Table of Contents
Context: India has set an ambitious target to increase its nuclear power capacity to 100 GW by 2047, a significant leap from the current 8.2 GW.
The Finance Minister announced the government’s intention to amend the Atomic Energy Act and the Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage Act. This is expected to favor U.S. interests by potentially indemnifying nuclear suppliers.
More in News
- The U.S. government and U.S. Ambassador Eric Garcetti has been lobbying India to amend the law to make it easier for U.S. companies to sell nuclear reactors to India.
- U.S. administrations have been unhappy that the law places some minimal responsibilities on nuclear manufacturers in the event of an accident.
What is Nuclear Energy?
Nuclear energy comes from the core of an atom, which is the tiny part that makes up everything around us. There is a lot of energy in this core, held together by something called the “strong force.” Nuclear power plants harness this energy to generate electricity for homes and businesses.
To use nuclear energy for electricity, we need to release it by splitting atoms in a process called nuclear fission. A nuclear reactor, or power plant, has machines that control this splitting to produce electricity. The fuel used in reactors is small pellets made from uranium. When uranium atoms are split they release tiny particles that cause more uranium atoms to break, creating a chain reaction. This reaction produces a lot of heat.
Uranium is the most widely used mineral for generating nuclear energy. The place where the process of nuclear fission takes place to generate electricity is called a nuclear power plant. Nuclear energy is considered a non-renewable energy source. This is because the materials used to generate nuclear energy are exhaustible.
|
Nuclear Energy Summit in Brussels |
|
Current Status & Targets
Current Status
- Installed Nuclear Capacity: ~7 GWe (as of 2024).
- Operational Reactors: 22 reactors.
- Fuel Dependence: Heavily reliant on imported uranium due to limited domestic reserves.
- Technology: Pressurised Heavy Water Reactors (PHWRs) dominate; Fast Breeder Reactors (FBRs) under development.
Targets
- 100 GWe by 2047 as part of the “Viksit Bharat” vision.
- Expanding PHWRs: 700 MWe PHWRs are planned as the backbone of expansion.
- Fast Breeder Reactors (FBRs): To enable closed nuclear fuel cycles.
- Thorium-Based Reactors: Developing Advanced Heavy Water Reactors (AHWRs) and Molten Salt Reactors (MSRs).
- Bharat Small Reactors (BSRs): Small modular reactors for decentralized power supply.
Current Nuclear Energy Landscape
- Use: Only 31 countries currently use nuclear energy for generating electricity, with 7 more aiming to join.
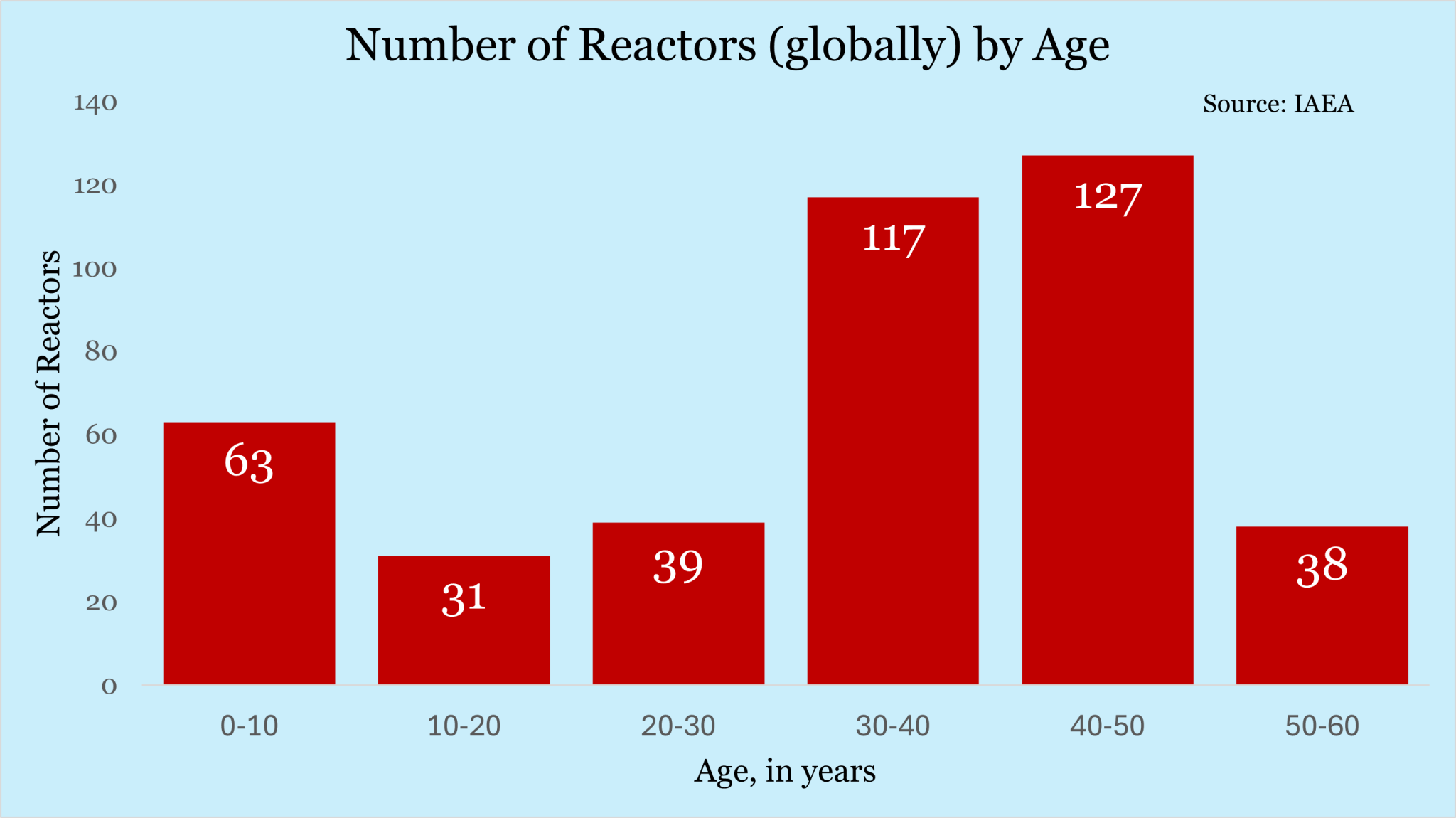
- Operational Reactors: Decreased from 437 in 2003 to 411 now.
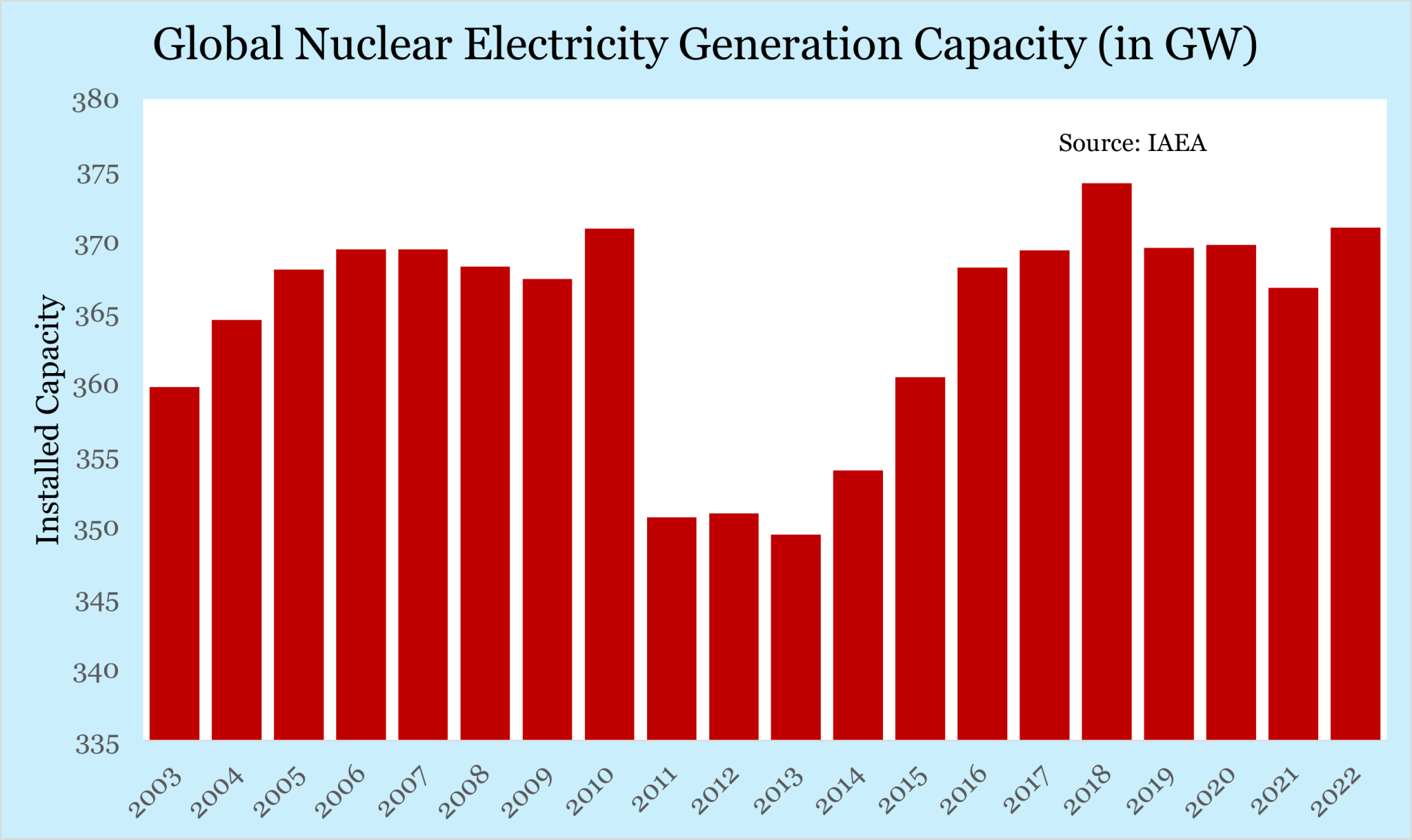
- Electricity Generation Capacity: Increased marginally from 360 GW in 2003 to 371 GW now.
