Table of Contents
Mission Indradhanush for PSBs
Mission Indradhanush, launched in 2015 by the Ministry of Finance of the Indian government, is a comprehensive program designed to address challenges faced by Public Sector Banks (PSBs). The program, influenced by the P J Nayak Committee report on bank governance, aims to restructure PSBs and enhance their competitiveness against private sector banks. It seeks to revive economic development by reducing political interference in PSBs and improving credit quality. In February 2021, the government announced plans to privatize two PSBs, indicating ongoing debates about reforms in the banking sector.
Read about: MCLR Marginal Cost of Funds Based Lending Rate
Need of Mission Indradhanush
The Public Sector Banks (PSBs) have faced significant challenges in recent years, particularly in infrastructure financing, due to delays in approvals and land acquisition, resulting in stalled projects. This has adversely affected the profitability of PSBs as they had to make provisions for restructuring projects and handling high levels of non-performing assets (NPAs).
These circumstances have posed obstacles for the government in reviving investments and accelerating economic growth. Thus, emphasizing the need for Mission Indradhanush, which aims to address these challenges and reorganize the operations of PSBs to enhance their performance and ability to support economic development.
Read about: Indian Financial System
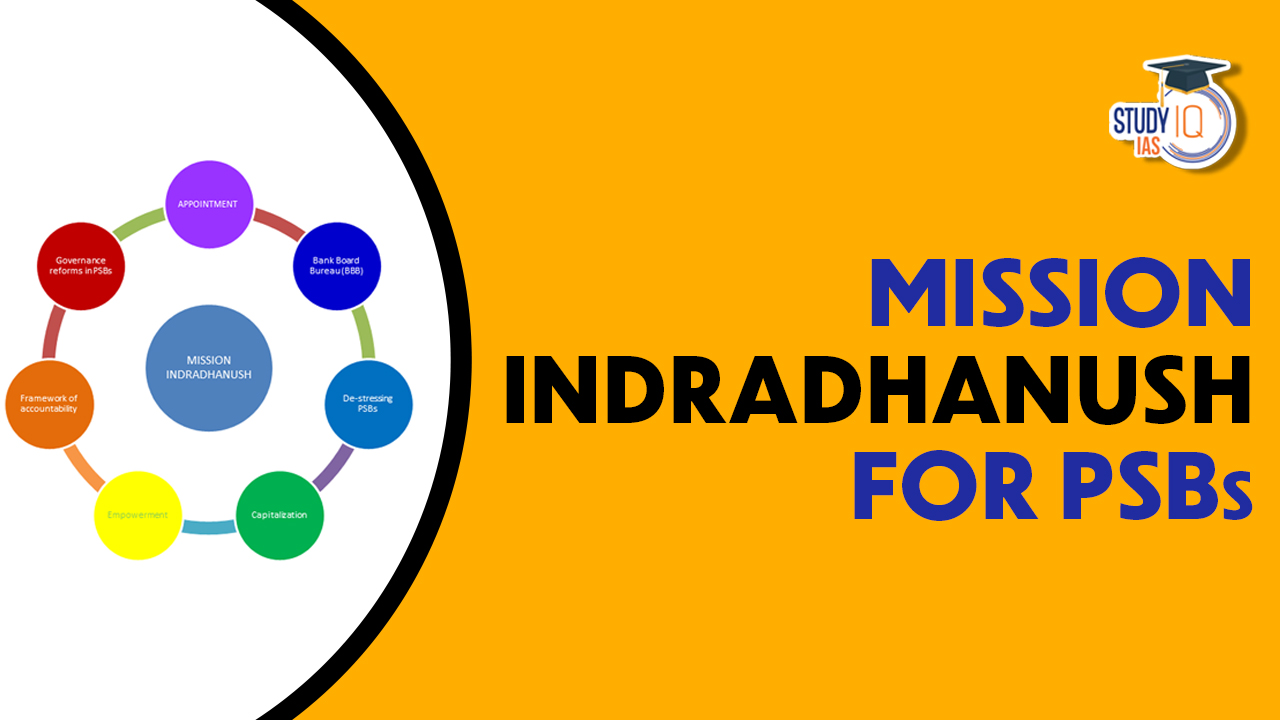
Components of Mission Indradhanush
Mission Indradhanush encompasses several components proposed by the PJ Nayak Committee on banking reforms. The mission’s seven components aim to address challenges faced by public sector banks (PSBs) and include:
| Components | Details |
| Appointments | Separation of Chairman and Managing Director positions, with a non-executive chairman assigned to ensure checks and balances, following transparent and meritocratic selection processes. |
| Bank Board Bureau | Replacing the Appointments Board, the Bureau consists of distinguished professionals and officials responsible for appointing Whole-time Directors and non-Executive Chairmans of PSBs, as well as formulating growth strategies. |
| Capitalization | Adequate capital infusion to maintain a safe buffer over and above Basel III norms, with gradual capital infusion of Rs. 25,000 crore in debt-laden banks. |
| De-Stressing the PSBs | Addressing stalled projects and increased NPAs, enabling policy decisions, reorganizing existing loans, establishing Debt Recovery Tribunals, and bolstering asset reconstruction. |
| Empowerment | Encouraging banks to make independent decisions aligned with commercial interests, establishing effective Grievances Redressal Mechanisms, and providing flexibility in manpower hiring. |
| Framework of Accountability | Introducing Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to evaluate PSB performance, streamlining vigilance processes for quick action on frauds. |
| Governance Reforms | Commencing with the “Gyan Sangam” conclave, decisions were made on optimizing capital, digitizing processes, enhancing risk management, and promoting financial inclusion. |
These components collectively aim to strengthen the governance, operational efficiency, capitalization, and accountability of PSBs, ensuring their ability to compete and contribute to the growth of the banking sector and the economy.
Read about: Difference Between Organised and Unorganised Sector
4R Strategy under Mission Indradhanush
Under the mission Indradhanush, the government has implemented a comprehensive 4R approach to address the challenges in the banking sector:
Recognition
Banks are required to accurately value their assets, aligning them with their true value as emphasized by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
Recapitalization
To safeguard the capital position of banks, equity infusion is necessary once the asset values have been recognized, meeting the demands of the banks.
Resolution
Stressed assets in the corporate sector should be either sold or rehabilitated, as the government is willing to facilitate such actions.
Reform
It is crucial to rectify future incentives for the private sector and corporate firms to prevent the recurrence of similar problems, addressing the concerns raised by various stakeholders.
This 4R strategy focuses on the clear recognition of non-performing assets (NPAs), capital infusion, effective resolution of stressed accounts, and implementing reforms in the banking sector and wider fiscal ecosystem. By adopting this approach, the mission Indradhanush aims to create a more accountable and transparent banking system.
Read about: National Payments Corporation of India
Mission Indradhanush for PSBs UPSC
Mission Indradhanush for PSBs is an important topic for UPSC as it aligns with the UPSC Syllabus on Indian Economy and Banking sector reforms. It is crucial for UPSC aspirants to have a deep understanding of the comprehensive reforms undertaken in the public sector banks. Knowledge of Mission Indradhanush is relevant for UPSC prelims, mains, and interviews. Aspirants can refer to UPSC Online Coaching materials and UPSC Mock Test to gain comprehensive insights and prepare effectively for such topics.
Also Read: Informal Economy in India

 Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve, Map, Climate,...
Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve, Map, Climate,...
 Repo Rate and Reverse Repo Rate, Impact ...
Repo Rate and Reverse Repo Rate, Impact ...
 Foreign Contribution Regulation Act (FCR...
Foreign Contribution Regulation Act (FCR...





















