Table of Contents
Context: Over the past decade, Lok Sabha members elected from Delhi’s seven constituencies have failed to utilise Rs 100 crore out of their entitled Rs 311.5 crore funds under the Members of Parliament Local Area Development (MPLAD) scheme.
Members of Parliament Local Area Development (MPLAD) Scheme
| About MPLAD Scheme | |
| Established | 1993 |
| Type | Central Sector Scheme |
| Purpose | MPs recommend developmental works for asset creation and amenities in sectors such as drinking water, primary education, public health, sanitation, and roads. |
| Administration |
|
| Period of Spending |
|
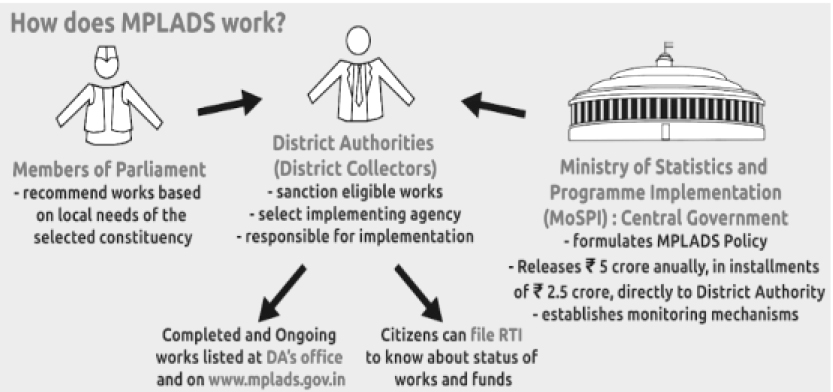
Key Features of MPLAD Scheme
- Annual Fund Allocation: Each MP constituency receives Rs. 5 crore annually under the MPLADS.
- Recommendation by Lok Sabha MPs: Lok Sabha Members can recommend projects within their constituencies.
- Recommendation by Rajya Sabha MPs: Rajya Sabha Members can recommend projects in one or more districts of their elected state.
- Recommendation by Nominated MPs: Nominated Members of both Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha can choose one or more districts from any state for project implementation.
- Mandatory Allocation for SC/ST Areas: MPs must recommend at least 15% of the annual entitlement for Scheduled Caste areas and 7.5% for Scheduled Tribe areas.
- Contribution Outside Constituency/State: Elected MPs can recommend projects worth up to Rs. 25 lakh per year outside their constituency or state.
- Fund Transfer: Funds are directly transferred by the Centre to the district authorities, not to MPs.
- MP’s Role: MPs only recommend projects; the district authority handles sanctioning, execution, and completion.
Project Implementation and Challenges of MPLAD Scheme
- Recommendation and Execution: MPs recommend projects to district administration which then seeks approval from the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI).
- Fund Disbursal: Dependent on MPs submitting monthly progress reports (MPRs).
- Uncompleted Projects: Many remained incomplete due to a lack of MPRs.
Issues and Clarifications
- Lack of Initiative: MPs’ active participation is essential for proposing projects, ensuring fund release, and monitoring progress.
- Guideline on Sanctioning Funds: The minimum amount for any work is usually not less than Rs 2.5 lakh unless deemed beneficial by the district authority.
- Assets Funded: MPLADS funds are used for public assets on government-owned or government-controlled land and institutions.
- Carry Forward: Funds not utilised are carried forward to the next financial year or next MP.


 National Pest Surveillance System (NPSS)
National Pest Surveillance System (NPSS)
 Utkal Divas 2025: Odisha Foundation Day ...
Utkal Divas 2025: Odisha Foundation Day ...
 India launched Operation Brahma for Assi...
India launched Operation Brahma for Assi...





















