Table of Contents
Context: SC has ordered a complete stop on the practice of manual scavenging in six metros – Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, Kolkata, Bengaluru and Hyderabad.
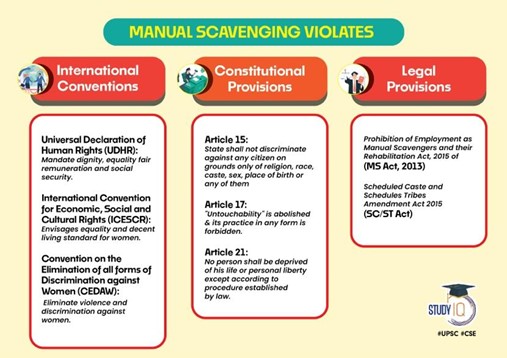
Manual Scavenging
- The Employment of Manual Scavengers and Construction of Dry Latrines (Prohibition) Act, 1993 defines ‘manual scavenger’ as “a person engaged in or employed for manually carrying human excreta”.
- Manual scavenging undermines SDGs related to clean water and sanitation (Goal 6), decent work and economic growth (Goal 8), reduced inequalities (Goal 10) and peace, justice and strong institutions (Goal 10).
Initiatives taken to prevent Manual Scavenging
- The Prohibition of Employment as Manual Scavengers and their Rehabilitation Act, 2013: This Act supersedes the 1993 Act and prohibits all forms of manual excrement cleaning of insanitary latrines, open drains, or pits. It also focuses on the rehabilitation of manual scavengers and provides measures for their welfare.
- Safaimitra Suraksha Challenge: Launched by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs on World Toilet Day in 2020, it aims to make sewer cleaning completely mechanized by providing proper gear and oxygen tanks to workers in case of unavoidable emergencies.
- The National Action for Mechanised Sanitation Ecosystem (NAMASTE) scheme aims to improve the safety and dignity of sanitation workers in India. It was launched in 2023-24 and is being implemented in over 4,800 urban local bodies (ULBs) across the country.
Directions issued by SC in Balram Singh Vs Union of India & Others (2023)
- Complete Eradication of Manual Sewer Cleaning: Union Government to:
- Frame policies and issue directives to all statutory bodies (corporations, railways, cantonments, etc.) for the phased eradication of manual sewer cleaning.
- Ensure outsourced sewer work does not require individuals to enter sewers for any purpose.
- States and Union Territories to: Adopt and implement the Union Government’s guidelines across all municipalities, local bodies, and agencies in their jurisdictions.
- Rehabilitation of Affected Workers: Full rehabilitation measures for sewer workers and families of those who have died.
- Enhanced Compensation for Sewer Deaths: Compensation for deaths caused by hazardous cleaning increased from ₹10 lakh to ₹30 lakh.
- Development of a Centralized Portal and Dashboard to:
- Maintain data on sewer deaths and affected workers.
- Track compensation disbursement and rehabilitation measures.
- Provide information on existing policies and initiatives.
| National Commission on Safai Karmchari (NCSK) |
|


 Light Weight Modular Missile (LMM) — I...
Light Weight Modular Missile (LMM) — I...
 Species Survival Commission (SSC) – IU...
Species Survival Commission (SSC) – IU...
 Global Hunger Index (GHI) 2025: India Ra...
Global Hunger Index (GHI) 2025: India Ra...




















