Table of Contents
Energy Resources
Energy is the ability to do work and is essential for life. An energy resource can provide heat, power, or electricity. Materials that store energy are called fuels. Over time, human energy use has increased significantly today, people consume about 110 times more energy per person than early humans, who mainly needed food and firewood. Most of our energy comes from fossil fuels, which are non-renewable and can harm the environment. All energy sources, except direct solar heating, ultimately depend on Earth’s materials.
Energy Resources Types
Natural sources of energy can be divided into two categories
- Conventional Sources of Energy
- Non-Conventional Sources of Energy.
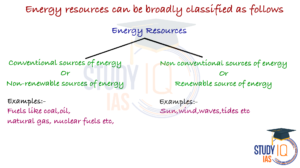
Difference between Conventional Sources of Energy and Non-Conventional Sources of Energy
| Conventional Sources of Energy | Non-Conventional Sources of Energy |
| These resources are exhaustible and run out eventually. | These resources are in-exhaustible and never run out. |
| These resources release smoke and ash, which contribute to pollution. | Typically, these resources don’t cause any pollution. |
| The upkeep, storage, and transmission of these resources are exceedingly costly. | These resources are less expensive, and they are also simple to manage. |
| Coal, natural gas, petroleum, and water power are among the examples. | Solar, biomass, wind, biogas, tidal, and geothermal energy are some examples. |
Conventional Energy Sources
1. Coal
One of the vital minerals, coal is primarily employed in the production of thermal energy and the smelting of iron ore.
- Coal is mainly found in two geological eras: Gondwana and Tertiary deposits.
- In India, over 80% of non-coking coal reserves are bituminous coal.
- The Damodar Valley has the largest Gondwana coal deposits in India, located in the Jharkhand-Bengal coal belt.
- Major coalfields in this area include Jharia (the largest), Raniganj, Bokaro, Giridih, and Karanpura.
- Other significant coal regions are the river valleys of Godavari, Mahanadi, and Sone.
- Key coal mining areas include Singrauli (Madhya Pradesh), Singareni (Telangana), Pandur (Andhra Pradesh), Talcher and Rampur (Odisha), and Korba (Chhattisgarh).
- Tertiary coal deposits are found in Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, Meghalaya, and Nagaland.
- Brown coal, or lignite, is present in coastal regions of Gujarat, Jammu and Kashmir, Tamil Nadu, and Pondicherry.
2. Petroleum
Hydrocarbons in liquid and gaseous forms that vary in chemical composition, colour, and specific gravity make up crude petroleum.
- Crude oil is essential for internal combustion engines in cars, trains, and airplanes.
- It is also used in petrochemical industries to make products like fertilizers, rubber, fibers, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics.
- Crude oil is found in sedimentary rocks from the Tertiary era.
- The Oil and Natural Gas Commission was set up in 1956 to explore and produce oil.
- Before 1956, Digboi in Assam was the only oil refinery, but new reserves have since been discovered in western and eastern India.
- Major oil-producing areas in Assam include Digboi, Naharkatiya, and Moran.
- Gujarat has significant oil reserves in places like Ankleshwar, Kalol, and Mehsana.
- The Mumbai High oil field, located offshore, began production in 1976.
- Oil and natural gas have also been found in the Krishna-Godavari and Kaveri basins.
- Crude oil needs refining to remove impurities before it can be used.
- India has two types of refineries: market-based (like Barauni) and field-based (like Digboi).
3. Natural Gas
In order to transport and market natural gas, the Gas Authority of India Limited was established as a public sector enterprise in 1984. It is found in all oil fields alongside oil, however, there are exclusive reserves in Tripura, Rajasthan, Gujarat, and Maharashtra as well as along the eastern coast (Tamil Nadu, Odisha, and Andhra Pradesh).
Non-Conventional Energy Sources
Coal, petroleum, natural gas, and nuclear energy all use finite raw materials as their primary energy source. Only renewable energy sources like sun, wind, hydro geothermal, and biomass are considered sustainable energy sources. These energy sources are more environmentally responsible and evenly dispersed. After the initial cost is covered, non-conventional energy sources will offer more consistent, eco-friendly, and less expensive energy.
1. Nuclear Energy
- In recent years, nuclear energy has become a reliable power source.
- Uranium and thorium are important minerals for nuclear energy production.
- Uranium reserves are found in the Dharwar rocks.
- Uranium ores are located in the Singbhum Copper belt and in districts like Kullu (Himachal Pradesh), Durg (Chhattisgarh), and Alwar and Jhunjhunu (Rajasthan).