- Global Share: Nuclear energy accounts for less than 10% of global commercial electricity generation, with its share declining for almost three decades.
Nuclear Energy in India
India acknowledges the role of nuclear energy in its plans to reduce carbon emissions (decarbonization).
| Important Data Related to Nuclear Energy in India | |
| Current Status |
|
| Plans for Expansion |
|
| Participation in International Efforts |
|
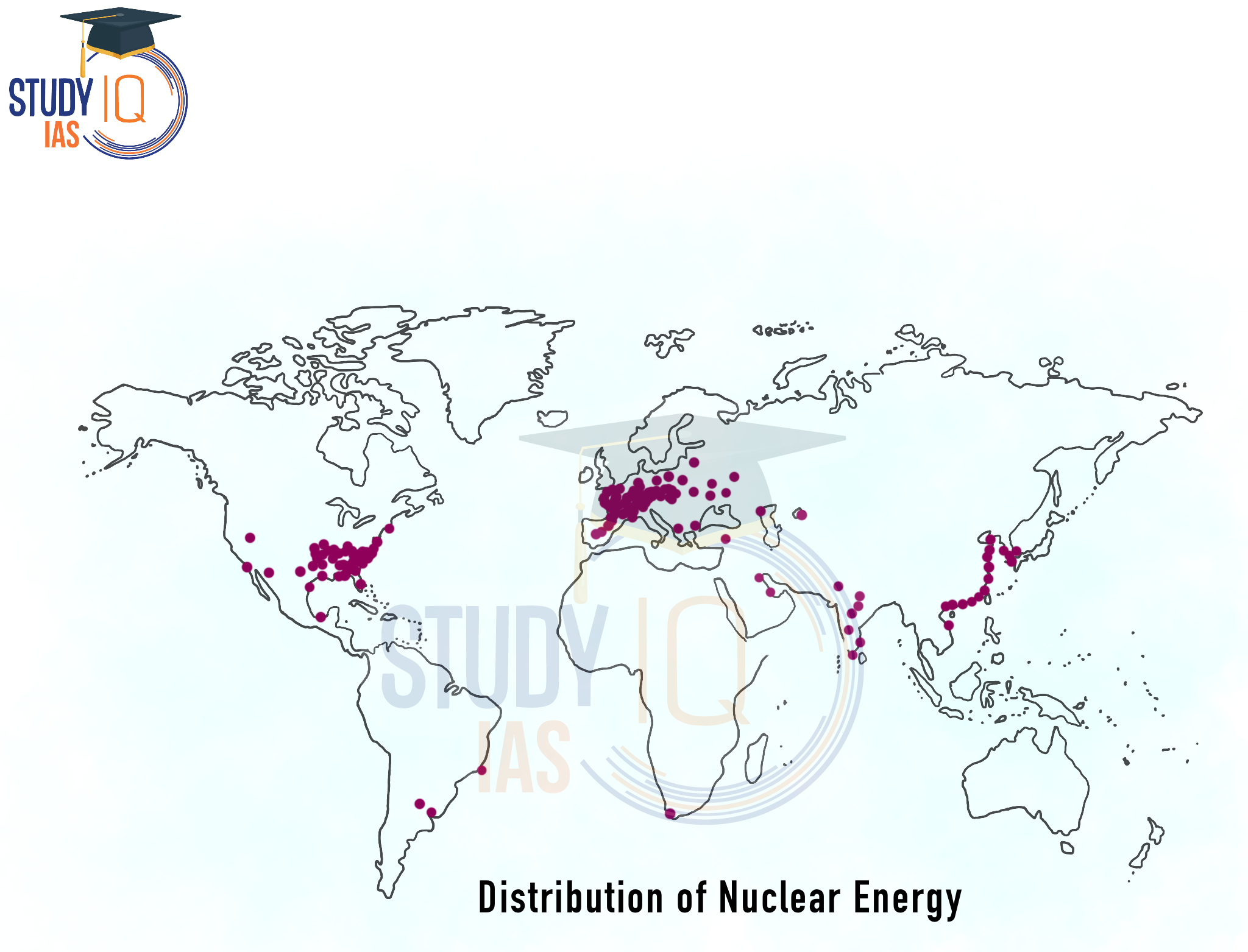
Global Distribution of Nuclear Energy
The largest producers of nuclear power in the world are the United States, the countries of the Commonwealth of Independent States, Canada, the United Kingdom, France, Japan, and Germany. In the United States, nuclear energy makes up about 9% of all energy produced. In the United Kingdom, it provides 50% of the electricity, while in Japan, it accounts for 15%, and in Germany, 7%. India is leading among developing countries, getting 3% of its energy from nuclear power plants.
Incidents Influencing Laws
- Bhopal Gas Disaster (1984): Led to the Supreme Court’s “absolute liability” ruling in the Delhi Oleum gas leak case (1986), holding enterprises engaged in hazardous activities strictly liable for harm.
- Fukushima Nuclear Disaster (2011): Highlighted the catastrophic economic potential of nuclear accidents. Estimated cleanup costs ranged from ¥35 trillion to ¥80 trillion (₹20 lakh crore to ₹46 lakh crore). The accident also exposed design flaws (Mark 1 containment).
