Context: The Franklin Fire, which began recently in Malibu, California, has impacted around 22,000 people. According to experts Santa Ana’ winds and climate change are fueling these wildfires.
About Santa Ana Winds
- These are dry and warm (often hot) winds in the Southern California area that blow in from the desert — which includes the Great Basin of the western United States.
- It is named after Southern California’s Santa Ana Canyon.
- Origin: These winds blow when high pressure builds over the Great Basin – Area between the Rocky Mountains and Sierra Nevada (a mountain range in the Western United States) and the pressure is low over California’s coast.
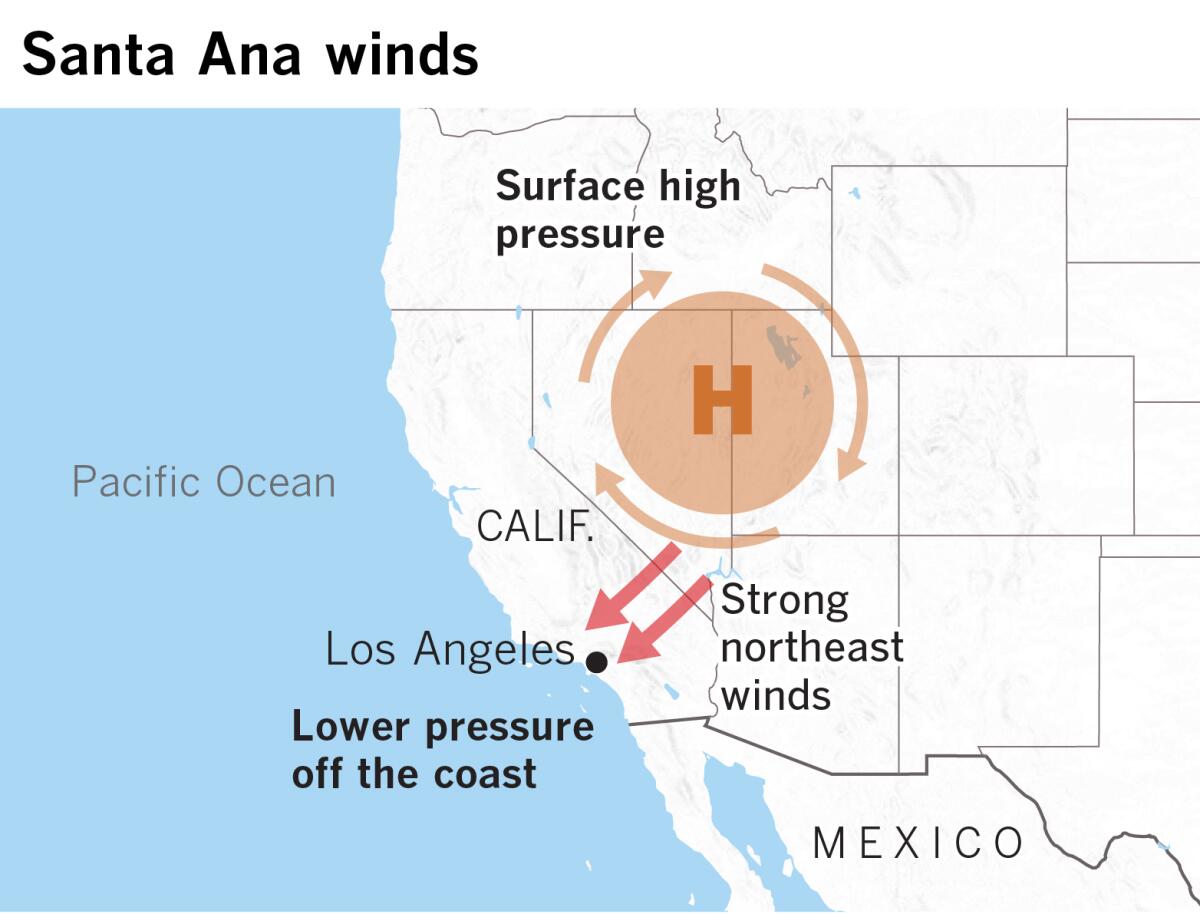
- The pressure difference triggers powerful winds to move from the Basin’s inland deserts, located to the east and north of Southern California, over the mountains toward the Pacific Ocean.
- As these winds descend the mountains, they compress and heat up, causing their humidity to drop—sometimes to less than 20%, or even below 10%.
- This extremely low moisture dries out vegetation, making it highly flammable.
- Santa Ana winds generally occur from October to January.
- Santa Ana Winds are a natural phenomenon but Climate change has prolonged wildfire seasons and also Increased the intensity and frequency of wildfires in California.


 Cabinet Committee on Security Suspends I...
Cabinet Committee on Security Suspends I...
 Places in News for UPSC 2025 for Prelims...
Places in News for UPSC 2025 for Prelims...
 Harnessing Spiritual Aastha for River Re...
Harnessing Spiritual Aastha for River Re...






















