Table of Contents
On October 18, 2024, Israel confirmed the elimination of Yahya Sinwar, the leader of Hamas, marking a significant turning point in the ongoing conflict between Israel and Hamas. Yahya Sinwar, widely known as the “Butcher of Khan Younis,” was held responsible for orchestrating the deadly October 7, 2023, attack on Israel that resulted in widespread casualties and ignited the current war in Gaza. His death is seen as a crucial victory for Israel, symbolizing the nation’s retribution for the mass killings that took place last year.
Israel Confirms Yahya Sinwar’s Elimination: Israel’s Revenge Complete
Israel has officially confirmed the elimination of Yahya Sinwar, the leader of Hamas, in a targeted military operation. Sinwar, who was often called the “Butcher of Khan Younis,” was accused of masterminding the brutal October 7, 2023, attacks on Israel that led to the ongoing war in Gaza. On October 18, 2024, Israeli Defense Forces (IDF) successfully neutralized Sinwar in the Tal El Sultan area of southern Gaza, marking a critical moment in Israel’s efforts against Hamas.
Israeli Foreign Minister Eli Cohen announced that Sinwar’s death represents a significant victory in Israel’s broader mission of retribution for the deadly attacks that killed many civilians. While Hamas has yet to officially confirm his death, sources within the militant group indicate that the leader was indeed killed during the Israeli operation.
This elimination strikes a major blow to Hamas leadership, fulfilling what many in Israel see as a crucial act of revenge, though the wider implications for the ongoing conflict in Gaza remain uncertain.
Global Shock as Six Israeli Hostages Killed by Hamas
On September 2, 2024, the world was shocked to learn that six Israeli hostages, captured by Hamas during the conflict, were found dead in Gaza. The hostages included civilians and a soldier who were brutally killed, likely in retaliation for Israeli military actions. The global reaction has been one of condemnation, with widespread protests in Israel demanding action and negotiations. India, however, has remained silent, reflecting its cautious diplomatic stance amid its strategic ties with Israel and its broader foreign policy approach. The silence underscores India’s delicate balance in navigating international relations and conflict resolution.
Hamas Chief Ismail Haniyeh Killed in Iran
Israel-Hamas War
Israel Declared a State of War after being hit by 5,000 rockets From Gaza Strip through the Hamas Group. The Israeli military reported that Hamas carried out a coordinated operation, which included rocket assaults and a terrorist infiltration into Israeli territory. Palestinian fighters initiated a significant assault on Israel on October 7 2023, penetrating southern Israel and launching a barrage of rockets from the Gaza Strip.
Dubbed “Operation Al-Aqsa Storm,” this operation represents one of the most substantial confrontations between the two parties in years. The assault commenced with rocket attacks from various locations in Gaza and featured unexpected tactics, including the use of paragliders and fighters within Israel.
All Eyes on Rafah
The “All Eyes on Rafah” campaign rallies global support via social media, spotlighting Rafah amidst Gaza’s conflict. Originating from WHO’s Rick Peeperkorn, it gained traction as Israel targeted the city’s alleged militant strongholds. With 1.4 million seeking refuge in Rafah, the campaign calls for awareness and action amid civilian casualties.
Despite widespread solidarity, critics argue it overlooks Hamas’ actions and focuses solely on Israeli military operations. Social media amplifies the campaign’s message, drawing attention to Gaza’s humanitarian crisis. “All Eyes on Rafah” epitomizes grassroots efforts for peace amid escalating tensions, emphasizing the urgency of international intervention and dialogue.
UN Chief Invokes Rare Article 99 Over Gaza War
UN Secretary-General Antonio Guterres invoked Article 99 of the UN Charter, an unusual step allowing him to alert the Security Council to potential threats to international peace. Guterres urged the council to address the Gaza war and prevent a humanitarian catastrophe. Despite Israel’s intensified actions in Gaza’s second-largest city, the Security Council has not issued a ceasefire resolution. Guterres, who had never before used Article 99, highlighted the urgency. The article’s last invocation was between 1959 and 1966, underscoring its rarity.
