Table of Contents
Context: Recently Bharti Airtel and Reliance Jio have signed separate agreements with SpaceX to bring Starlink internet services to India.
About Starlink Satellite Project
| Aspect | Details |
| Launched | 2019 |
| What is Starlink Satellite Project? | It is a SpaceX project aimed at building a broadband network using a cluster of thousands of orbiting satellites. |
| Purpose | To build a broadband network providing satellite-based internet to the remotest corners of the world. |
| Method | Deployment of a constellation of low Earth orbit (LEO) satellites. |
| Altitude | Starlink satellites will be positioned in the altitude range of 350 km to 1,200 km within the LEO, which extends up to 2,000 km above Earth’s surface. |
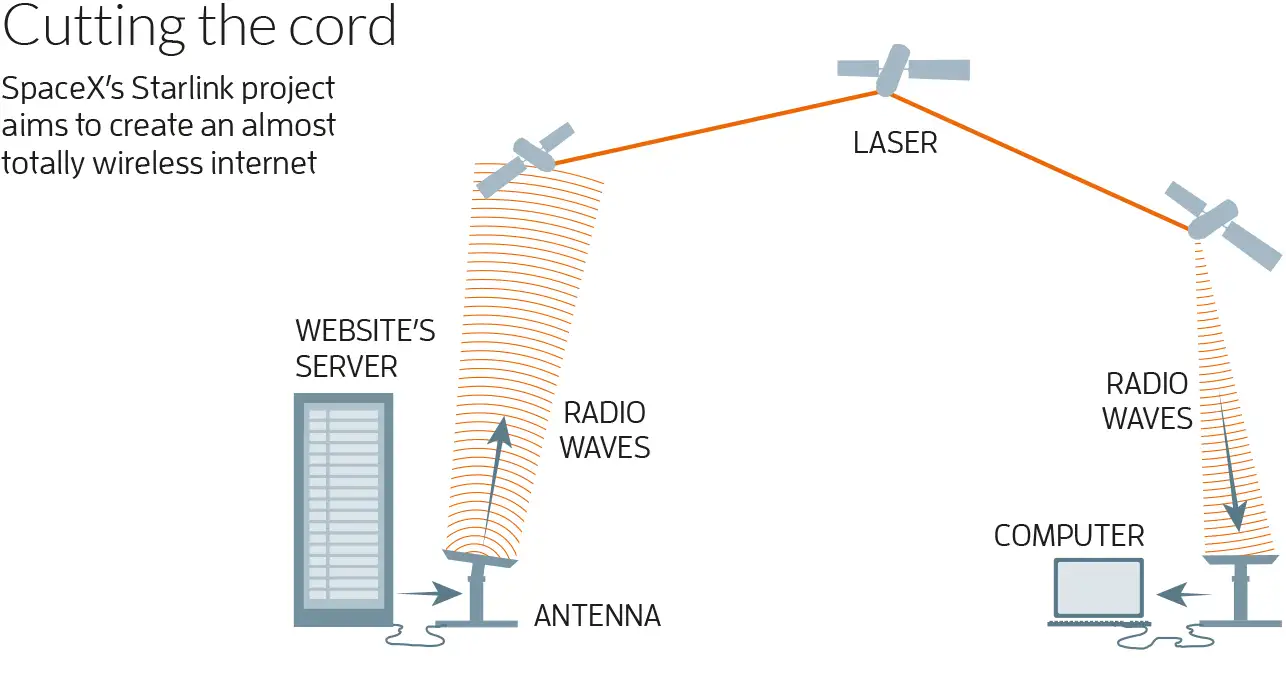
About Starlink
- Starlink is a satellite-based internet service developed by SpaceX (founded by Elon Musk).
- It uses a constellation of low Earth orbit (LEO) satellites (orbiting at ~550 km) to deliver high-speed, low-latency broadband.
- It supports high data-rate activities like streaming, gaming and video calls, making it popular in: Remote areas, Disaster zones & Locations with restricted internet access.