- Three Mile Island Accident (1979): Revealed that the reactor supplier, Babcock & Wilcox, had identified a safety hazard but failed to provide operators with clear instructions to mitigate it.
Evolution of Indian Law
- Dilution of “Absolute Liability” (2010): The government created a special law for nuclear accidents, diluting the principle of absolute liability.
- Channeling of Liability: Primary liability channelled to the operator (NPCIL).
- Liability Cap: Capped at ₹1,500 crore.
- “Right of Recourse”: It allows the operator to recoup compensation from the supplier if the accident was caused bya “supply of equipment with patent or latent defects or sub-standard services.”
Nuclear Energy Advantages
There are several advantages to using nuclear energy as a source of power, including:
Reliability
Nuclear power plants operate around the clock, generating consistent and reliable power, even during extreme weather conditions.
Efficiency
Nuclear power plants are very efficient, turning over 60% of the fuel’s energy into electricity. In comparison, other energy sources often convert less than 40%.
They also produce low emissions. Unlike traditional power sources like coal or natural gas, nuclear power plants do not release harmful pollutants into the environment, making them a cleaner energy option.
Abundance
Uranium, the fuel used in nuclear reactors, is common and easy to find, making it a good source of energy. Nuclear energy is a popular way to generate electricity for homes, businesses, and other buildings. It doesn’t release greenhouse gases or pollute the air.
