Table of Contents
Red Sea
The Red Sea is a long, narrow body of water stretching about 1930 km from Suez, Egypt to the Bab el-Mandeb Strait which leads to the Gulf of Aden and Arabian Sea. It separates the coasts of Egypt, Sudan, and Eritrea on the west from Saudi Arabia and Yemen on the east. The sea is up to 190 miles wide and reaches a depth of 3040 meters covering around 450,000 square km.
Known for its hot and salty waters, the Red Sea is a busy route for ships traveling between Europe and Asia, link to the Mediterranean Sea through the Suez Canal. The sea’s name comes from the color changes in its water, which is usually blue-green but can turn reddish brown due to algae blooms.
Read More: Atlantic Ocean
Red Sea Formation
The Red Sea is one of the youngest marine areas on Earth, formed by slow seafloor spreading over the last 4 to 5 million years. It is currently expanding at a rate of 1 to 2 centimeters per year.
Read More: Adriatic Sea
Red Sea Bordering Countries
Six countries border the Red Sea namely
- Egypt,
- Saudi Arabia,
- Yemen,
- Sudan,
- Eritrea, and
- Djibouti
Read More: Caribbean Sea
Red Sea Map
The Red Sea is bordered by six countries. Here is the detailed map of the Red Sea.
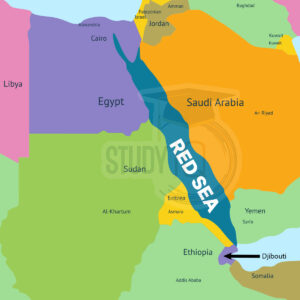
Read more: Indian Ocean
Red Sea Physical Features
The Red Sea is in a low area that separates North Africa and Arabia, two large parts of the Earth’s crust. Inland from the coasts, the land goes up to more than 6560 feet high, with the southern part being the highest. At the northern end, the Red Sea splits into the Gulf of Suez to the northwest and the Gulf of Aqaba to the northeast. The Gulf of Suez is shallow, about 180 to 210 feet deep, and has a wide area of flat land around it. On the other hand, the Gulf of Aqaba is much deeper at 5,00 feet and has a narrow area of flat land around it.
Read More: Arabian Sea
Red Sea Salinity
One of the saltiest bodies of water in the world is the Red Sea, for a variety of reasons. Low precipitation and high evaporation It has a slender southern link to the Gulf of Aden, an arm of the Indian Ocean, and no large rivers or streams flow into the sea.
With an average salinity of 40, its salinity varies from 36 in the southern half to 41 in the northern part near the Gulf of Suez. (On the Practical Salinity Scale, or PSU, the average salinity of the oceans is 35, or 3.5% of actual dissolved salts.)
Read More: Sea of Okhotsk
Red Sea Biodiversity & Climate
The Red Sea is home to a variety of marine life, including sea turtles, dugongs, dolphins, and many unique fish species. Coral reefs are mainly found along the northern and central coasts, but they become less common in the southern area where the water is murkier. In 1983, the Egyptian government created Ras Mohammed National Park to protect this special marine life. The park has rules to safeguard the native animals and plants, making it a popular spot for scuba divers.
- The Red Sea region gets very little rainfall, though there were times in the past with more precipitation.
- The climate is usually good for outdoor activities in fall, winter, and spring, with temperatures ranging from 46 to 82 °F (8 to 28 °C).
- Summer temperatures can soar up to 104 °F (40 °C), and high humidity makes outdoor activities uncomfortable.
- In the northern Red Sea area, winds mainly come from the north and northwest.
- Strong westerly winds, known as “Egyptian” winds, can occur in winter, bringing fog and blowing sand.
- South of 14° N, the prevailing winds are from the south to southeast, while strong northwest winds blow down from the north during June to August.
Read More: Sea of Japan
Red Sea Economic Aspects
The Red Sea region has five main types of mineral resources:
- Petroleum (oil) deposits
- Evaporite deposits (minerals formed by evaporation, like salt and gypsum)
- Sulphur
- Phosphates
- Heavy metals
The Red Sea is a important commerce waterway that connects Europe and Asia (through Suez Canal). Recreational diving sites are found in the sea.
Read More: South China Sea
Why Red Sea is Red?
The Red Sea’s name is derived from seasonal blooms of the red-coloured algae Trichodesmium erythraeum on the water’s surface. This theory is the most widely accepted explanation for the name. Others argue that it is related to the frequent usage of colours in Asiatic languages to denote the four cardinal directions, with “red” denoting “south” and the Black Sea possibly denoting “north.”
Read More: East China Sea
Red Sea UPSC
Inlet of the Indian Ocean between Africa and Asia, the Red Sea is one of the saltiest bodies of water in the world. Huge coral reefs in the Red Sea are home to a variety of plants and animals, including enormous anemones, hawksbill turtles, red lionfish, and clownfish.
Read about: Pacific Ocean


 Important Lakes of India, State wise and...
Important Lakes of India, State wise and...
 Buddhism History, Origin, Sect, Councils...
Buddhism History, Origin, Sect, Councils...
 Andaman and Nicobar Islands, History, Cl...
Andaman and Nicobar Islands, History, Cl...





















