Table of Contents
Context: Parametric insurance emerges as a crucial alternative for enhancing disaster resilience globally.
Promise of Parametric Insurance: Background
- 2023 was the warmest year on record.
- As per a report, natural disasters caused losses amounting to $280 billion, with only about $100 billion insured.
- There was a significant disparity in insurance coverage between developed and developing economies.
- With the increase in extreme weather events, the insurance industry must find alternative coverage methods.
Current Insurance Methods
- Indemnity-based Insurance: The traditional method involves physical damage assessment for payouts.
- Challenges: Verification of losses is difficult, especially in economically disadvantaged communities with little asset records.
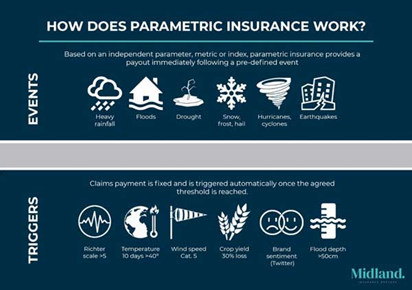
What is Parametric Insurance?
- Parametric insurance products, which do not require physical verification of losses, trigger payments based on measurable parameters of a weather event (e.g., rainfall exceeding 100 mm for two consecutive days, specific flood levels, or wind speeds).
- These products have been embraced by disaster-prone island countries and are gaining traction globally due to their effectiveness in climate adaptation and their role in building trust between states and insurers.
Current Application and Examples
- Global Initiatives: Morocco received a $275 million parametric insurance payout after a 6.8 magnitude earthquake, facilitated by the World Bank.
- India’s Experience
- The Co-operative Milk Marketing Federation in Kerala has implemented parametric insurance for dairy farmers against lower milk yields due to heat stress on cattle.
- The Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana, a traditional crop insurance based on loss verification.
- The Restructured Weather Based Crop Insurance Scheme, a new parametric product that does not require field verification.
- Nagaland was the first Indian state to purchase a parametric cover for extreme precipitation in 2021, leading to a competitive bidding process for improved coverage terms in its subsequent iteration.
- Parametric products are also used for insuring against disasters like cyclones, extreme precipitation, and heat in various Indian states.
Ensuring Effective Use
- Key Factors:
- Precise thresholds and monitoring.
- Experience sharing between governments.
- Transparent price discovery through mandatory bidding.
- Effective retail payout dissemination.
- Encouraging long-term premium payments by households.
- Success Examples: New Zealand and Turkey’s parametric insurance for earthquakes.
- India’s Potential: Utilisation of Aadhaar-based payment systems and regional pooling of risks, similar to the Pacific and Caribbean Catastrophe Risk Insurance Companies.
- Regional Collaboration:
- South Asia’s Climate Vulnerability: Considering regional risk pooling and collaborative bargaining with global insurance companies to enhance climate resilience.


 Places in News for UPSC 2025 for Prelims...
Places in News for UPSC 2025 for Prelims...
 New Phase of Operation Chakra to Combat ...
New Phase of Operation Chakra to Combat ...
 Soyuz Aircraft: History, Design and Sign...
Soyuz Aircraft: History, Design and Sign...





















