent Work and Economic Growth: Encourage consistent, equitable, and sustainable economic growth, complete and productive employment, and respectable employment for all.
- Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure: Construction of robust infrastructure, encouragement of inclusive and sustainable industrialization, and support of innovation.
- Reduced Inequality: Lessen inequality both within and across nations
- Sustainable Cities and Communities: Make human settlements and cities inclusive, secure, hardy, and sustainable.
- Responsible Consumption and Production: Ensure sustainable patterns of production and consumption.
- Climate Action: To combat climate change and its effects, take immediate action.
- Life Below Water: Conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas, and marine resources.
- Life on land: Protect, restore, and encourage sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems, sustainably managed forests, fight against desertification, and prevent, reverse, and stop biodiversity loss.
- Peace, justice, and strong institutions: Promote inclusive and peaceful societies for sustainable development, ensure that everyone has access to justice, and create inclusive institutions at all levels.
- Partnership for the goals: the global collaboration for sustainable development should be strengthened and revitalized.
Sustainable Development Goals Core Elements
In order to build a more sustainable future for all people, the United Nations General Assembly adopted a set of global goals known as the Sustainable Development Goals or SDGs. The main components of these sustainable development objectives are listed below.
Economic Growth
The SDGs seek to advance sustainable economic growth that benefits all people, especially the most marginalized and vulnerable. This includes making sure that economic growth is inclusive, abundant in jobs, and long-term sustainable.
Social Inclusion
By guaranteeing that everyone has an equal opportunity to engage in the economy and society, regardless of their background or circumstances, sustainable development goals seek to promote social inclusion. Addressing challenges like poverty, injustice, and discrimination is part of this.
Environmental Sustainability
By encouraging sustainable development that preserves and regenerates the natural environment, sustainable development goals seek to safeguard the world and its resources for coming generations. Addressing problems like climate change, deforestation, biodiversity loss, and land degradation is part of this.
Sustainable Development Goals in India
India is a UN member and a participant in the UN General Assembly’s SDG project. The Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) India Index Baseline Report, which examines the nation’s development in detail, was also released by the NITI Aayog. The progress India has made towards achieving these 17 Sustainable Development Goals is detailed here; The Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MNREGA) was implemented across the nation to give unskilled labourers meaningful employment while also raising their level of living.
The National Food Security Act was put into place to guarantee affordable access to food grains for everyone. To end open defecation in India, the government of India established its flagship program, Swachh Bharat Abhiyan. The target generation of renewable energy is 175 GW. By adopting renewable energy sources like solar energy, wind energy, and others, we can lessen our reliance on non-renewable resources like fossil fuels by the year 2022.
The Heritage City Development and Augmentation Yojana (HRIDAY) and Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT) programs were introduced to enhance the nation’s infrastructure. India has made clear that it is determined to combat climate change after signing the Paris Agreement.
Sustainable Development Goals Significance
The goal of sustainable development is to balance social, economic, and environmental concerns in order to build a more sustainable future. Many factors make sustainable development vital, including In order to reduce the detrimental effects of human activity on natural resources, sustainable development emphasizes sustainable practices.
Additionally, it raises economic growth, creates jobs, and raises people’s standards of living. By minimizing the use of non-renewable resources, boosting resource efficiency, and reducing waste, sustainable development encourages the efficient use of resources. Encouraging the use of renewable energy sources, lowering greenhouse gas emissions, and supporting sustainable transportation systems, also combats climate change.
Sustainable Development Goals Impact
By 2030, sustainable development objectives are expected to improve the quality of life on Earth. The plan was approved in 2015, and reports provided by the UNDP up until 2020 show that numerous activities have been made for the benefit of the country and an increase in people’s standard of living worldwide.
The Maternal Mortality Rate has decreased as a result of the Sustainable Development Goals, which have also helped to alleviate poverty, enhance public health, raise awareness of both communicable and non-communicable diseases, as well as the importance of childhood vaccinations. Better medications are being developed, and mental illness is also being prioritized as a serious concern.
Overall, the Sustainable Development Goals aim to improve the quality of life for all by removing poverty, enhancing health, creating jobs, empowering women, reducing inequalities, and adhering to all seventeen targets set by the UN within the allotted time period of 15 years.
Sustainable Development Goals Challenges
Setting larger-scale sustainable development objectives presents some difficulties. The biggest obstacles occasionally prevent the achievement of the objectives for sustainable development.
- The achievement of sustainable development goals is hampered by the continuation of inequality in some nations.
- The youth unemployment rate.
- The acceleration of the growth in CO2 concentrations and global warming.
- The deterioration of ocean chemistry
Sustainable Development Goals 2030
The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and SDGs were introduced by the United Nations (UN) in order to mainstream sustainable development. Over the next 15 years, this global, integrated, and revolutionary agenda intends to inspire activities that will end poverty and create a more sustainable society.
By 2030, there are 169 particular goals that must be accomplished. Action is needed on all fronts to achieve the goals; everyone has a part to play, including businesses, governments, civil society organizations, and everyday people.
Sustainable Development Goals UPSC
The UPSC may ask questions related to the SDGs, such as the 17 goals and their targets, the progress made towards achieving the SDGs, challenges in implementing the SDGs, and the role of various stakeholders in achieving the SDGs. To prepare for questions related to the SDGs, it is important to have a clear understanding of each of the 17 goals and their targets, as well as the interlinkages between them. Students can read all the details related to UPSC by visiting the official website of StudyIQ UPSC Online Coaching.


 UDAN Scheme, Objectives, Funding and Ach...
UDAN Scheme, Objectives, Funding and Ach...
 5 Years of SVAMITVA Scheme and Its Benef...
5 Years of SVAMITVA Scheme and Its Benef...
 Anaemia Mukt Bharat: India’s Fight Aga...
Anaemia Mukt Bharat: India’s Fight Aga...





















