Table of Contents
Context: Recently the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) of RBI has decided to cut the repo rate by 25 basis points to 6%.
Repo Rate and Reverse Repo Rate
- Repo Rate: The interest rate that the RBI charges when commercial banks borrow money from it is called the repo rate.
- Reverse Repo Rate: The interest rate that the RBI pays commercial banks when they park their excess cash with the central bank is called the reverse repo rate.
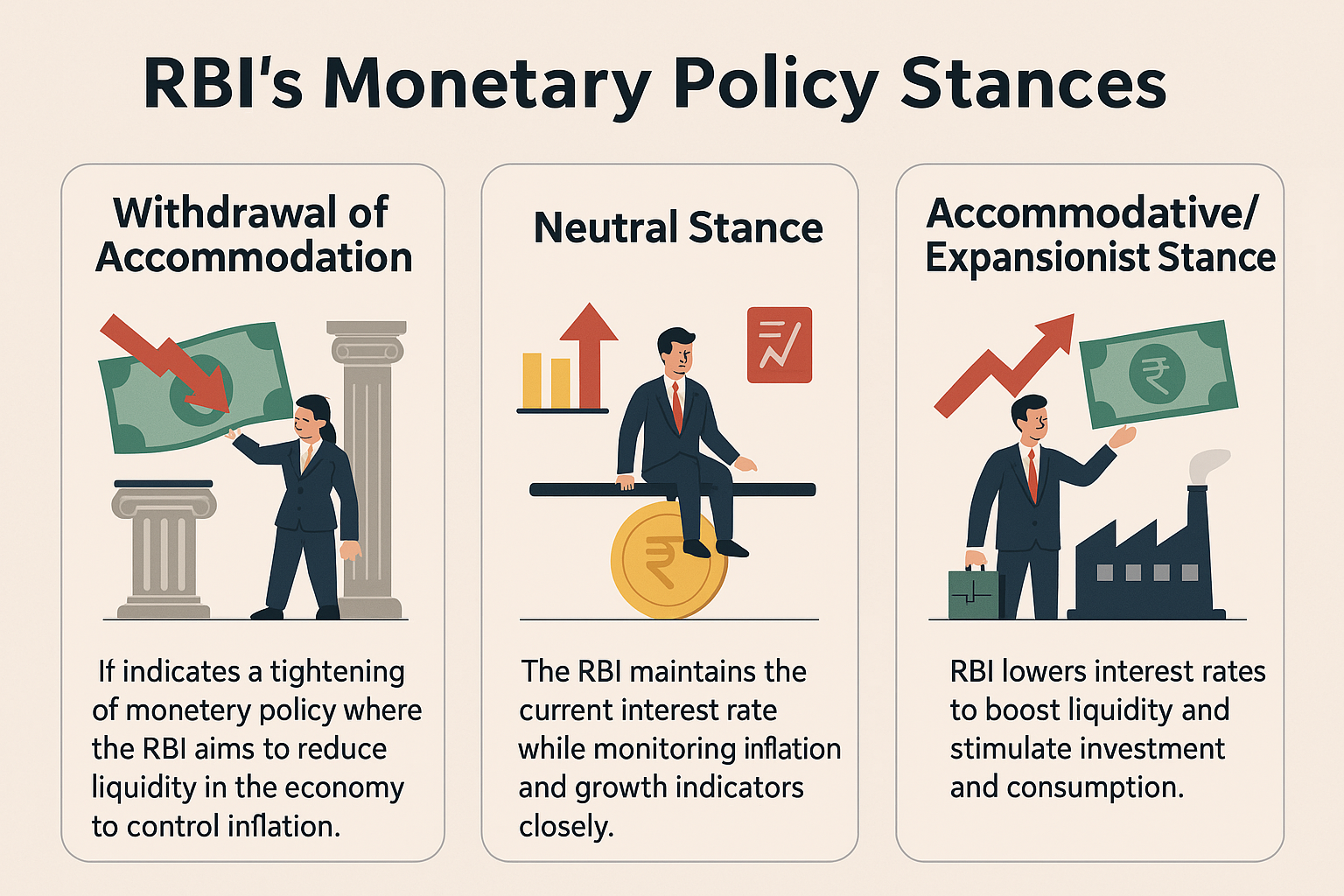
How is the Repo Rate Used by the MPC?
