Table of Contents
Missiles of India
A missile is also referred to as a guided missile in military jargon. A guided missile is a self-propelled flying weapon that is typically driven by a fighter jet engine or rocket motor. An object that can be launched, shot, or pushed toward a target is referred to as a missile in everyday speech. In most competitive tests, the defense is a significant and engaging component that is combined with the General Knowledge section.
The Missiles of India is used for a variety of defense-related reasons. Fundamentally, its arsenal of ballistic missiles serves as a platform for the delivery of nuclear weapons to both China and Pakistan. India’s development of longer-range ballistic missiles and its diversification of its delivery vehicles beyond mobile land-based missiles are both driven by military requirements.
In the age of modernity, India is working with Russia to develop cruise missiles and ship-launched ballistic missiles in order to become a strong country.
Read about: Gallantry Awards in India
Types of Missiles in India
- Surface-To-Air Missiles – SAM
- Air-to-air missiles AAM
- Surface-to-surface missiles
- Ballistic Missile Defence (BMD)/Interceptor Missiles
- Cruise Missiles
- Submarine Launched Ballistic Missiles
- Anti-Tank Missiles
Read about: Earthquakes in India
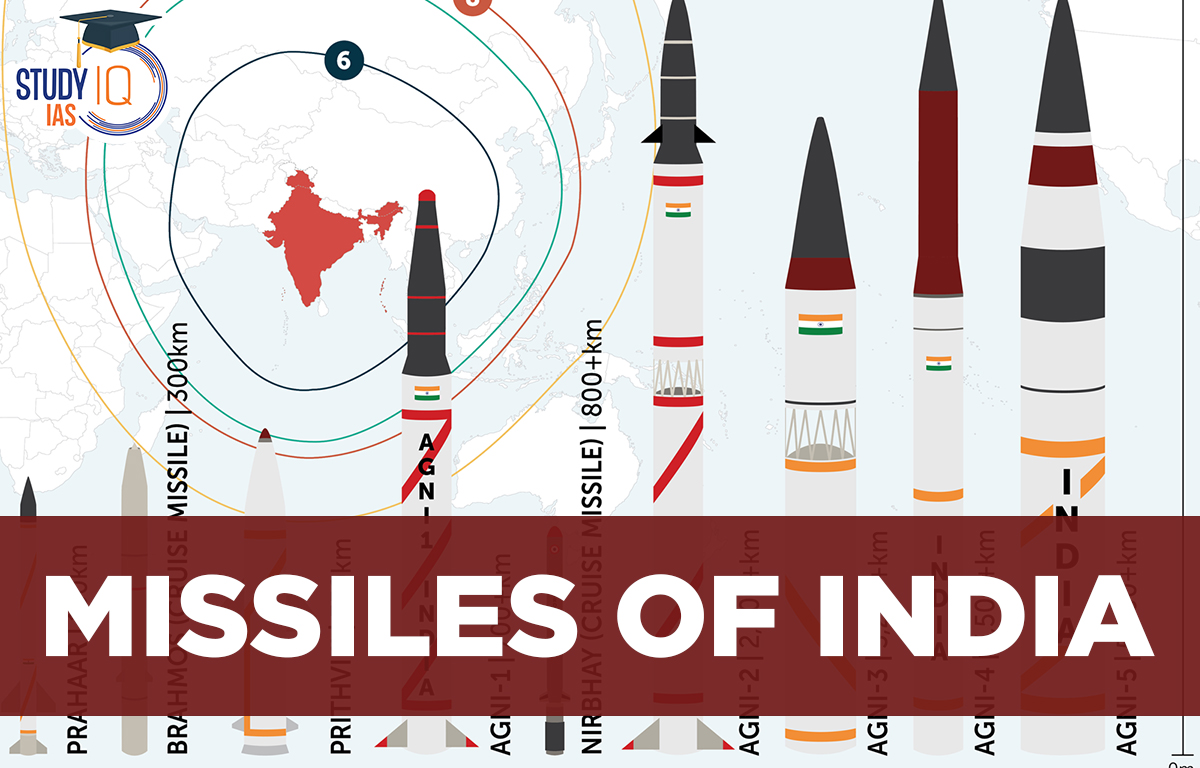
List of Missiles in India
Air-to-Air missiles
| Name of the Missile | Type | Range |
| MICA | Air-to-Air Missiles | 500 m to 80 km |
| Astra | Air-to-Air Missiles | 80-110 km |
| Novator K-100 | Medium Range air-to-air missile | 300–400 km |
Surface-To-Air Missiles
| Name of the Missile | Type | Range |
| Trishul | Short-Range surface to air missile | 9 km |
| Akash Missile | Medium-range surface-to-air missile | 30-35km |
| Barak 8 | Long-Range surface to air Missile | 100 km |
Surface-to-Surface Missiles
| Name of the Missile | Type | Range |
| Agni-I | Medium-range ballistic missile | 700-1250 km |
| Agni-II | Intermediate-range ballistic missile | 2,000–3,000 km |
| Agni-III | Intermediate-range ballistic missile | 3,500 km – 5,000 km |
| Agni-IV | Intermediate-range ballistic missile | 3,000 – 4,000 km |
| Agni-V | Intercontinental ballistic missile | 5000 – 8000 Km |
