Table of Contents
The South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC), established on December 8, 1985, is a regional intergovernmental organization comprising eight South Asian nations: Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka. Collectively, these countries account for about 21% of the world’s population, covering approximately 3% of the global land area. Check out SAARC Countries, Functions, Objectives, Map, and Importance in this article.
South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation
SAARC is an organization of eight South Asian nations on the political and economic aspects. Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, the Maldives, Sri Lanka, and Pakistan served as the founding members of SAARC and formally adopted its charter in 1985. In 2007, Afghanistan became the eighth member country of SAARC. The primary goal of SAARC is to advance social improvement, economic growth, and cultural development throughout South Asia.
Additionally, SAARC aims to enhance the well-being of the people, strengthen group self-reliance, and accelerate economic and social development. Along with fostering trust and understanding among its members, the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation aims to promote regional integration. All decisions must be made unanimously, and the Association does not discuss or vote on bilateral or controversial issues.
Read More: NATO Countries
SAARC Full Form
SAARC is a regional organization which is an abbreviation of the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation. At present, SAARC comprises eight member Countries of the South Asian Region.
Read More: BIMSTEC Countries
SAARC Headquarters
The SAARC’s headquarters and secretariat are located in Kathmandu, Nepal. On December 8th, 1985, the SAARC Charter was signed in Dhaka and established it.
SAARC Members List
There are eight member States of SAARC which are listed below:
| S. No. | Name of the SAARC Countries | Capital City |
| 1. | Afghanistan | Kabul |
| 2. | Bangladesh | Dhaka/Dacca |
| 3. | Bhutan | Thimphu |
| 4. | India | New Delhi |
| 5. | Maldives | Malé |
| 6. | Nepal | Kathmandu |
| 7. | Pakistan | Islamabad |
| 8. | Sri Lanka | Colombo (Executive and Judicial); Sri Jayewardenepura Kotte (Legislative) |
SAARC Observer Countries
There are currently nine Observer Countries in SAARC.
| S. No. | Name of the SAARC Observer Countries |
| 1. | Australia |
| 2. | China |
| 3. | The European Union |
| 4. | Iran |
| 5. | Japan |
| 6. | The Republic of Korea |
| 7. | Mauritius |
| 8. | Myanmar |
| 9. | United States of America |
SAARC Countries Map
For a better understanding, refer to the following SAARC Countries Map below:
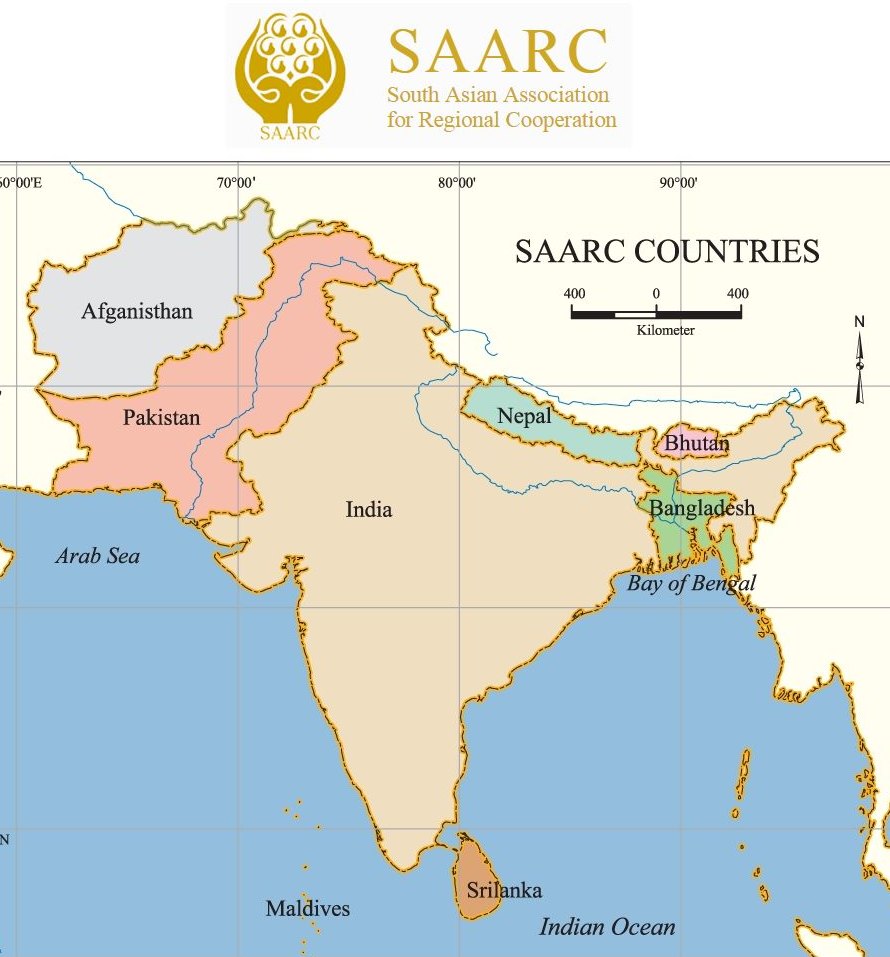
SAARC History
In November 1980, the concept of regional cooperation in South Asia was originally proposed. In Colombo, Sri Lanka, in April 1981, the foreign secretaries of the seven founding countries, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka—met for the first time. At the 13th annual conference in 2005, Afghanistan joined SAARC as a new member.