- Thorium is mainly sourced from monazite and ilmenite in beach sands along the coasts of Kerala and Tamil Nadu.
- The richest deposits of monazite are in Palakkad and Kollam (Kerala), near Vishakhapatnam (Andhra Pradesh), and the Mahanadi river delta (Odisha).
- The Atomic Energy Commission was established in 1948, but progress increased after the Bhabha Atomic Research Centre was founded in 1954.
- Major nuclear energy projects are located in Tarapur (Maharashtra), Rahatbhata (Rajasthan), Kalpakkam (Tamil Nadu), Narora (Uttar Pradesh), Kaiga (Karnataka), and Kakarapara (Gujarat).
2. Solar Energy
- Solar energy is generated by capturing sunlight with photovoltaic cells.
- There are two main ways to harness solar energy: photovoltaics and solar thermal technology.
- Solar thermal energy is usually cheaper, environmentally friendly, and easy to install compared to non-renewable sources.
- Solar power is 10% more efficient than nuclear power and 7% more efficient than coal or oil systems.
- It is commonly used in appliances like heaters, crop dryers, and cookers.
- Gujarat and Rajasthan in western India have the highest potential for solar energy development.
3. Wind Power
- Wind power is a clean and unlimited source of electricity.
- Turbines convert wind’s kinetic energy into electrical energy.
- India is building 250 wind turbines with a total capacity of 45 megawatts in 12 locations, mostly along the coast.
- The government supports wind energy to reduce oil import costs.
- India has the potential to generate over 50,000 megawatts of wind energy, but only about 25% is currently usable.
- The best states for wind energy in India are Rajasthan, Gujarat, Maharashtra, and Karnataka.
4. Tidal and Wave Energy
- Ocean currents provide a constant source of energy.
- Efforts to harness this energy date back to the 17th and 18th centuries.
- The west coast of India experiences strong tidal waves.
- India has great potential for tidal energy production along its coasts.
- However, this potential has not yet been fully tapped.
5. Geothermal Energy
- Extreme heat is released when magma rises from the Earth’s interior.
- This thermal energy can be harnessed and converted into electrical energy.
- Hot water from geysers also produces thermal energy, known as geothermal energy.
- Geothermal energy is considered a potential backup energy source today.
- People have used hot springs and geysers since the Middle Ages.
- India has operational geothermal energy plants, such as the one in Manikaran, Himachal Pradesh.
6. Bio-energy
- Bio-energy comes from biological materials like waste from homes, industries, and farms.
- It can be converted into gas for cooking, heat energy, or electricity.
- Using bio-energy helps process waste and garbage while generating energy.
- This can improve the quality of life for rural residents in developing countries.
- It also helps reduce environmental pollution and dependence on fuel wood.
- The Okhla project in Delhi turns city garbage into energy.
Energy Resources Conservation
The difficulty of sustainable development necessitates fusing the pursuit of economic growth with environmental considerations. Traditional resource usage practices generate a significant amount of trash and contribute to other environmental issues. Therefore, conserving resources for future generations is necessary for sustainable growth. The necessity to save resources is critical.
Alternative energy sources including solar, wind, wave and geothermal power provide an endless source of energy. To replace the finite resources, these should be developed. Utilizing scrap metals will allow for the recycling of metals in the case of metallic minerals. Utilizing scrap is particularly important for metals like copper, lead, and zinc, where India has limited deposits. Utilizing alternatives for rare metals may also cut down on usage. Reduced export of strategic and rare minerals is necessary to extend the useful life of the current reserve.
Energy Resources UPSC
Conserving means taking care of and preserving these resources for future generations. As a UPSC aspirant, you should be well aware of the location of various oil refineries and the collaboration of India with various countries in upgrading the refineries. Also, the conservation of energy on an individual level is crucial and switching from conventional to non-conventional energy or alternative energy resources should be encouraged and emphasized. This topic of geography holds immense importance from both Prelims and Mains point of View. The details in the article would help candidates preparing for UPSC 2025.
Other Indian Geography Topics
Other Fundamental Geography Topics


 Jallianwala Bagh Massacre, Date, History...
Jallianwala Bagh Massacre, Date, History...
 Important Lakes of India, State wise and...
Important Lakes of India, State wise and...
 Buddhism History, Origin, Sect, Councils...
Buddhism History, Origin, Sect, Councils...





