Nuclear energy uses less fuel, like uranium and plutonium, meaning a small amount of material can create a lot of energy compared to other sources like coal or oil. Nuclear energy is not just for electricity in healthcare, radiation helps diagnose and treat diseases like cancer. In farming, nuclear radiation is used to change crops genetically.
Medical
Nuclear energy is used in medical procedures, such as cancer treatments, to destroy cancer cells.
Industrial
Nuclear energy is used to heat industrial processes, such as the production of ceramics, plastics, and petrochemicals.
Research
Nuclear energy is used in scientific research, including the study of genetics, astronomy, and geology.
Nuclear Energy Disadvantages
Despite its many advantages, there are also several disadvantages to using nuclear energy, including:
Cost
Building and maintaining a nuclear power plant can be extremely expensive.
Safety
Nuclear power plants pose a significant safety risk, as a nuclear meltdown or accident can have serious environmental and health consequences.
Waste
Nuclear power plants produce highly radioactive waste that must be carefully managed and stored for many years. The generation of nuclear energy produces radioactive waste which is extremely toxic and harmful to the environment. There are concerns over the transportation, storage, and disposal of radioactive waste.
Proliferation
The technology used to generate nuclear energy can also be used to create nuclear weapons, leading to the risk of nuclear proliferation.
Exhaustible
Materials used to generate nuclear energy are exhaustible. For example, uranium. The nuclear sector is now financially burdened by stringent rules governing maintenance, staffing levels, operator training, and plant inspections. The general public sometimes views commercial nuclear power as a dangerous or unstable process.
Nuclear Power Plants
Some of the largest and most advanced nuclear power plants in the world include:
- Kashiwazaki-Kariwa in Japan
- Paluel in France
- Bruce Power in Canada
- Palo Verde in the United States
- India
| Nuclear Power Plants in India | |
| Kakrapar Atomic Power Station – 1993 | Gujarat |
| (Kalpakkam) Madras Atomic Power Station – 1984 | Tamil Nadu |
| Narora Atomic Power Station- 1991 | Uttar Pradesh |
| Kaiga Nuclear Power Plant -2000 | Karnataka |
| Rajasthan Atomic Power Station – 1973 | Rajasthan |
| Tarapur Atomic Power Station – 1969 | Maharashtra |
| Kudankulam Nuclear Power Plant – 2013 | Tamil Nadu |
Nuclear Energy Fusion
Nuclear fusion is the process of combining two or more atomic nuclei to form a heavier nucleus. This process releases energy, which can be used to generate electricity. Unlike nuclear fission, which splits atomic nuclei and can create harmful radiation and waste, fusion does not produce these dangerous byproducts.
Arguments Against Indemnifying Nuclear Suppliers
- Reduces Accountability and Safety Standards: If suppliers are indemnified, they have no financial incentive to ensure the highest safety standards.
- Past accidents (Fukushima, Three Mile Island) show that design flaws in reactors can lead to catastrophic failures.
- Violates the Polluter Pays Principle: The “absolute liability” doctrine established by the Supreme Court (after Bhopal Gas Tragedy) holds hazardous industries fully responsible for damages.
- Indemnifying suppliers contradicts this legal principle and shifts the burden to taxpayers.
- Financial Burden on Indian Government & Taxpayers: If a nuclear disaster occurs, the entire compensation and cleanup costs (potentially in lakhs of crores) would fall on the Indian government.
- This is unfair, as foreign suppliers would walk away without any financial responsibility.
- Dangerous Precedent for Future Industrial Accidents: Indemnifying nuclear suppliers could set a precedent for other hazardous industries (chemical plants, oil refineries, etc.) to demand similar legal immunity.
- This weakens corporate accountability across sectors.
- Contradicts India’s 2010 Nuclear Liability Law: The Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage Act (2010) ensures that suppliers can be held liable for defective equipment.
- Indemnification would completely remove this critical protection.
- Encourages Reckless Business Practices: When suppliers know they won’t be held liable, they may cut corners in design, safety, and manufacturing to maximize profits.
- General Electric (GE) ignored safety warnings about its Mark 1 reactor design, which contributed to the Fukushima disaster.
Problems with American Reactors (AP1000)
- Excessively High Costs: The AP1000 reactors in the U.S. saw cost overruns of 250%, with a final price tag of $36.8 billion for two reactors in Georgia.
- Given India’s lower electricity tariffs, recovering such high costs would be economically unviable.