| Prithvi I | Short-Range Ballistic Missile | 150 km |
| Prithvi II | Short-Range Ballistic Missile | 350 km |
| Dhanush | Short-Range Ballistic Missile | 350 – 600 km |
| Shaurya | Medium-Range Ballistic Missile | 750 to 1,900 km |
| Prahaar | Short-Range Ballistic Missile | 150 km |
Cruise Missiles
| Name of the Missile | Type | Range |
| BrahMos | Supersonic cruise missile | 290 km |
| BrahMos II | Hypersonic cruise missile | 300km |
| Nirbhay | Subsonic cruise missile | 1,000 -1500 km |
Defense Missile
| Name of the Missile | Type of Missile | Range |
| Prithvi Air Defence | Exo-atmospheric Anti-ballistic missile | Altitude- 80km |
| Prithvi Defence Vehicle | Exo-atmospheric Anti-ballistic missile | Altitude- 30km |
| Advanced Air Defence | Endoatmospheric Anti-ballistic missile | Altitude- 120km |
Read about: Exogenic and Endogenic Forces
Submarine Launched Ballistic Missiles
| Name of the Missile | Type | Range |
| Ashwin | Ballistic Missile | 150-200km |
| Sagarika | Ballistic Missile | 700 – 1900 Km |
| K-4 | Ballistic Missile | 3,500–5,000 km |
| K-5 | Ballistic Missile | 6,000 km |
Anti-Tank Missile
| Name of the Missile | Type | Range |
| Amogha | Anti-Tank Guided Missile | 2.8 km |
| Nag | Anti-Tank Guided Missile | 4km |
| Helina | Anti-Tank Guided Missile | 7-8km |
Read about: Natural Vegetation in India
Missiles of India Important Facts for UPSC
- The 1983 launch of the Integrated Guided Missile Development Program (IGMDP).
- The goal of this programme was to build the Trishul, Akash, Nag, Prithvi, and Agni-I missile systems in the nation.
- The intermediate-range surface-to-surface missiles mentioned above.
- The “Missile Woman” of India is Tessy Thomas, an Indian scientist who serves as the Director General of Aeronautical Systems and the former Project Director for the Agni-IV missile in the Defence Research and Development Organization (DRDO).
- Prithvi was the nation’s first surface-to-surface missile with a single stage and liquid fuel.

 AI and its Regulation in India, Limitati...
AI and its Regulation in India, Limitati...
 Tuberculosis (TB), Symptoms, Causes and ...
Tuberculosis (TB), Symptoms, Causes and ...
 Silicon Photonics Enables Low-power AI A...
Silicon Photonics Enables Low-power AI A...





