Gaza Hospital Attack: Israel Killed 500 in Gaza Hospital
An Israeli airstrike on Al-Ahli Arab Hospital in Gaza City claimed the lives of over 500 Palestinians, with Gaza’s health ministry confirming the toll. Israel attributed the devastating incident to a misfired rocket from the Palestinian Islamic Jihad, making it one of the deadliest hospital attacks in decades. The international community has widely condemned the event, sparking protests at Israeli embassies in multiple nations.
The occupied West Bank witnessed clashes between demonstrators and Palestinian security forces, underscoring discontent with the Palestinian Authority’s leadership. While U.S. President Joe Biden heads to Israel, a planned summit with regional leaders has been cancelled, while a deepening humanitarian crisis ensues in Gaza due to restricted aid access.
Operation Ajay
Operation Ajay is an Indian government initiative launched to repatriate its citizens from the conflict zone in Israel and Palestine. It was initiated due to heightened tensions following Hamas attacks in Israel. The operation primarily utilizes specially chartered flights for the evacuation of an estimated 18,000 Indians residing in the region, with the Indian Navy on standby for additional support if required. External Affairs Minister Dr. S Jaishankar announced the operation, emphasizing the government’s commitment to ensuring the safety and welfare of Indian nationals during the period of increased conflict.
Gaza−Israel Conflict Escalated: State of War
The Israel Defense Forces committed to responding and formally characterized the situation not merely as an escalation but as the nation being ‘in a State of War.’ Underscoring the surprise element of the attack that spared no civilians, Lieutenant Colonel Jonathan Conricus, former spokesperson of the Israel Defense Forces, stressed that this Hamas-led assault, supported by Iran with provisions of weapons, personnel, equipment, and financial resources, constituted a substantial and unacceptable escalation.
Operation Al-Aqsa Flood
Tensions in the Israel-Palestine conflict have intensified as Hamas’s military group initiated “Operation Al-Aqsa Flood,” launching more than 5,000 rockets into Israel.
Israel Invokes Article 40 Aleph to Declare War After 50 Year
In 1973, during the Yom Kippur War, also known as the October War or Ramzan War, Article 40 Aleph was employed for the first time. On Sunday, October 8 2023, the Israeli Political-Security Cabinet officially declared war by invoking Article 40 Aleph, marking the first instance since 1973. This decision followed Hamas’s infiltration into southern Israel on Saturday, October 7, involving fighters, the launch of 5,000 rockets, and the capture of individuals. In response to these actions, Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu announced the commencement of “a long and difficult war.”
Rafah Border Crossing
The Rafah border crossing between Gaza and Egypt has opened for the first time since the Israel-Hamas war erupted. The Rafah Border Crossing is the sole crossing point between Egypt and the Gaza Strip, located on the Gaza–Egypt border. It’s the southernmost post of exit from Gaza and borders Egypt’s Sinai peninsula.
