Table of Contents
This year marks the 10-year completion of Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY). Since its implementation, it has accelerated financial inclusion in India.
Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana
The Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY), launched by the Government of India in 2014, stands as a beacon of financial inclusion in the country. It aims to provide banking services to the unbanked and underprivileged sections of society, thereby empowering them economically.
PMJDY, a national mission, has garnered remarkable success since its inception. With over 400 million accounts opened, it has significantly contributed to bridging the financial inclusion gap in India.
PMJDY provides a platform for universal access to banking services by ensuring that every household has at least one basic bank account, along with access to financial literacy, credit, insurance, and pension benefits.
Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana Overview
| Aspect | Description |
| Initiation | Launched by the Government of India on August 28, 2014. |
| Objective | To ensure financial inclusion by providing banking services to the unbanked and underprivileged sections of society. |
| Success | Over 400 million accounts opened, making it one of the largest financial inclusion initiatives globally. |
| Implementation Phases |
|
| Eligibility | Individuals must be at least 10 years old, residents of India, and |
We’re now on WhatsApp. Click to Join
Objectives of PMJDY
The objective of the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) is to promote financial inclusion and ensure access to banking services for all households in India, especially the unbanked and underprivileged sections of society. Key objectives include:
- Universal Banking Access: Provide basic banking facilities such as savings and deposit accounts to every household.
- Financial Empowerment: Empower individuals economically by facilitating access to financial services, credit, insurance, and pension schemes.
- Reducing Inequality: Bridge the gap between the banked and unbanked population, thereby reducing economic disparities.
- Direct Benefits Transfer: Enable efficient and transparent transfer of government subsidies and welfare benefits directly into bank accounts.
- Promoting Digital Payments: Encourage the adoption of digital payment methods to promote financial literacy and reduce cash dependency.
Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana Features
| Feature | Description |
| Banking the unbanked | Easy account opening with minimal paperwork, relaxed KYC requirements, e-KYC, zero balance, and zero charges. |
| Securing the unsecured | Issuance of indigenous debit cards with free accident insurance coverage of Rs. 2 lakhs for cash withdrawals and payments at merchant locations. |
| Funding the unfunded | Provision of other financial products like micro-insurance, overdraft for consumption, micro-pension, and micro-credit. |
| Universal access to banking facilities | Ensuring every household has a basic savings bank account. |
| Overdraft facility | Basic savings accounts come with an overdraft facility of Rs. 10,000 for every household. |
| Financial literacy program | Conducted at the village level to educate people about basic financial concepts. |
| Credit Guarantee Fund | Created to cover defaults in overdraft accounts. |
| Insurance | Accident cover up to Rs. 1,00,000 and life cover of Rs. 30,000 for accounts opened between Aug 15, 2014, and Jan 31, 2015. |
| Pension schemes | Schemes like Swavlamban through Business Correspondents for the unorganized sector. |
Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana Eligibility
- Age Requirement: Individuals must be at least 10 years old to be eligible for PMJDY.
- Residency: Applicants must be residents of India.
- Identity Documents: Eligible individuals should possess specified identity documents such as Aadhaar.
- No Existing Bank Account: Having no prior bank account is a prerequisite for opening a PMJDY account.
- Targeted Demographic: The scheme aims to cater to the unbanked and underprivileged sections of society, promoting financial inclusion.
What is its Significance?
- It stands as one of the largest financial inclusion initiatives globally.
- It promotes inclusive growth by offering affordable financial services to low-income and underserved segments of the population.
- It has integrated the savings of the poor into the formal financial system, liberating them from exploitative money lenders.
- It plays a crucial role in channelling all government benefits directly into beneficiaries’ accounts thereby advancing the Union Government’s Direct Benefits Transfer (DBT) initiative.
- It has supported digitalization, e-commerce, and payment systems.
