Table of Contents
Language is an essential facet of human communication, acting as a bridge between cultures, facilitating knowledge transfer, and fostering identity. With over 7,000 languages spoken worldwide, it is crucial to explore both the most spoken languages and the oldest languages in the world, especially in the context of UPSC preparation for the General Studies paper on culture, history, and society.
List of Languages of the World 2025
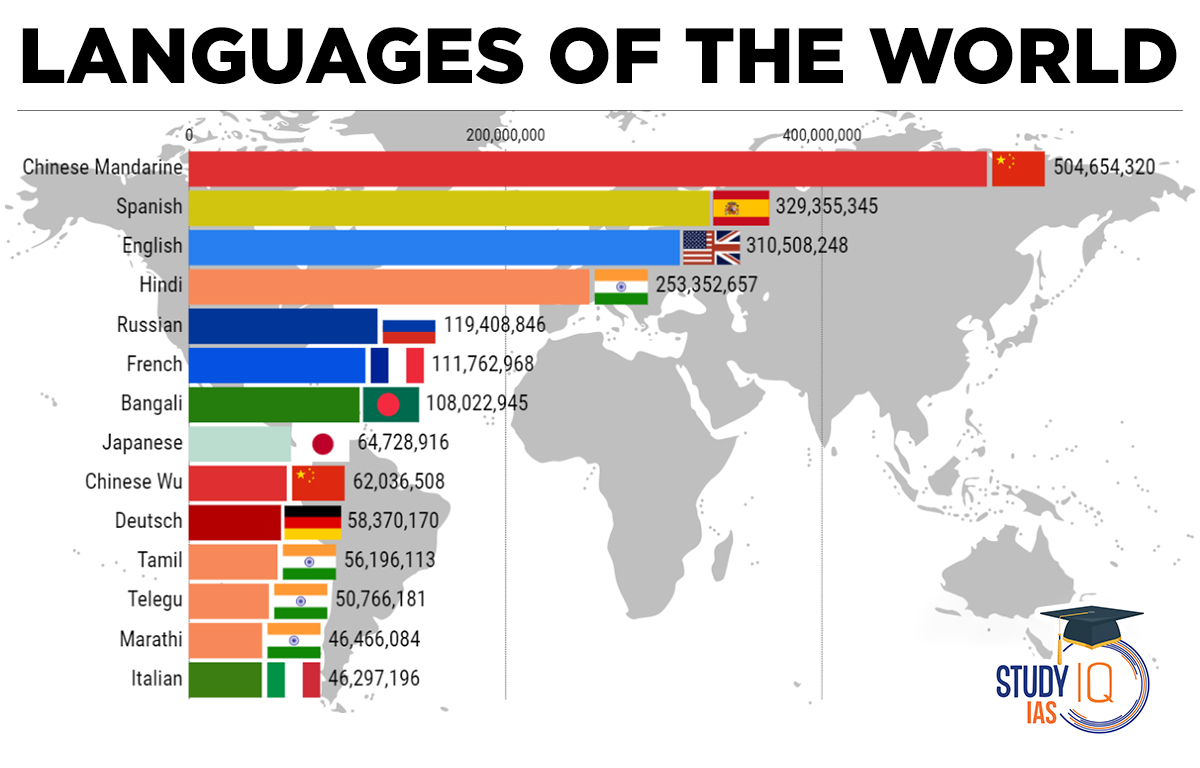
Languages of the World by the number of speakers are listed below, along with their family.
| Language | Family | Total No of Speakers |
| English | Indo-European | 1.452 billion |
| Mandarin Chinese
(incl. Standard Chinese, but excl. other varieties) |
Sino-Tibetan | 1.118 billion |
| Hindi (excl. Urdu) | Indo-European | 602.2 million |
| Spanish | Indo-European | 548.3 million |
| French | Indo-European | 274.1 million |
| Modern Standard Arabic (excl. dialects) | Afro-Asiatic | 274.0 million |
| Bengali | Indo-European | 272.7 million |
| Russian | Indo-European | 258.2 million |
| Portuguese | Indo-European | 257.7 million |
| Urdu (excl. Hindi) | Indo-European | 231.3 million |
| Indonesian (excl. Malay) | Austronesian | 199.0 million |
| Standard German | Indo-European | 134.6 million |
| Japanese | Japonic | 125.4 million |
| Nigerian Pidgin | English Creole | 120.7 million |
| Marathi | Indo-European | 99.1 million |
| Telugu | Dravidian | 95.7 million |
| Turkish | Turkic | 88.1 million |
| Tamil | Dravidian | 86.4 million |
| Yue Chinese (incl. Cantonese) | Sino-Tibetan | 85.6 million |
| Vietnamese | Austroasiatic | 85.3 million |
| Tagalog | Austronesian | 82.3 million |
| Wu Chinese (incl. Shanghainese) | Sino-Tibetan | 81.8 million |
| Korean | Korean | 81.7 million |
| Iranian Persian (excl. Dari and Tajik) | Indo-European | 77.4 million |
| Hausa | Afro-Asiatic | 77.1 million |
| Egyptian Spoken Arabic (excl. other Arabic dialects) | Afro-Asiatic | 74.8 million |
| Swahili | Niger-Congo | 71.4 million |
| Javanese | Austronesian | 68.3 million |
| Italian | Indo-European | 67.9 million |
| Western Punjabi (excl. Eastern Punjabi) | Indo-European | 66.4 million |
| Kannada | Dravidian | 64.0 million |
| Gujarati | Indo-European | 62.0 million |
| Thai | Kra–Dai | 60.7 million |
| Amharic | Afroasiatic | 57.5 million |
| Bhojpuri | Indo-European | 52.5 million |
| Eastern Punjabi (excl. Western Punjabi) | Indo-European | 51.7 million |
| Min Nan Chinese (incl. Hokkien) | Sino-Tibetan | 49.7 million |
| Jin Chinese | Sino-Tibetan | 47.1 million |
| Yoruba | Niger-Congo | 45.6 million |
| Hakka Chinese | Sino-Tibetan | 44.1 million |
| Burmese | Sino-Tibetan | 43.0 million |
| Sudanese Spoken Arabic | Afro-Asiatic | 42.3 million |
| Polish | Indo-European | 40.6 million |
| Algerian Spoken Arabic | Afro-Asiatic | 40.3 million |
| Lingala | Niger-Congo | 40.3 million |
Oldest Language in the World
Some languages have deep historical roots. Here are a few of the world’s oldest languages, which provide insight into the earliest forms of human communication:
- Tamil: Widely regarded as the oldest language, with a rich literary tradition. Spoken by over 120 million people.
- Sanskrit: An ancient language that forms the basis of many modern Indian languages.
- Greek: Known for its significant contributions to philosophy and science.
- Sumerian: The oldest known written language, dating back to 3500 BC.
- Egyptian: The language of ancient Egypt, dating back to 3300 BC.
Toughest Language of the World
Mandarin Chinese is widely regarded as the most difficult language in the world to learn. They lack Alphabets and use symbols instead, and it is estimated that the average Chinese local knows more than 8000 symbols, whereas reading a newspaper requires more than 3000 symbols.
