Table of Contents
Context: SpaceX partnered with Airtel and Jio to expand Starlink services across India.
What is Meant By Satellite Internet?
- Satellite Internet is a type of internet connection that uses satellites to provide broadband service.
- It does not require cables, fibre or phone lines.
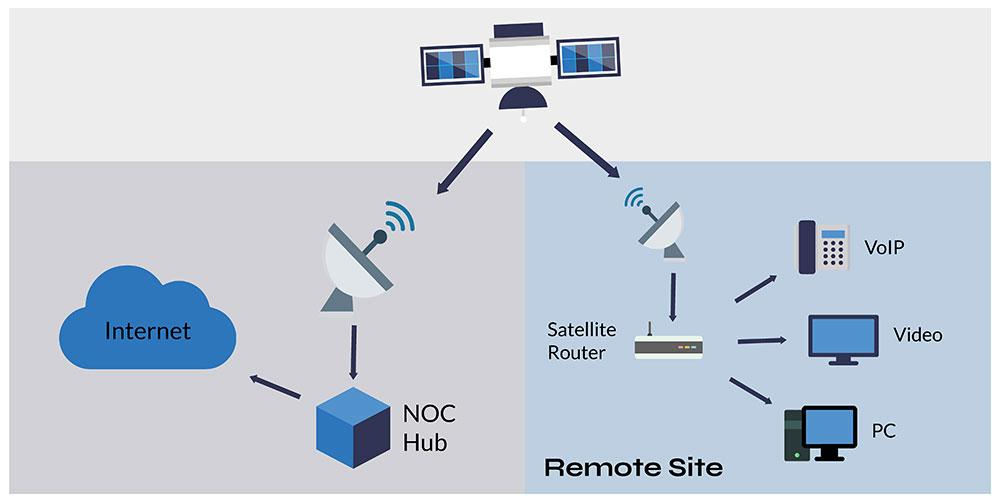
How Does Satellite Internet Work?
- User Device to Satellite: The user’s device sends signals to a satellite in space.
- Satellite to Ground Station: The satellite transmits the signal to a ground station, which is connected to the Internet.
- Data Retrieval and Transmission: The ground station retrieves requested data and sends it back via the satellite to the user’s dish.
|
Fact |
|
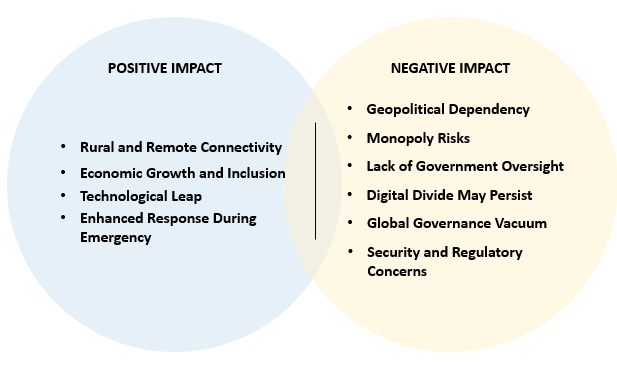
What are the Advantages of the Partnership Between SpaceX and Indian Telecom Companies?
- Rural and Remote Connectivity: Brings high-speed internet to regions without fibre optics or cellular towers.
- Eg., India is the world’s second-largest Internet market, yet 670 million people (out of 1.4 billion) lack Internet access (as per a 2024 GSMA report).
- Enhances digital access for remote schools, health centres, and local governance.
- Economic Growth & Inclusion: Enables rural entrepreneurship, online services, e-commerce, and financial inclusion.
- Potential job creation in installation, servicing, and support sectors.
- Technological Leap: Gives India access to cutting-edge LEO satellite tech.
- Can serve as a bridge while ISRO and others scale indigenous alternatives.
- Enhanced Response During Emergencies: Satellite internet can provide backup during natural disasters or emergencies where ground networks fail.
- Eg., It provides crucial internet connectivity to war-torn Ukraine and its military.
Use code “BLOG“ to Avail of “20% OFF“ Applicable on All Courses Including Books & Test Series
Challenges Associated with Satellite Internet Partnerships
Geopolitical Dependency: Starlink is a US-based company, which creates concerns over sovereignty and strategic control.
- Critical infrastructure being controlled by a foreign private player raises alarms in case of conflicts or political tensions (e.g. Ukraine war incident).
|
Fact |
| US negotiators told Ukraine the US could shut off Starlink if the minerals deal was not reached |
- Monopolistic Market Structure: SpaceX has ~7,000 satellites, giving it a first-mover advantage and dominance in the Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellite internet market.
-
- Lack of competition (e.g. OneWeb, Project Kuiper) may lead to pricing power, dependency, and reduced consumer choice.
- Digital Divide May Exist: If pricing remains high, rural and low-income populations may not benefit, leading to a “digital divide in orbit.”
- Without government subsidies or tiered pricing, universal access will remain a distant dream.
- Strategic Exclusion of Public Sector: BSNL, India’s state-owned telecom with rural reach, is not part of the partnership.
- This reduces public oversight and direct control over the tech.
- Regulatory and Security Concerns: Issues related to data sovereignty, technology transfer, and local data storage need strict enforcement.
- Cybersecurity vulnerabilities increase with external tech dependencies.
- Global Governance Vacuum: Issues like orbital debris, space traffic, and spectrum management lack robust international regulations, increasing the risk of a “tragedy of the orbital commons.”
|
Fact |
| The “Tragedy of the Orbital Commons” is a space-age version of the classic problem “Tragedy of the Commons” — where individuals, acting in their own self-interest, overuse and degrade a shared public resource, leading to long-term harm for everyone. |
Way Forward
- Strengthen Indigenous Capabilities: ISRO and private Indian space startups should be encouraged to build a homegrown satellite constellation for true Digital Sovereignty.
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPP): Include BSNL and other public sector units to balance strategic oversight with private efficiency.
- Enforce Strategic Conditions: Mandate local data storage, tech transfer, and regulatory compliance to ensure national interests are protected.
- Promote Competitive Environment: Create a level playing field for new entrants like OneWeb India, Tata-Telesat, etc., to avoid a Starlink monopoly.
- Affordable Access Models: Design tiered pricing, and rural packages, and promote innovation at the bottom of the pyramid to ensure inclusivity.
- Push for International Frameworks: Lead global efforts for satellite internet governance, orbital debris management, and fair spectrum allocation under platforms like UN COPUOS.


 Comprehensive Remote Sensing Observation...
Comprehensive Remote Sensing Observation...
 Perovskite Solar Cells, Objective and Ch...
Perovskite Solar Cells, Objective and Ch...
 Navy-Marine Expeditionary Ship Interdict...
Navy-Marine Expeditionary Ship Interdict...





















