Table of Contents
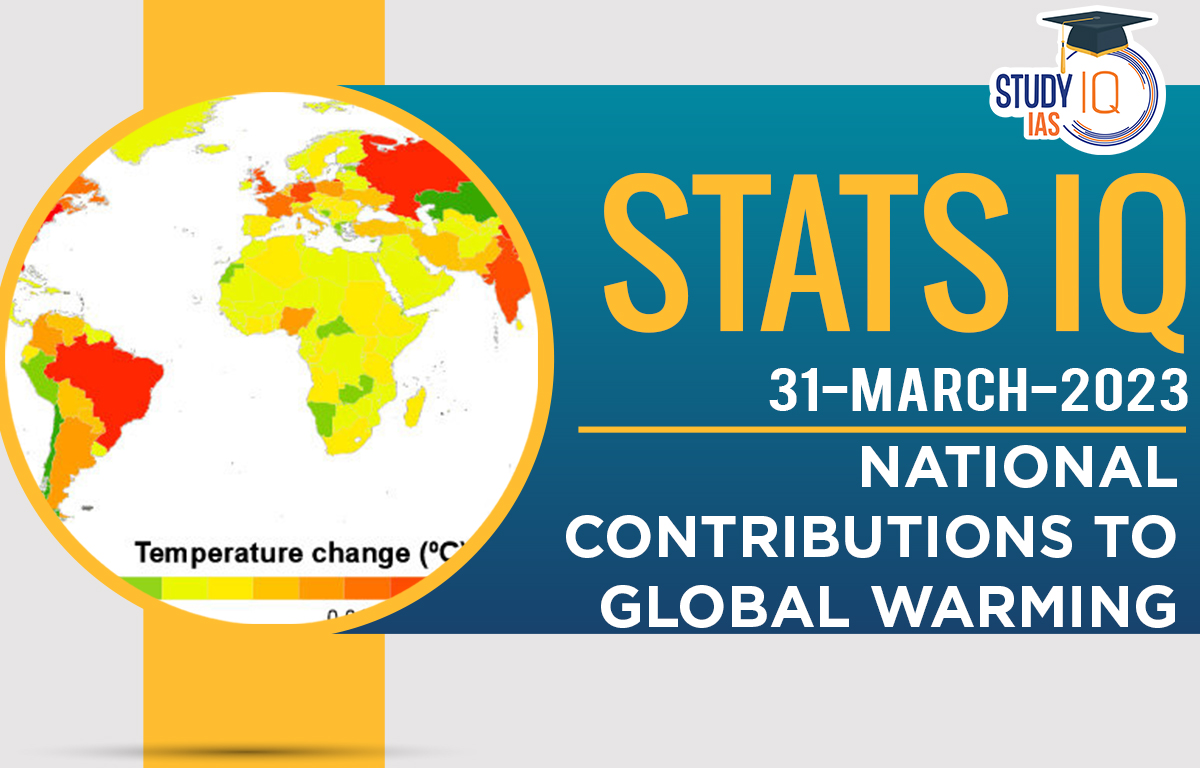
Context: A new research shows how countries have contributed to global warming through their emissions of key greenhouse gases since 1850.
- It is built on records of historical emissions of carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O) from the pre-industrial period to 2021.
Contributors to Warming (1850-2021)
- Individual Nations:
- The United States ranked 1st among all countries with 0.28°C of rise in temperature.
- China stood second with 0.20°C of warming.
- Russia ranked 3rd with 0.10°C of warming.
- Brazil ranked 4th with 0.08°C of warming.
- India ranked 5th in the list with a contribution of 0.08 degrees Celsius in warming.
- Developing countries: The combined contributions to warming from Brazil, South Africa, India and China rose from 17% in 1992 to 23% in 2021.
- Developed countries: The contribution from the industrialized OECD countries fell slightly from 47% to 40%.
- Others: Indonesia, Germany, the United Kingdom, Japan and Canada each contributed 0.03-0.05°C of warming.
Greenhouse Gases Emissions
- CO2 is responsible for 1.11°C of warming compared to methane’s 0.41°C and nitrous oxides 0.08°C.
- Up to 2021, 69.1% of the total warming caused by the three gases was related to emissions of CO2 alone.
- UK (CO2 makes up 87.6%% of warming); U.S. (83.3%); Russia (76.1%); Indonesia (71.3%); Brazil (64.7%); China (64.3%).
Fossil Emissions
- Additional contributions to warming are caused by fossil fuel emissions.
- Since 1992, the additional warming caused by global fossil fuel emissions over four times greater than the additional warming caused by land use change.
Causes of Warming
- In half of the world’s countries, the land-use and forestry contribute to all emissions since 1850.
- The contributions of Brazil, Indonesia and Argentina are dominated by emissions linked to historical deforestation and agricultural expansion since 1850.

 Bihar Police SI Exam Date 2025 Out: Chec...
Bihar Police SI Exam Date 2025 Out: Chec...
 Delhi Police Admit Card 2025 Out – Dow...
Delhi Police Admit Card 2025 Out – Dow...
 Future of India–Bangladesh Relationshi...
Future of India–Bangladesh Relationshi...

























