Table of Contents
Context: A hydrogen fuel cell-based backup power solution has been developed for Uninterrupted Power Supply to Telecom Towers.
Need for Hydrogen Fuel Cells in Telecom Towers
- India has over 1 million telecom towers, with tens of thousands in remote areas where grid access is limited.
- Traditional diesel generators are commonly used as backup power sources but have several drawbacks:
- High operational costs
- Significant carbon emissions
- Maintenance issues
- Solution: Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells (PEMFCs) offer a cleaner, cost-effective, and reliable
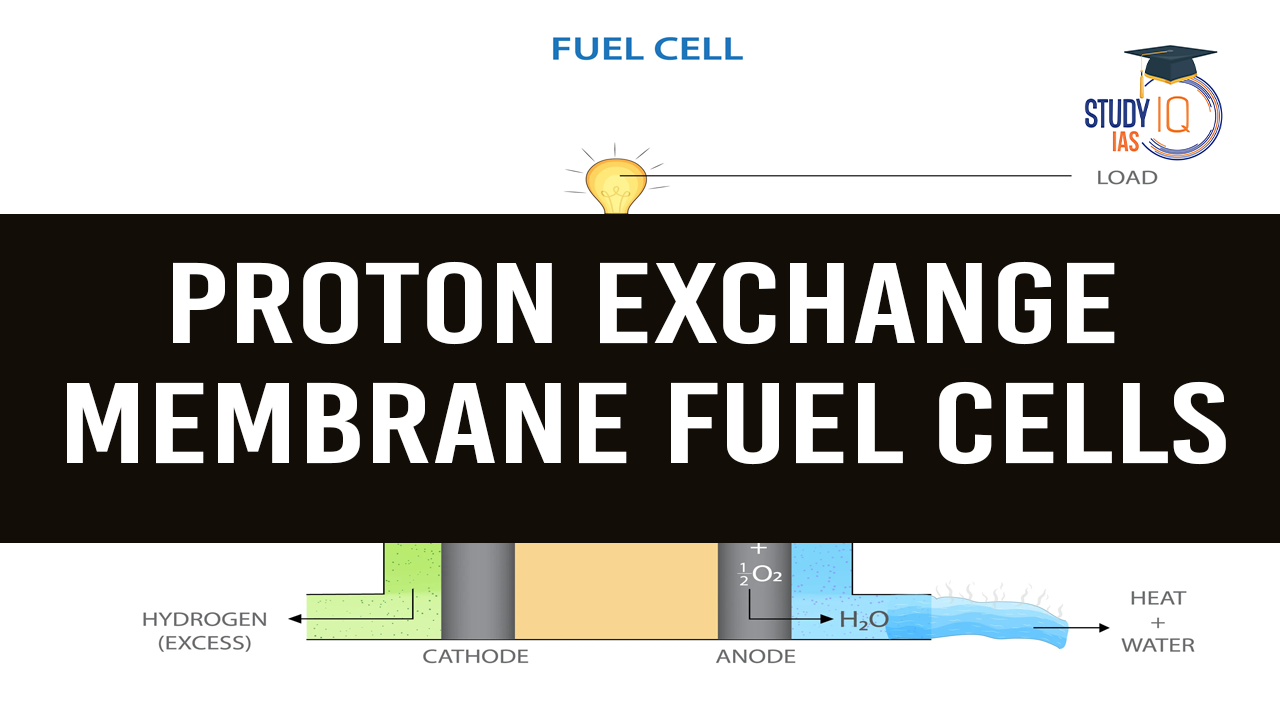
About Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells (PEMFCs)
- PEM Fuel Cells generate electricity using hydrogen, producing only water vapor as a by-product.
- It follows a plug-and-play model, making deployment easy and effective.
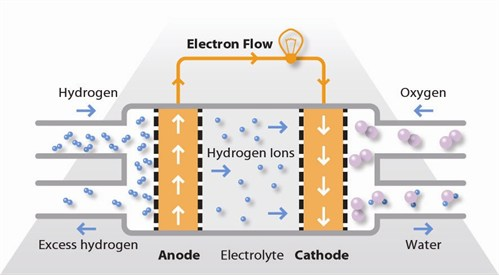
Working Principle
- Hydrogen gas (H₂) is fed into the anode and oxidized, releasing protons.
- Protons pass through a polymer membrane to reach the cathode.
- At the cathode, they react with oxygen (O₂) from the air to generate electricity and water (H₂O).
Key Advantages
- Zero emissions (water is the only by-product).
- High power density in a compact design.
- Fast start-up times and low operating temperatures.
- Low maintenance compared to diesel generators.

 RNA-Based Antiviral for Deadly Agricultu...
RNA-Based Antiviral for Deadly Agricultu...
 Comprehensive Remote Sensing Observation...
Comprehensive Remote Sensing Observation...
 Perovskite Solar Cells, Objective and Ch...
Perovskite Solar Cells, Objective and Ch...





