At more than 73 characters, the alphabet for the Cambodian language is the longest. One of the hardest languages to learn on your own is the Cambodian language.
Most Spoken Languages of the World
- English: The most widely spoken language, with over 1.4 billion speakers globally. It is the de facto official language of many countries and is the language of aviation, business, and the internet.
- Mandarin Chinese: Spoken by over 1.1 billion people, primarily in China, but also in Taiwan, Singapore, and among the global Chinese diaspora.
- Spanish and French: Both of these languages have a significant presence across Europe, Latin America, and even parts of Africa.
Classical Languages of the World
Every language with an independent literary tradition and a sizable and lengthy body of written literature is considered to be classical. As spoken languages diverge more from the classical written language over time, classical languages are frequently dead languages or exhibit a high degree of diglossia. Chinese, Sanskrit, Arabic, Greek, and Latin are classical languages of the world.
Classical Languages of India
In India, six languages are currently classified as ‘Classical’:
- Tamil (declared in 2004),
- Sanskrit (2005),
- Kannada (2008),
- Telugu (2008),
- Malayalam (2013), and
- Odia (2014).
Check here Classical Languages of India in detail!
List of Official Languages in Different Country
More than 190 official languages from various nations are listed in the table below.
| Languages of the World | |
| Countries | Official Languages |
| Albania | Albanian |
| Ethiopia | Amharic |
| Algeria, Bahrain, Chad, Comoros, Egypt, Iraq, Israel, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Libya, Mauritania, Morocco, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Syria, Tunisia, United Arab Emirates, Yemen | Arabic |
| Sudan | Arabic, English |
| Armenia | Armenian |
| Azerbaijan | Azerbaijan |
| Bangladesh | Bengali |
| Vanuatu | Bislama |
| Myanmar (Burma) | Burmese |
| Andorra | Catalan |
| Malawi | Chichewa |
| China | Chinese, Mandarin |
| Czech Republic | Czech |
| Denmark | Danish |
| Afghanistan | Dari |
| Maldives | Dhivehi |
| Belgium, Suriname | Dutch |
| Bhutan | Dzongkha |
| Antigua and Barbuda, Australia, The Bahamas, Barbados, Belize, Cameroon, Canada, Fiji, The Gambia, Ghana, Grenada, Guyana, Jamaica, Kiribati, Lesotho, Liberia, Marshall Islands, Mauritius, Micronesia, Federated States of Namibia, Nauru, New Zealand, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Sierra Leone, Solomon Islands, South Sudan, Tonga, Trinidad and Tobago, Tuvalu, United Kingdom, United States of America, Zambia | English |
| Singapore | English, Malay, Chinese, Tamil |
| Pakistan | English, Urdu |
| Estonia | Estonian |
| Finland | Finnish |
| Benin, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Republic of the Congo, Côte-d’Ivoire, Djibouti, France, Gabon, Haiti, Mali, Monaco, Niger, Senegal, Switzerland, Togo | French |
| Netherlands | Frisian |
| Georgia | Georgian |
| Austria, Liechtenstein, Germany | German |
| Greece | Greek |
| Bolivia, Paraguay | Guaraní |
| India | Hindi, English |
| Hungary | Hungarian |
| Iceland | Icelandic |
| Indonesia | Indonesian |
| Ireland | Irish |
| Italy, Vatican City (Holy See) | Italian |
| Japan | Japanese |
| Kazakhstan | Kazakh |
| Cambodia | Khmer |
| The Democratic Republic of the Congo | Kikongo |
| Rwanda | Kinyarwanda, French, English |
| North Korea, South Korea | Korean |
| Kyrgyzstan | Kyrgyz |
| Laos | Lao |
| Latvia | Latvian |
| Lithuania | Lithuanian |
| Luxembourg | Luxembourgish |
| Macedonia | Macedonian |
| Madagascar | Malagasy |
| Malaysia, Brunei | Malay |
| Malta | Maltese |
| Moldova | Moldovan |
| Mongolia | Mongolia |
| Montenegro | Montenegrin |
| Zimbabwe | Ndebele, English, Shona |
| Nepal | Nepali |
| Norway | Norwegian |