- The project was launched in 2019 and aims to deploy 42,000 small satellites in low Earth orbit (LEO) (under 2,000 km altitude).
- Currently, around 7,000 Starlink satellites are operational in space at an altitude of 547 km.
Advantages of Starlink Project
- Reduced Latency: Due to the satellites being in LEO, there is a reduced latency between sender and receiver.
- Accessibility: Capable of delivering internet to remote areas where traditional methods, like fibre-optic cables, have failed.
Disadvantages of Starlink
- Space Debris: The simultaneous launch of thousands of new satellites will significantly increase the load on near-Earth space. Inevitably, some of these satellites will crash, contributing to the space debris population.
- Risky Flights: Starlink has often been accused of conducting flights that come dangerously close to other satellites.
- Interference with Observations: Astronomers worry that the size and scope of projects like Starlink will interfere with observations of the universe due to the bright, orbiting objects.
- Climate Impact: The deorbiting of old satellites will burn a significant amount of metal in the Earth’s atmosphere, which could lead to unpredictability in the planet’s climate.
| What is Satellite Internet? |
|
Comparison with Geostationary Satellite Internet
- Advantages of Geostationary Satellites:
- Better Coverage: Fewer satellites (approximately 3 or 4) are needed to cover the entire Earth.
- Stationary Appearance: Satellites appear stationary relative to Earth, simplifying linkage.
- Disadvantages of Geostationary Satellites:
- High Latency: Due to their higher placement at 35,786 km above the Earth’s equator, they experience higher latency.
India and Space Internet
Indian Space Policy-2023
- Allows non-government entities (NGEs) to provide national and international space-based communication services via self-owned, procured, or leased geostationary and non-geostationary satellite orbit systems.
GMPCS License Holders
- Only two firms have a Global Mobile Personal Communication by Satellite (GMPCS) licence from the Department of Telecommunications:
- Reliance Jio
- Bharti Airtel Ltd. in partnership with the United Kingdom government’s OneWeb, merged with the French firm Eutelsat.
How Does Starlink Control Access?
- Signal Encryption: Prevents hacking or interception of satellite transmissions.
- Geofencing: Terminals are geographically restricted to areas authorized for service.
- Eg. A Starlink device bought in the U.S. might not work in India unless its geographic location is reconfigured.
Challenges
- Precise international border coverage is difficult due to:
- Contested borders.
- Satellites transmit across moving boundaries.
- Devices purchased abroad may bypass restrictions if not regulated.
Starlink’s Regulatory Status in India
- Unapproved Service: Starlink has not received regulatory approval in India under the Indian Wireless Act and Indian Telegraph Act.
- Legislation: Section 6 of the Indian Wireless Act and Section 20 of the Indian Telegraph Act prohibit the use of satellite-based communication devices like Thuraya or Iridium phones without approval.
- App Availability: Despite bans, the Starlink app is downloadable in India, unlike restricted apps like TikTok.
Why Are the Starlink Deals Significant for India?
- Bridging the Digital Divide:
- India is the world’s second-largest Internet market, yet 670 million people (out of 1.4 billion) lack Internet access (as per a 2024 GSMA report).
- Enhancing Nationwide Connectivity: Starlink can provide broadband in remote and underserved areas where fibre-optic or wireless networks are scarce.
Potential Economic and Social Impact
- Supports digital inclusion by providing high-speed Internet in rural areas.
- Boosts education, healthcare, and e-commerce in remote regions.
- Enables better disaster response by ensuring uninterrupted connectivity in emergencies


 Vitamin D Deficiency: Causes, Symptoms a...
Vitamin D Deficiency: Causes, Symptoms a...
 GAURAV: Long Range Glide Bomb (LRGB)
GAURAV: Long Range Glide Bomb (LRGB)
 Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM), Cau...
Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM), Cau...





