| Year | Event | Details |
|---|---|---|
| 1979 | Proposal for SAARC | The idea of regional cooperation was first proposed by Ziaur Rahman, President of Bangladesh. |
| 1981 | First Official Meeting | Foreign Secretaries of South Asian countries met in Colombo, Sri Lanka to discuss regional cooperation. |
| 1983 | Adoption of SAARC Declaration | The Declaration on South Asian Regional Cooperation was adopted in Kathmandu, Nepal. |
| 1985 | Establishment of SAARC | SAARC was formally established with the signing of the SAARC Charter on December 8, 1985 in Dhaka, Bangladesh. |
| 1985 | First SAARC Summit | Held in Dhaka, Bangladesh; the key objectives and functions of SAARC were outlined. |
| 2004 | Signing of SAFTA Agreement | The South Asian Free Trade Area (SAFTA) agreement was signed to promote intra-regional trade. |
| 2006 | SAFTA Comes Into Effect | SAFTA agreement came into effect on January 1, 2006. |
| 2007 | Afghanistan Joins SAARC | Afghanistan became the 8th member of SAARC during the 14th Summit in New Delhi, India. |
| 2007 | SAARC Food Bank Established | To ensure food security in the region. |
| 2008 | SAARC Development Fund | Launched to fund development projects in member countries. |
| 2014 | 18th SAARC Summit | Held in Kathmandu, Nepal; focused on enhancing regional connectivity and trade. |
| 2016 | 19th SAARC Summit (Cancelled) | Scheduled to be held in Islamabad, Pakistan, but was cancelled due to the Uri terror attack and subsequent tensions between India and Pakistan. |
| Present | Political and Economic Challenges | SAARC remains inactive due to political tensions, especially between India and Pakistan. |
SAARC Objectives
According to the SAARC Charter, the Association’s objectives are:
- To advance the welfare of South Asians and to enhance their standard of living;
- To promote the region’s economic growth, social advancement, and cultural development while giving everyone the chance to live in dignity and reach their full potential;
- To encourage and reinforce South Asian countries’ collective self-reliance;
- To foster understanding, trust, and respect for one another’s concerns;
- To encourage active cooperation and mutual aid in the realms of economics, society, culture, technology, and science;
- To improve collaboration with other emerging nations;
- To improve their mutual cooperation in international platforms on issues of common interest; and
- To collaborate with regional and global groups that share similar goals.
SAARC Functions
According to its charter, SAARC has the following functions:
- To raise the standard of living of South Asians in order to improve their well-being.
- Everybody is able to live their lives to the fullest extent of their potential and dignity, contributing to social, cultural, and economic progress.
- To advance and reinforce the idea of self-sufficiency among South Asian nations.
- To support the member nations in their efforts to coordinate and collaborate with other developing nations.
SAARC Principles
SAARC organization is based on the following principles that shall underpin cooperation within the SAARC framework:
- Adherence to the values of sovereign equality, territorial integrity, political independence, non-intervention in the internal affairs of other States, and mutual benefit.
- Bilateral and multilateral cooperation must still exist, but this new form of cooperation must enhance it.
- Such cooperation must not conflict with duties under bilateral and multilateral agreements.
Principal Organs of SAARC
The principal Organs of SAARC are discussed below in the table:
| Meeting of Heads of State or Government | Usually, summits are conducted every two years and are hosted by the Member States in alphabetical order. |
| Standing Committee of Foreign Secretaries | The Committee establishes priorities, allocates resources, monitors overall progress, and coordinates funding and project approvals. |
| Secretariat | On January 16, 1987, the SAARC Secretariat was founded in Kathmandu. Its duties include coordinating and overseeing how SAARC activities are carried out, providing support for association meetings, and acting as a channel for communication between SAARC and other international organisations. The secretariat consists of the secretary-general, seven directors, and general services personnel. The Council of Ministers appoints the secretary-general on a rotating basis for a three-year non-renewable tenure. |
Area of Cooperation in SAARC
There are major key areas where SAARC countries cooperate with each other,
- Human Resource Development and Tourism
- Agriculture and Rural Development
- Environment, Natural Disasters and Biotechnology
- Economic, Trade and Finance
- Social Affairs
- Information and Poverty Alleviation
- Energy, Transport, Science and Technology
- Education, Security and Culture and Others
Importance of SAARC
SAARC accounts for 3.8% (US$2.9 trillion) of the world’s GDP, 21% of its people, and 3% of its territory. Therefore, SAARC as an organization is significant for the following reasons:
- It is one of the most fertile and heavily populated regions on Earth. The SAARC countries coordinate their efforts since they share customs, attire, food, and cultural values.
- The common issues faced by all SAARC nations include poverty, illiteracy, malnutrition, natural disasters, internal turmoil, industrial and technological backwardness, low GDP, and poor socio-economic conditions. By raising their living standards, SAARC nations have been able to advance in common areas and find common solutions to these problems.
- The top nations providing troops to UN peacekeeping missions are SAARC members.


 International Standards of Accounting an...
International Standards of Accounting an...
 150th Summit of Inter-Parliamentary Unio...
150th Summit of Inter-Parliamentary Unio...
 BIMSTEC Countries 2025, Area of Cooperat...
BIMSTEC Countries 2025, Area of Cooperat...





