Inflation Control
The MPC adjusts the repo rate to manage inflation.
- A higher repo rate makes borrowing costlier for banks, reducing the money supply in the economy and thereby controlling inflation.
- Conversely, a lower repo rate boosts lending and stimulates economic activity.
Liquidity Management
- By altering the repo rate, the MPC influences liquidity in the financial system.
- A higher rate tightens liquidity, while a lower rate eases liquidity conditions.
Economic Growth
The repo rate affects overall interest rates in the economy.
- Lowering the repo rate promotes borrowing and investment, supporting economic growth.
- Raising it can slow growth to manage overheating or inflationary pressures.
Exchange Rate Stability
Changes in the repo rate can impact the value of the rupee by affecting capital flows and investor sentiment.
Components of Repo Rate
- Preventing “squeeze” in the economy: As a result of inflation, the central bank modifies the Repo rate. As a result, it aims to steer the economy via containing inflation.
- Hedging and Leverage: The RBI attempts to leverage and hedge by buying assets and bonds from banks and giving money in exchange for deposited collateral.
- Short-Term Borrowing: The RBI provides short-term loans, up to an overnight period, following which banks buy back their deposited securities at a set price.
- Collateral and Securities: Gold, bonds, and other types of collateral are accepted by the RBI.
- Cash Reserve or Liquidity: As a precaution, banks borrow money from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to maintain liquidity or cash reserves.
Impact of Repo Rate on Economy
Decrease in Repo Rate
When the RBI wants to encourage economic activity in the economy, it reduces the repo rates.
- Doing this enables commercial banks such as the SBI to bring down the interest rates they charge (on their loans) as well as the interest rate they pay on deposits.
- This, in turn, incentivises people to spend money, because keeping their savings in the bank now pays back a little less, and businesses are incentivised to take new loans for new investments because new loans now cost a little less as well.
Increase in Repo Rate
- RBI tries to control inflation in the economy by increasing the repo rate. By doing this, it makes borrowing a costly affair for businesses and industries and this in turn slows down investment and money supply in the market.
- It eventually and negatively impacts the growth of the economy, which helps in controlling inflation.
Monetary Policy
- Monetary and credit policy in India refers to the set of tools and measures used by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to influence the overall money supply, interest rates, and credit flow in the economy.
- It is published by the RBI’s Monetary Policy Committee.
Expansionary Monetary Policy
It involves increasing the money supply in an economy, usually implemented by lowering key interest rates to boost economic activity.
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) may reduce policy rates like Repo, Reverse Repo, MSF, and Bank Rate. This leads to increased bond prices, lower interest rates, and enhanced capital investment.
- Domestic bonds become less attractive, reducing the demand for domestic currency and lowering the exchange rate.
- This boosts exports, reduces imports, and improves the balance of trade.
Contractionary Monetary Policy
It aims to decrease the money supply, often by raising key interest rates, which can slow economic growth. When RBI adopts this policy, it increases policy rates.
- This results in decreased bond prices and higher interest rates, leading to reduced capital investment.
- Domestic bonds become more attractive, increasing the demand for domestic currency and the exchange rate.
- Consequently, exports decrease, imports increase, and the balance of trade diminishes.
