Table of Contents
Context: Amara Raja Energy & Mobility Limited is navigating the shift towards lithium-ion batteries while leveraging its legacy in lead-acid technology amidst evolving market demands and the push for sustainability and circularity.
Impact of Lithium-Ion on Lead-Acid Segment
- Superior Energy Density: Lithium-ion’s superior energy density has made it preferred for applications where form factor is limited, such as telecom for 5G small cell sites.
- Lead-Acid Relevance: In areas where size is not a constraint, such as industrial UPS, lead-acid batteries continue to be relevant. They are being adapted for power applications with technologies like stamped grids for higher discharge needs.
- Adapting to Changes: As applications evolve, lead-acid batteries are being optimised for shorter backup times and higher loads. For completely new applications, alternative chemistries like lithium-ion are considered.
We’re now on WhatsApp. Click to Join
Sector-wise Demand Trends
- Telecom and 5G: Transitioning to lithium-ion for smaller cell formats due to form factor requirements. Lead-acid remains in use for larger cell towers.
- UPS and Data Centres: Lead-acid dominates UPS, but lithium-ion is preferred for data centres due to its smaller form factor.
- Railways and Solar: A mix of lead-acid and lithium-ion is observed, with the choice depending on specific requirements.
- Energy Storage: Neither lead-acid nor lithium-ion currently meet the cost-effectiveness criteria for grid-level energy storage compared to fossil fuels.
Automotive Sector Trends
- Two-Wheelers: Rapid adoption of EVs driven by competitive total cost of ownership. Lead-acid batteries continue to grow in the ICE segment.
- Four-Wheelers: Initial high costs and supply chain inefficiencies limit EV adoption. Hybrid vehicles are becoming popular for their fuel economy and ownership experience.
- Auxiliary Power Source: Lead-acid batteries are used in hybrid and electric vehicles for critical safety functions, ensuring reliability even when the main battery is off.
Challenges and Opportunities with New Entrants
- Increasing Competition: New players like Reliance Industries and Ola Electric introduce challenges for legacy manufacturers but also opportunities for collaboration and development.
- Capability Building: The entry of new competitors resets competitive dynamics, encouraging legacy players to innovate and leverage existing customer relationships.
Circularity and Sustainability
- Recycling Efficiency: Lead-acid batteries boast a recycling rate of 99%, with a significant portion of raw materials being sourced from recycled inputs, exemplifying a successful circular economy model.
- Addressing Informal Recycling: Despite advancements, a significant amount of recycling is done unsafely by the informal sector. Policy enhancements and the establishment of formal recycling capacities are needed to improve safety and environmental impact.
What is Circular Economy?
The circular economy is an economic model that aims to minimize waste, maximize resource efficiency, and promote sustainability.
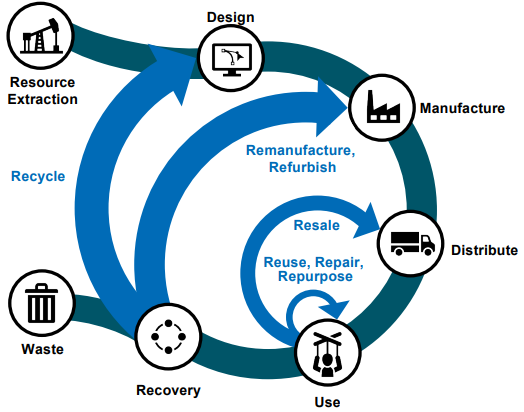
- It is designed to move away from the traditional linear economy, where products are manufactured, used, and then discarded as waste.
- In a circular economy, products, materials, and resources are kept in use for as long as possible, and their value is retained through multiple cycles of use and recycling.


 Topological Materials: The Future of Qua...
Topological Materials: The Future of Qua...
 China’s Deep Sea Station in South Chin...
China’s Deep Sea Station in South Chin...
 Project ICE-CRUNCH: India-Switzerland Co...
Project ICE-CRUNCH: India-Switzerland Co...





















