Table of Contents
Context: In its first meeting with newly appointed external members, the MPC voted 5-1 to maintain the benchmark interest rate at 6.5% for the 10th successive monetary policy review since April 2023. The committee unanimously agreed to change the policy stance from “withdrawal of accommodation” to “neutral,” opening the door for potential rate cuts in future meetings.
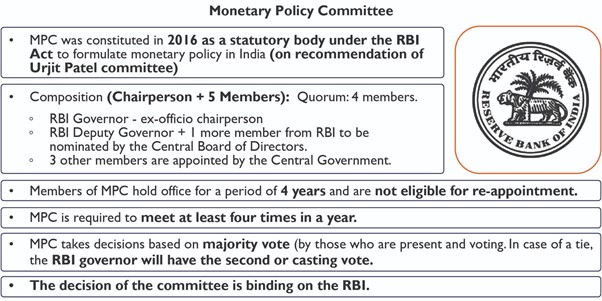
About Monetary Policy
- It is a policy of the central bank to regulate money supply in the economy to achieve certain objectives like price stability, accelerating economic growth or exchange rate stabilisation.
- RBI uses various tools to achieve these objectives. Some of them are:
- Repo rate: It is the interest rate charged by the RBI on overnight loans given to the commercial banks under the Liquidity Adjustment Facility.
- Standing Deposit Facility (SDF): It is a monetary policy tool that RBI uses to absorb excess liquidity from commercial banks.
- Liquid adjustment facility (LAF): It is a facility provided by RBI to scheduled commercial banks to avail of liquidity in case of need or to park excess funds with RBI on an overnight basis against the collateral of government securities.
- Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR): The amount of money that banks must keep with the RBI as a percentage of their net demand and time liabilities (NDTL). A higher CRR reduces the funds available for banks to lend, tightening liquidity in the market.
- Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR): The percentage of a bank’s total deposits that must be invested in government securities or other approved securities. A higher SLR reduces the money available for banks to lend, limiting cash flow in the economy.
RBI’s Monetary Policy stances
- Withdrawal of Accommodation:
- It indicates a tightening of monetary policy where the RBI aims to reduce liquidity in the economy to control inflation.
- Under this RBI may increase interest rates to make borrowing costlier, thereby discouraging spending and investment.
- Neutral Stance:
- It signifies that the RBI is neither actively trying to stimulate the economy nor suppressing it. It allows for flexibility to adjust rates based on evolving economic conditions.
- The RBI maintains the current interest rate while monitoring inflation and growth indicators closely.
- Accommodative/Expansionist Stance:
- It aims to support economic growth by making borrowing cheaper and encouraging spending.
- RBI lowers interest rates to boost liquidity and stimulate investment and consumption.
UPSC PYQQ. If the RBI decides to adopt an expansionist monetary policy, which of the following it would not do? (2020)
Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 2 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: B |


 SAMARTH Udyog Bharat 4.0: Transforming I...
SAMARTH Udyog Bharat 4.0: Transforming I...
 BHIM 3.0 Launched by NPCI: Key Features,...
BHIM 3.0 Launched by NPCI: Key Features,...
 150th Summit of Inter-Parliamentary Unio...
150th Summit of Inter-Parliamentary Unio...





















