Table of Contents
Lead Poisoning Meaning
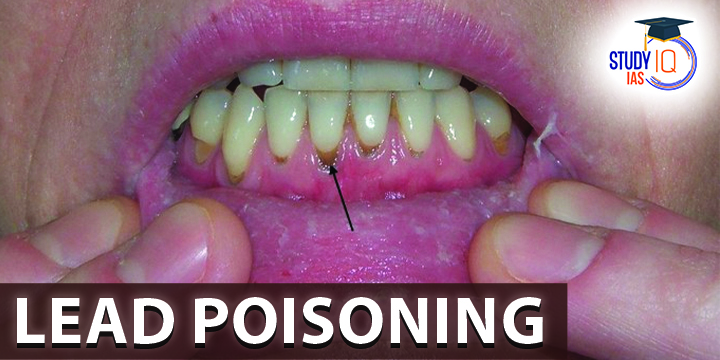
Lead Poisoning is a type of metal poisoning that result in increase in lead concentration in the body. Lead exposure can occur by contaminated air, water, dust, food, or consumer products.
Sources of Lead Poisoning
- The major Source of Lead Poisoning was vehicular emission. However, use of lead in petrol was phased out in 2000.
- Battery recycling, lead mining, smelting, welding, soldering and automobile repatriating are other main sources.
- Adulterated spices (turmeric), cosmetics (sindoor), paints, pesticides, toys and traditional medicines have traces of lead.
- Drinking water supplied through lead pipes or lead soldered pipes may contain lead.
- Pottery glaze on cookware and serving dishes makes up a significant source of lead exposure for children and adults.
Effects of Lead Poisoning on The Human Body
- Neurological Problems: Tingling, numbness or weakness in the legs or hands. Some have brain-related symptoms such as low IQ and memory loss.
- Reproductive problems: Low sperm count, miscarriages and variation in menstrual cycle.
- Blood: Anemia, blood pressure and effects on blood cells.
- Gastrointestinal: Abdominal pain, poor appetite, weight loss, constipation etc.
- Renal: Lead can damage kidney cells, leading to chronic kidney problems.
- Infants: Lead can lead to premature birth, reduced birth weight as well as slow growth of the infant. They also suffer from pale skin and hearing problems.
Lead Poisoning Report
- Brought out by: Lead Poisoning Report was jointly prepared by government think tank Niti Aayog and the Council of Scientific & Industrial Research (CSIR).
- Affected states: Bihar, Madhya Pradesh, Jharkhand, Uttar Pradesh, Chhattisgarh and Andhra Pradesh have the highest average blood lead levels (BLL) among Indian states.

- These states account for 40 per cent of India’s population suffering from poor health indicators.
- Average lead levels: The average BLL for India is 4.9 μg / dl for children less than two years old. Some 23 states have an average BLL that is above five microgram per decilitre (μg / dl).
- India has over 275 million children (about one half of all children in India) with BLLs more than considered safe (five micrograms per deciliter). This is the uppermost level of Pb poisoning cases in children in any country.
- Global level: Around 1 in 3 children – up to approximately 800 million globally – have blood lead levels at or above 5 micrograms per decilitre (μg/dL)
- Impact: Lead pollution resulted in estimated five per cent loss of Indian Gross Domestic Product (GDP) due to lower economic productivity.
- It reduced lifetime earnings and also caused 230,000 premature deaths in India.
Lead Poisoning Prevention
- Identification of victims: People suffering from lead pollution needs to be identified through BLL monitoring and training health workers. This will help locate the most vulnerable groups.
- Identifying sources: Intensified research needs to be conducted to identify new sources of lead pollution. This will help policymakers to take mitigating measures.
- Battery handling: Being a major Source of lead Poisoning, battery recycling process needs to be regulated. Strict measures have to be implemented to prevent exposure.
- Regular testing: Regular testing of products, suspected of containing lead, has to be conducted. This includes food products, paints, toys and medicines. Gradual phasing out of toxic products is necessary.
- Awareness creation: Mitigating lead pollution needs state-level measures. There is a need to engage regional bureaucracy, local press and vernacular language to spread awareness about lead pollution.
- Treatment: Medicines use can bind lead so it can be eliminated from the body. Chelation therapy can be used in children when lead blood levels are higher.
- Legislative policy: Policies have to be brought on that control and regulate practices involving lead. Punishments have to be imposed for violating guidelines.


 Happy New Year 2026: StudyIQ Family’s ...
Happy New Year 2026: StudyIQ Family’s ...
 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (C...
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (C...
 Ancient Buddhist Site Discovered in Kash...
Ancient Buddhist Site Discovered in Kash...

