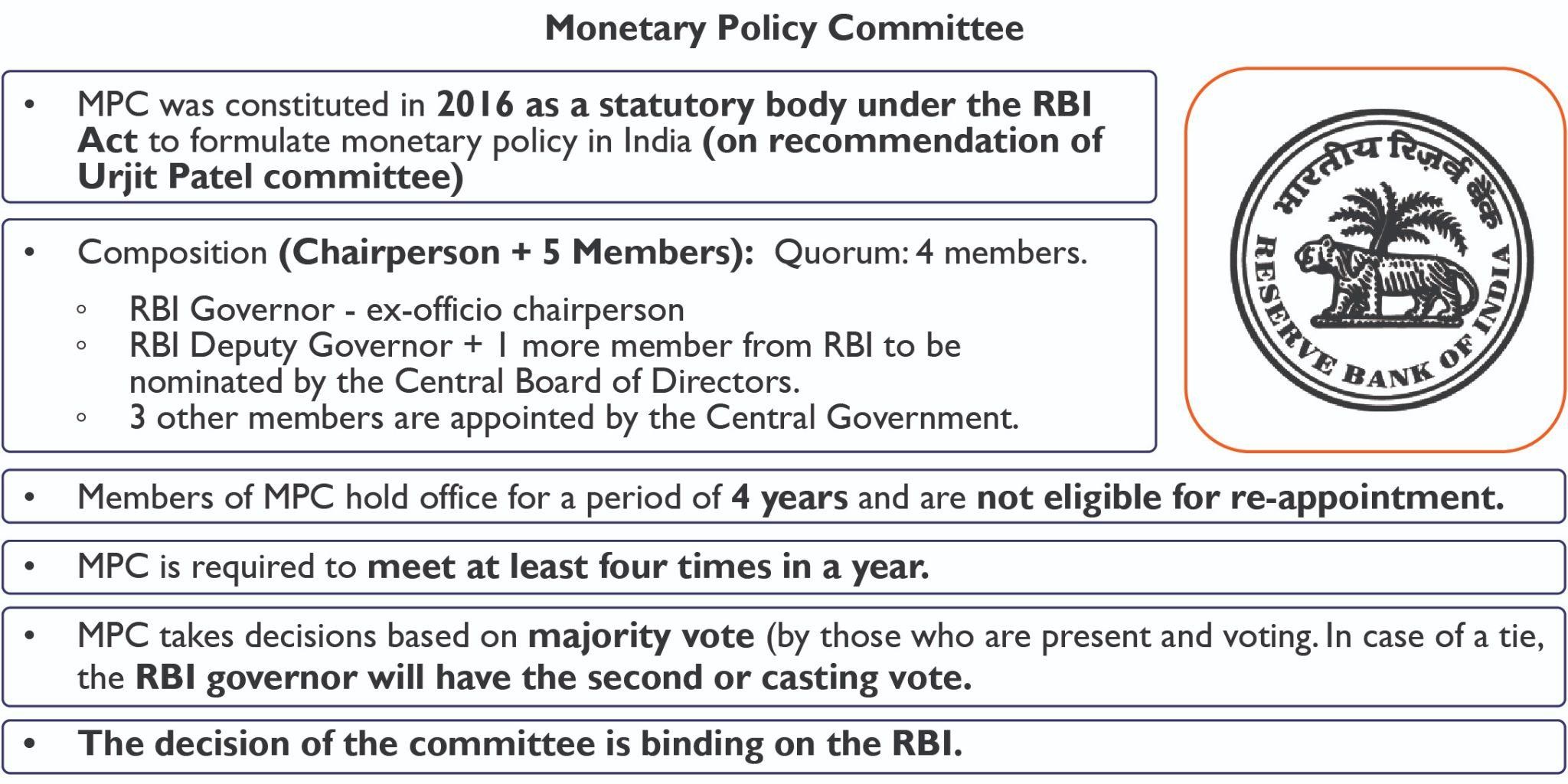
| Monetary policy Committee |
|
Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF)
- It is a monetary policy tool used by central banks, including the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), to manage liquidity in the banking system.
- This facility is primarily employed to influence short-term interest rates and maintain stability in the financial markets.
- The Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF) operates through two main components Repo Rate and Reverse Repo Rate.
| Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) |
|
| UPSC PYQ |
| Q. If the RBI decides to adopt an expansionist monetary policy, which of the following it would not do? (2020) 1. Cut and optimise the Statutory Liquidity Ratio 2. Increase the Marginal Standing Facility Rate 3. Cut the Bank Rate and Repo Rate Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 2 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Answer: B |


 Food Adulteration in India: Definition, ...
Food Adulteration in India: Definition, ...
 Sunrise Sectors in India, Key Characteri...
Sunrise Sectors in India, Key Characteri...
 Gold Price Surge in India, Key Drivers a...
Gold Price Surge in India, Key Drivers a...





