Achievements of PMJDY
Achievements of the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) include:
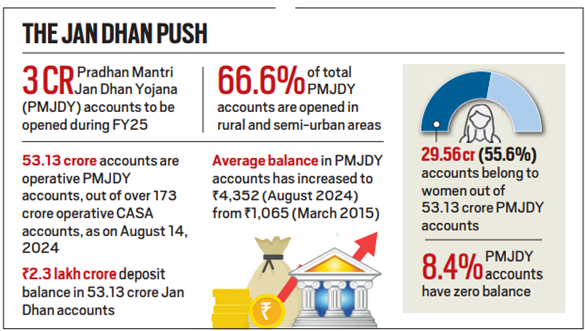
- Rural Inclusion: 6% are in rural and semi-urban areas.
- State-wise Performance: Uttar Pradesh has the highest number of PMJDY accounts (9.4 crore), followed by Bihar (6 crore).
- Positive Social Impacts: The scheme has led to a reduction in thefts in states like UP, Maharashtra, and Haryana, and a decrease in the consumption of intoxicants in states with more PMJDY accounts.
- Direct Benefits Transfer (DBT) Impact: Rs 38.49 lakh crore has been transferred via DBT over the last decade.
- Support for Digitalization: India recorded 55.7 billion UPI transactions as of July 2024.
Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Benefits
The benefits of the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) include:
- Access to Basic Savings Account: PMJDY provides individuals with access to a basic savings account, allowing them to securely deposit and withdraw money.
- No Minimum Balance Requirement: There is no requirement for a minimum balance in PMJDY accounts, making banking services accessible to all, including those with low incomes.
- Interest on Deposits: Deposits made into PMJDY accounts earn interest, allowing individuals to earn additional income on their savings.
- Rupay Debit Card: PMJDY account holders are issued Rupay Debit cards, enabling them to make cash withdrawals, payments at merchant locations, and online transactions.
- Direct Benefits Transfer (DBT): Government subsidies and welfare benefits are directly transferred to PMJDY accounts, ensuring efficient and transparent delivery of social welfare schemes.
- Overdraft Facility: After six months of satisfactory account management, PMJDY account holders become eligible for an overdraft facility, providing them with access to short-term credit.
- Insurance Coverage: PMJDY provides insurance coverage to account holders, including accidental insurance and life insurance, providing financial security in case of unforeseen events.
- Easy Fund Transfer: Money can be easily transferred across India through PMJDY accounts, facilitating remittances and transactions.
- Financial Inclusion: PMJDY aims to promote financial inclusion by ensuring banking services reach every household in the country, thereby empowering individuals economically.
- Reduction in Cash Dependency: Promotion of digital payments through Rupay Debit cards encourages a shift towards cashless transactions, promoting financial literacy and efficiency in transactions.
Way Forward
- Enhanced Financial Literacy Programs:
- Strengthen financial literacy initiatives for PMJDY account holders.
- Partner with educational institutions, NGOs, and financial bodies for comprehensive education programs.
- Promotion of Digital Payments:
- Encourage Rupay Debit card and mobile banking usage.
- Provide incentives for adopting digital payment methods.
- Expansion of Credit Facilities:
- Increase credit access for MSMEs and entrepreneurs via PMJDY accounts.
- Collaborate with financial institutions for tailored credit solutions.
- Innovation in Financial Products:
- Introduce micro-insurance, micro-pension, and micro-credit schemes.
- Explore partnerships with fintech companies for accessible financial products.
- Improvement of Banking Infrastructure:
- Expand banking services in rural and remote areas.
- Establish banking correspondents and mobile facilities for last-mile access.
- Monitoring and Evaluation:
- Implement robust monitoring mechanisms to assess PMJDY’s impact.
- Conduct regular surveys to identify improvement areas.
- Inclusive Approach:
- Address specific needs of marginalized groups, including women and persons with disabilities.
- Design tailored financial solutions for empowerment.
- Partnerships and Collaboration:
- Collaborate with stakeholders for resource leverage.
- Build strategic partnerships for sustainable implementation.


 Poshan Abhiyaan, POSHAN 2.0, Features an...
Poshan Abhiyaan, POSHAN 2.0, Features an...
 Employment Linked Scheme (ELS) announced...
Employment Linked Scheme (ELS) announced...
 Ladla Bhai Yojana, Features, Significanc...
Ladla Bhai Yojana, Features, Significanc...





















