Table of Contents
Context: The NISAR satellite was originally planned for launch in July, now been delayed to October-November due to issues on the U.S. side, requiring corrections to the spacecraft.
NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR)
- Development: NISAR is a satellite jointly developed by NASA and ISRO for Low Earth Orbit (LEO) observation.
- Size and Weight: It is an SUV-sized satellite, weighing around 2,800 kilograms.
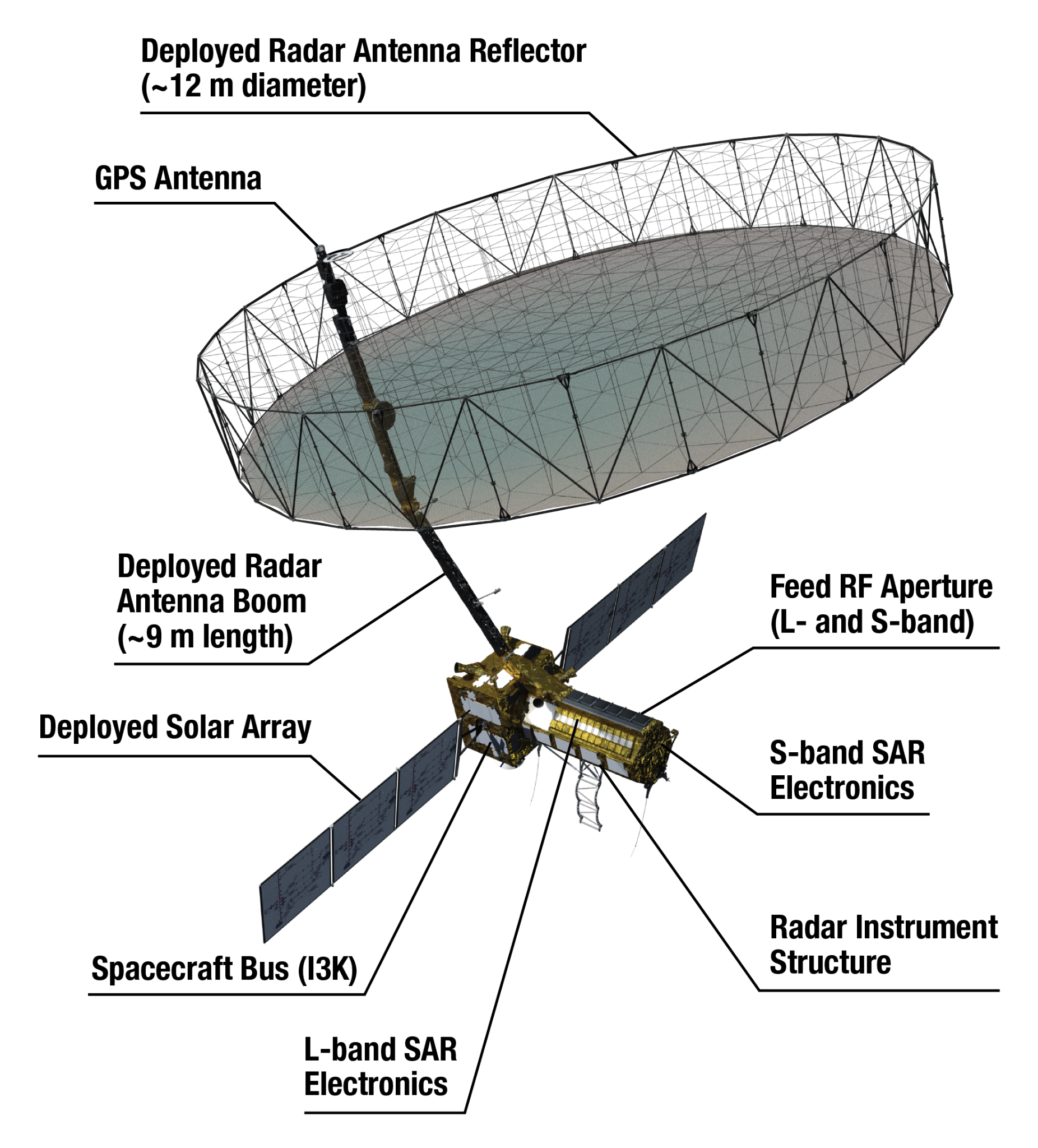
Details About NISAR Satellite
- Objective: To monitor tectonic movements, water bodies, water stress, vegetation cover, snow cover, and more.
- Earth Surface Monitoring: Tracks subtle changes in the Earth’s surface.
- Volcanic Eruptions: Spots warning signs of imminent volcanic eruptions.
- Groundwater Monitoring: Helps monitor groundwater supplies.
- Ice Sheet Tracking: Tracks the rate at which ice sheets are melting.
- Duration: 3 years.
- Function: Can fully cover Earth in 14-15 days.
- Imaging Frequency: Captures images of Earth’s land, ice sheets, and sea ice every 12 days.
- Surface Movement Detection: Detects the earth’s surface movement as small as 0.4 inches over an area.
Features of NISAR Satellite
- Dual Frequency: Equipped with L-band and S-band radars.
- NASA Contribution: L-band radar, GPS, solid-state recorder, and payload data subsystem.
- ISRO Contribution: S-band radar, GSLV launch system, and spacecraft.
- Antenna Reflector: Features a large 39-foot fixed antenna reflector to focus radar signals emitted and received by the upward-facing feed on the instrument structure.
| Other Missions by ISRO |
Chandrayaan-4:
Spadex (Space Docking Experiment):
Gaganyaan Mission:
Sukhrayaan Mission:
|
New Application Areas for Satellites
- Bharatiya Antariksha Station: Planned space station with the first module launch targeted by 2028.
- New Generation Launch Vehicle (NGLV): Named Surya, under development.
- Quantum Key Distribution Satellite: Aimed at secure communication.
- Software-Defined Radio Satellite: A communication satellite in development.
- Aircraft Monitoring Constellation (ADS): A satellite constellation to monitor all aircraft in Indian airspace and assist airport authorities in managing air traffic.


 Indus Water Treaty 1960 Suspended by Ind...
Indus Water Treaty 1960 Suspended by Ind...
 5 Years of SVAMITVA Scheme and Its Benef...
5 Years of SVAMITVA Scheme and Its Benef...
 Places in News for UPSC 2025 for Prelims...
Places in News for UPSC 2025 for Prelims...





















