Table of Contents
About Shale Gas
- It is a type of natural gas that is trapped in shale rock formations underground.
- Shale Rock:
- Shale is the most common sedimentary rock on Earth, making up about 70% of sedimentary rocks in the Earth’s crust.
- It is formed from the compaction of clay, silt, mud, and organic matter.
- It is a clastic sedimentary rock, e. it’s formed from the fragments and sediments of pre-existing rock that have undergone physical weathering.
- Composition of Shale gas:
- It is a mixture of hydrocarbon gases, primarily methane (70–90%)
- Other gases: Ethane, Propane, Butane, Carbon dioxide, Nitrogen, Helium and Hydrogen sulphide
- Extraction Process:
- Shale gas is extracted through a process called hydraulic fracturing or fracking.
- In this process, a mixture of water, chemicals and sand is pumped into a borehole at high pressure. The water pressure cracks the rock and the sand keeps the cracks open, allowing the gas to flow out.
- Usage: It is used to generate electricity and for domestic heating and cooking.
| Facts |
|
India’ Potential in Shale gas
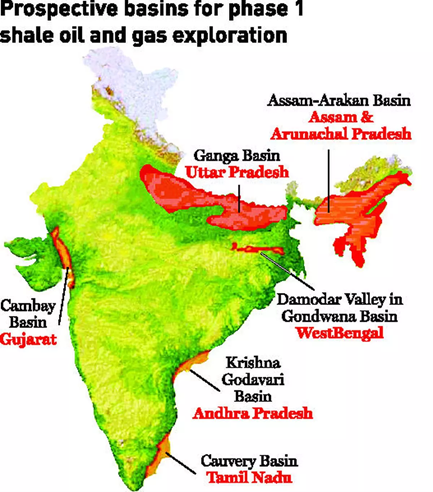
- Reserves: India has an estimated 96 trillion cubic feet (Tcf) of recoverable shale gas reserve
- Exploration: The Oil and Natural Gas Corporation (ONGC) and Oil India Limited (OIL) are exploring shale gas in India.
- Reserves:


 Transforming a Waste-Ridden Urban India:...
Transforming a Waste-Ridden Urban India:...
 Carbon Border Adjustment Tax (CBAM): Mea...
Carbon Border Adjustment Tax (CBAM): Mea...
 RBI Financial Stability Report 2025: Eco...
RBI Financial Stability Report 2025: Eco...

























