Table of Contents
Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is part of the Atlantic Ocean and is located between the continents of Eurasia and Africa, almost completely surrounded by land. It is bordered by 21 countries, including Albania, Algeria, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Cyprus, Egypt, France, Greece, Israel, Italy, Lebanon, Libya, Malta, Monaco, Montenegro, Morocco, Slovenia, Spain, Syria, Tunisia, and Turkey. To the west, the Mediterranean Sea connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the Strait of Gibraltar. To the east, it connects to the Black Sea through the Dardanelles Straits, and to the south, it links to the Red Sea via the Suez Canal. The Nile River in Africa flows into the Mediterranean Sea.
Countries Surrounding the Mediterranean:
In Europe – Spain, France, Italy, Malta, Monaco, Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, Albania, and Greece. In West Asia – Turkey, Syria, Lebanon, Israel, the Palestinian Gaza Strip, and Cyprus. In North Africa – Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya, and Egypt.
Coastline Length:
The Mediterranean Sea has a coastline of about 46000 km
Smaller Seas:
It includes 15 smaller seas, such as the Balearic Sea, Adriatic Sea, Levantine Sea, and Ionian Sea.
Rivers:
Major rivers flowing into the Mediterranean include the Ebro, Rhône, Po, Nile, and Tiber.
Largest Islands:
Some of the largest islands are Corsica, Crete, Cyprus, Chios, Euboea, Lesbos, Mallorca, Rhodes, Sicily, and Sardinia. Sicily is the largest.
Climate:
The region has a subtropical climate with mild, wet winters and hot, dry summers.
Read More: East China Sea
Mediterranean Sea in World Map
Here is the Map of the Mediterranean Sea to understand the geographical location of the Mediterranean Sea region:
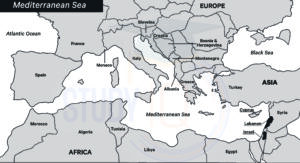
Mediterranean Sea Countries
Twenty-one countries share borders with the Mediterranean Sea, including Albania, Algeria, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Cyprus, Egypt, France, Greece, Israel, Italy, Lebanon, Libya, Malta, Monaco, Montenegro, Morocco, Slovenia, Spain, Syria, Tunisia, and Turkey.
The Mediterranean Sea connects to the Atlantic Ocean in the west through the Strait of Gibraltar, to the Black Sea in the east through the Dardanelles Straits, and to the Red Sea in the south via the Suez Canal. The Nile River from Africa flows into the Mediterranean.
The British Overseas Territories of Gibraltar, Akrotiri, and Dhekelia, as well as the Gaza Strip, also have coastlines along the Mediterranean. The term “Palestine” has been historically used to describe the area that includes Israel, the West Bank, and the Gaza Strip.
Read More: South China Sea
Mediterranean Sea Geography
The Mediterranean Sea is shaped like an oval, running long from east to west and shorter from north to south. It is surrounded by the coastlines of Europe, Africa, and Asia and is divided into two deep areas. The sea goes from the Strait of Gibraltar in the west to the Dardanelles and the Suez Canal in the east.
- Bays and Gulfs: The Mediterranean has big bays like the Gulf of Sidra in Libya, the Gulf of Gabès in Tunisia, and the Gulf of Antalya in Turkey.
- Straits: It connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the Strait of Gibraltar and to the Red Sea through the Suez Canal.
- Islands: There are large islands like Sardinia, Corsica, Sicily, and Ibiza, along with many smaller islands.
- Western Basin: The western part of the sea includes points in Spain, like Cape Spartel and Cape Trafalgar, and the west coast of Italy. The Strait of Messina connects points in Sicily.
Read More: Ocean Deposits
Mediterranean Sea Significance
The Mediterranean Sea has significant cultural, historical, economic, and environmental importance:
- Historical: The Mediterranean has been an important trade route for thousands of years and has seen the rise and fall of many civilizations, including the Ancient Egyptians, Phoenicians, Greeks, and Romans.
- Cultural: The Mediterranean basin is home to diverse cultures, including Europe, Africa, and the Middle East, and has greatly influenced art, architecture, literature, music, and religion.
- Economic: The Mediterranean is a major shipping lane for goods and oil, and its coastline is a popular tourist destination.
- Environmental: The Mediterranean is a semi-enclosed sea with a unique climate and ecosystem, making it a biodiversity hotspot, but also vulnerable to pollution and overfishing.
Mediterranean Sea UPSC
The Mediterranean Sea is an intercontinental body of water that divides Europe from Africa and spans from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to Asia in the east. It is frequently referred to as the birthplace of Western civilization.
Read More: Ocean Tides


 Role of Teachers in Educations, Student ...
Role of Teachers in Educations, Student ...
 India's achievements after 75 years of I...
India's achievements after 75 years of I...
 Bal Gangadhar Tilak Biography, Achieveme...
Bal Gangadhar Tilak Biography, Achieveme...

