- Unfinished and Abandoned Projects: Two AP1000 reactors in South Carolina were abandoned after $9 billion was wasted on delays and design flaws.
- This raises concerns about the feasibility of such reactors in India.
- Technical and Safety Issues: The Westinghouse AP1000 design has faced regulatory and safety challenges in multiple countries, including the U.S. and China.
- In China, the first AP1000 reactors faced major delays due to critical component failures.
- Dependency on Foreign Technology: India has a strong indigenous nuclear program (PHWRs, Fast Breeder Reactors).
- Importing AP1000 reactors makes India dependent on U.S. technology, which could be restricted due to geopolitical tensions.
- Not Competitive with Renewables: The per-unit electricity cost from AP1000 reactors is several times higher than that of solar, wind, and domestic nuclear reactors.
- Investing in expensive reactors locks India into costly electricity for decades.
- No Proven Track Record in India: Unlike Pressurized Heavy Water Reactors (PHWRs) that India has successfully deployed, AP1000 reactors have no operational history in India.
- This increases risks related to local adaptation, maintenance, and long-term sustainability.
Challenges for Use of Nuclear Energy
Fuel Supply Constraints
- High uranium demand: ~18,000 tons of uranium needed annually for 100 GWe capacity.
- Limited Domestic Uranium: India has low-grade uranium deposits and relies on imports.
- Global dependence: Countries like Canada, Kazakhstan, and Australia supply India.
Delays in Fast Breeder Reactors (FBRs)
- Prototype Fast Breeder Reactor (PFBR): 500 MWe reactor is still not operational after long delays.
- Slow progress in large-scale deployment of breeder reactors, limiting fuel recycling.
Thorium Utilization Bottlenecks
- Processing challenges: The thorium-uranium cycle requires advanced fuel cycle technologies.
- Lack of Industrial-Scale Deployment: Most thorium research remains at the lab level.
Infrastructure & Manufacturing Gaps
- Limited domestic reactor-building capacity.
- Dependence on foreign technology for some critical components.
- Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) lack commercial deployment experience.
Public & Regulatory Hurdles
- Public opposition to nuclear power due to safety concerns.
- Land acquisition & site selection issues for large-scale nuclear expansion.
Solutions and Way Forward
Fuel Supply Security
- Expand domestic uranium mining: Fast-track exploration and mining of reserves.
- Increase global uranium partnerships: Long-term supply deals with Kazakhstan, Russia, Canada, and Australia.
- Accelerate Thorium Fuel Cycle: Deploy HALEU-Thorium fuel in PHWRs to reduce uranium dependency.
Fast Breeder & Recycling Acceleration
- Operationalize PFBR: Resolve delays and expand FBR deployment.
- Invest in spent fuel reprocessing: Large-scale recycling of uranium and plutonium.
- Molten Salt Reactors (MSRs): Begin pilot deployment to improve fuel efficiency.
Infrastructure & Indigenous Manufacturing
- Scale up Bharat Small Reactors (BSRs) for decentralized power.
- Boost Private Sector Role: Involve Indian companies in reactor manufacturing and component supply.
- Leverage Retired Coal Plant Sites for new nuclear plants, avoiding land acquisition hurdles.
Public Awareness & Safety Measures
- Enhance safety standards: Strict regulatory oversight to build public trust.
- Transparent communication: Educate people on nuclear energy benefits.
- Disaster-Resilient SMRs: Deploy only designs that require minimal evacuation zones.
Policy & Financial Support
- Simplify nuclear regulations for faster approvals.
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPP) in Nuclear: Leverage private investment in small reactors.
- Boost R&D Funding: Increased budget for Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC) and Indira Gandhi Centre for Atomic Research (IGCAR).
| Other Important Articles | |
| Hydropower Plants in India | Major Ports in India |
| Minerals | Chromite Ore |
| Manganese Ore | Iron Ore |


 Bonnet Macaques: Habitat, Features, Beha...
Bonnet Macaques: Habitat, Features, Beha...
 Periyar Tiger Reserve, Map, Flora, Fauna...
Periyar Tiger Reserve, Map, Flora, Fauna...
 Project Cheetah in India, Objectives, Ch...
Project Cheetah in India, Objectives, Ch...

