| Palau | Palauan, English |
| Iran, Tajikistan | Persian |
| Poland | Polish |
| Angola, Brazil, Cape Verde, Guinea-Bissau, Mozambique, Portugal, Sao Tome and Principe | Portuguese |
| Peru | Quechua |
| Romania | Romanian |
| Russia, Belarus | Russian |
| Samoa | Samoan, English |
| San Marino | San Marino |
| Central African Republic | Sango |
| Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Kosovo, Serbia | Serbian |
| Seychelles | Seychellois Creole |
| Sri Lanka | Sinhala, Tamil |
| Slovakia | Slovak |
| Slovenia | Slovene |
| Somalia | Somali |
| South Africa | Sotho |
| Argentina, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Cuba, Dominica, Dominican Republic, Ecuador, El Salvador, Equatorial Guinea, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, Panama, Philippines, Spain, Uruguay, Venezuela | Spanish |
| Taiwan | Standard Chinese |
| Kenya, Tanzania | Swahili |
| Uganda | Swahili, English |
| Swaziland | Swati, English |
| Sweden | Swedish |
| East Timor (Timor-Leste) | Tetum |
| Thailand | Thai |
| Eritrea | Tigrinya |
| Guinea, Papua New Guinea | Tok Pisin |
| Botswana | Tswana |
| Bulgaria, Cyprus, Turkey | Turkish |
| Turkmenistan | Turkmen |
| Ukraine | Ukrainian |
| Uzbekistan | Uzbek |
| Vietnam | Vietnamese |
| Nigeria | Yoruba |
Important Facts about World Languages
Here are some important facts about world languages:
- Language Diversity: There are approximately 6,500 languages spoken across the world today. However, many of these languages are spoken by only a few thousand or even a few hundred people. As a result, many languages are becoming endangered.
- Endangered Languages: Around 40% of the world’s languages are classified as endangered, with fewer than 1,000 speakers remaining. This means many languages are at risk of disappearing in the coming decades.
- Most Spoken Languages: Despite the vast number of languages, only 23 languages are spoken by more than half of the world’s population. English, Mandarin, Hindi, and Spanish are some of the most spoken languages globally.
- Language Extinction: Currently, over 700 languages are considered extinct, meaning they no longer have any speakers. A language dies when it is no longer spoken or recorded.
- Papua New Guinea’s Linguistic Diversity: Papua New Guinea is the country with the most languages, boasting around 841 languages. However, many of these languages are in danger of extinction as they have only a few speakers.
- The U.S. and Official Language: The United States does not have an official language, despite the widespread belief that it is English. The country is linguistically diverse, with many languages spoken due to the immigrant population.
- The Rotokas Language: The Rotokas language, spoken in Papua New Guinea, is known for having the smallest alphabet in the world, consisting of only 11 letters.
- Basque’s Unique Status: Basque is a language spoken between Spain and France, and it is unique because it is unrelated to any other known language, making it a linguistic isolate.
- Global Language Death: A language is considered dead when there is no one left to speak it or to document it. As of now, 241 languages have become extinct.
- French as the “Language of Love”: French is often referred to as the “language of love,” partly due to its romantic sound and the cultural associations with romance, especially in countries like France and Italy.
- Global Language Influence: 23 languages are spoken by more than half of the world’s population, showcasing the global influence of a few dominant languages.

 Miss Universe Winners List From 1952 to ...
Miss Universe Winners List From 1952 to ...
 Significance and History of Diwali Festi...
Significance and History of Diwali Festi...
 Asia Cup Winners List (1984–2025): Ind...
Asia Cup Winners List (1984–2025): Ind...

























