Table of Contents
Precipitation Meaning
Precipitation is the process by which water vapour condenses in the atmosphere and falls to the ground under the influence of gravity. These phenomena result in rain and snow.
Precipitation, for example, occurs when a portion of the atmosphere becomes saturated with water vapour and condenses and precipitates when the temperature is appropriate. The cooling of air molecules and the addition of water vapour are the two processes that cause the air to become saturated.
This article will be useful for competitive exams such as the UPSC exam. This article discusses Precipitation. There is a brief discussion of precipitation in this article.
Read More: Evaporation and Condensation
What is Precipitation?
Precipitation refers to all liquid and solid water particles that fall from clouds and reach the ground. Drizzle, rain, snow, snow pellets, ice crystals, and hail are examples of these particles. The primary distinction between precipitation particles and cloud particles is one of size. A typical raindrop weighs the same as one million cloud droplets. Precipitation particles have high falling speeds due to their large size and can survive the fall from the cloud to the ground.
Precipitation Formation Conditions
There are some important conditions required for the formation of Precipitation such:
- Moisture must be present in the atmosphere.
- There must be enough nuclei present to facilitate condensation.
- Condensation of water vapour requires favourable weather conditions.
- Condensation products must reach the earth.
Read More: Types of Winds
Precipitation Types
Precipitation is important in the water cycle because it is responsible for the deposit of freshwater on the planet. Depending on the form, it can be divided into three categories:
- Water in liquid form
- Ice Form
- When liquid water comes into contact with the surface, it freezes.
Read More: Types of Rainfall
Precipitation Examples
We could see precipitation in a variety of forms depending on the forms:
| Examples of Precipitation |
| In Liquid Form precipitation occurs in the Drizzle and Rain Forms. |
| Depending on the form, we could see precipitation in a variety of ways like Freezing Rain and Freezing Drizzle. |
| Frozen Precipitated water forms are Snow, Ice Needles, Hail, Graupel and Sleet. |
Read More: Types of Clouds
Precipitation Forms
Water vapour precipitation can be classified into several types and has several methods of formation, some of which are listed below.
1. Rain Drops
Coalescence occurs when water droplets combine to form larger water droplets and when water droplets freeze onto a crystal of ice. The rate of fall of small droplets is considered negligible, which is why clouds do not fall from the sky.
Precipitation is only possible when these droplets coalesce with the help of turbulence, which causes water droplets to collide, producing even larger droplets. Droplets eventually descend and become heavy with coalescence and resistance, eventually falling as rain.
2. Flakes of Snow
Snow crystals form when the temperature freezes the tiny cloud droplets, and because water droplets are more numerous than ice crystals, the crystals can grow in size at the expense of water droplets as the droplets evaporate due to water vapour. Because of their mass, these droplets fall from the atmosphere as snowflakes.
Read More: List of Major Local Winds
3. Hail
Hail forms in storm clouds, like other types of precipitation, when supercooled droplets collide with dust and dirt. The hailstones are blown up by the storm’s updraft and then lifted again after the updraft passes.
Precipitation is defined in meteorology as any result of atmospheric water vapour condensation that falls under the influence of cloud gravity. Drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel, and hail are the most common types of precipitation.
Precipitation occurs when water vapour (at 100% relative humidity) saturates a portion of the atmosphere, causing the water to condensate and ‘precipitate’ or fall. Fog and mist are colloids rather than precipitation because water vapour does not condense sufficiently to precipitate. Cooling the air or adding water vapour to the air are two processes that may contribute to air saturation. Precipitation forms when smaller droplets collide with other raindrops or ice crystals within a cloud. Showers are short, heavy bursts of rain that fall in scattered areas.
Precipitation is an important part of the water cycle and is responsible for the accumulation of much of the world’s fresh water. A total of 505,000 km3 (121,000 mi3) of water falls as precipitation each year, with 398,000 km3 (95,000 cu mi) falling over the oceans. Given the Earth’s surface area, this means that the annual precipitation is 990 millimetres (39 in) on average.
Read More: Types of Rocks
Cyclonic Precipitation
Cyclonic activity causes cyclonic rain and it occurs along the fronts of the cyclone. It is formed when two masses of air with opposing density, temperature, and humidity collide. The layer between them is known as the front. The front is divided into two parts: a warm front and a cold front.
The warm lighter wind increases slightly over the heavier cold air at the warm front. The warm air cools as it rises, and the moisture in it condenses to form clouds. This rain falls gradually over a period of hours to days.
Read More: Structure of the Atmosphere
Orographic Precipitation
The saturated air mass is forced to rise when it comes across a mountain. As the rising air expands, the temperature drops and the moisture condenses. The main feature of this type of rain is that it falls more heavily on windward slopes. When these winds reach the other slope after raining on the windward side, they drop away and their temperature rises. As a result, their ability to absorb moisture increases, and these leeward slopes remain dry and stainless. The rain-shadow area is located on the leeward side of the island.
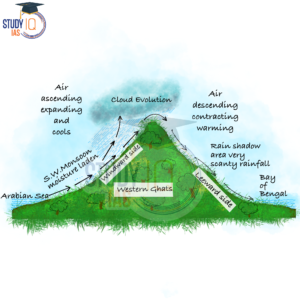
Read More: Climate of India
Chemical Precipitation
Chemical precipitation is the process of converting a liquid to a solid by either rendering the liquid insoluble or supersaturating the solution. In an aqueous solution, the precipitation reaction occurs when two ionic bonds combine, forming an insoluble salt known as a precipitate.
Read More: Seasons of India
Precipitation UPSC
Precipitation occurs when tiny droplets of water, ice, or frozen water vapour combine to form masses that are too large to be held above the earth’s surface. They then fall to the ground as rain.
Precipitation refers to all forms of water that fall to the earth from the atmosphere. Rainfall, snowfall, hail, frost, and dew are the most common forms. Only the first two contribute significantly to the total amount of water. Precipitation intensity varies with time and space.


 Role of Teachers in Educations, Student ...
Role of Teachers in Educations, Student ...
 India's achievements after 75 years of I...
India's achievements after 75 years of I...
 Bal Gangadhar Tilak Biography, Achieveme...
Bal Gangadhar Tilak Biography, Achieveme...

