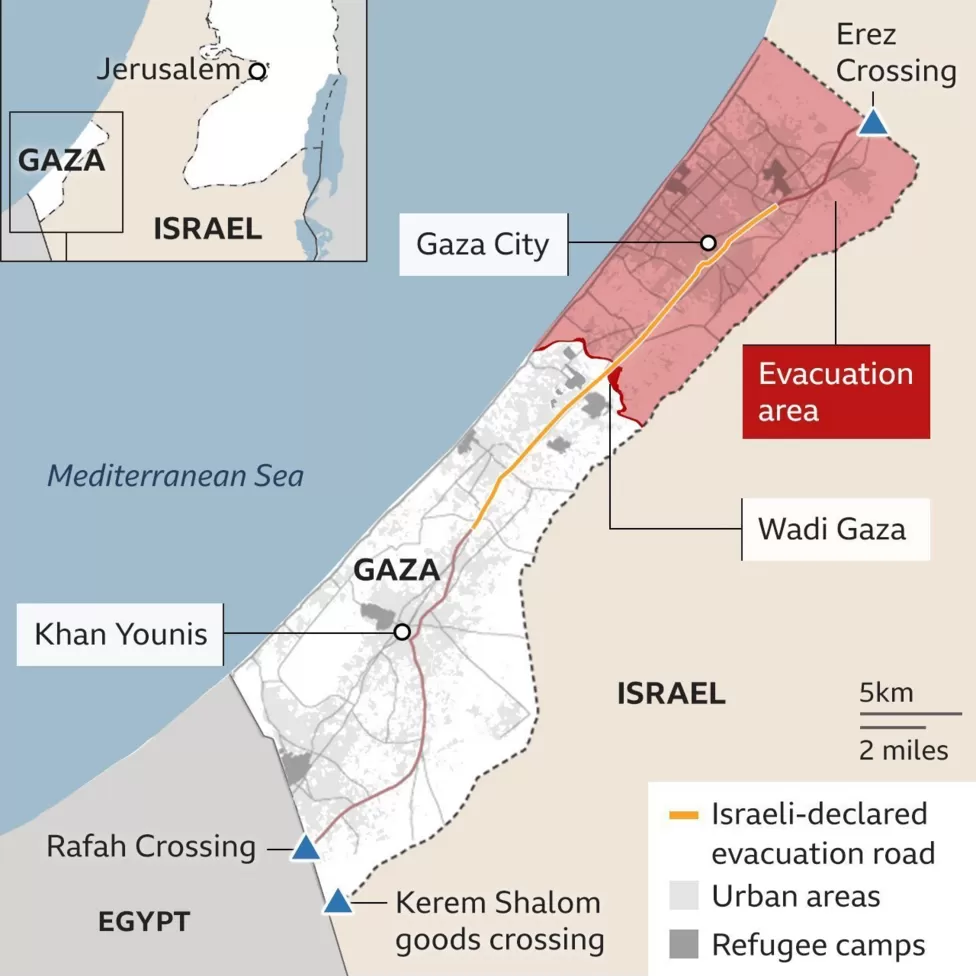
Significant Geopolitical Importance of Rafah Border Crossing
- Historically, it’s had significant geopolitical importance.
- After the 1967 Six-Day War, Israel controlled the crossing, but it was returned to Egypt after the 1979 peace treaty.
- The border was divided, affecting local families when Israel withdrew from the Sinai in 1982. The Israeli disengagement from Gaza in 2005 transferred control of the Gazan side to the Palestinian Authority.
- The European Union Border Assistance Mission Rafah (EUBAM) monitored the crossing post-disengagement.
- The crossing has also been a point of contention in Israeli-Palestinian relations, as exports through Rafah were restricted, leading to the development of a smuggling tunnel economy.
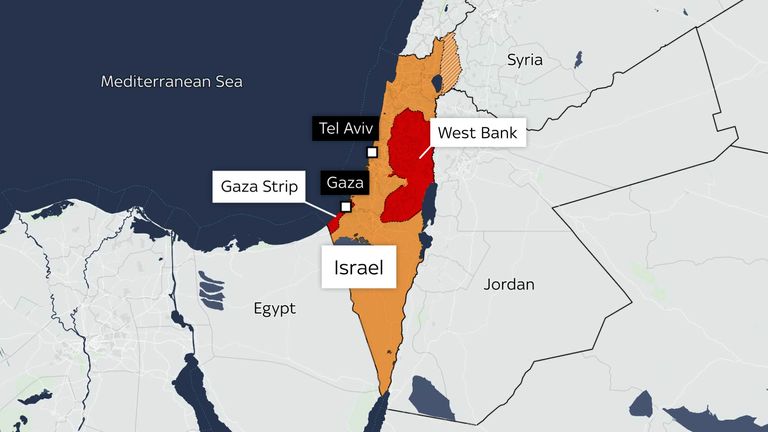
What is the Israel-Palestine Conflict?
The Israel-Palestine conflict is a longstanding and deeply rooted political and territorial dispute between Israelis and Palestinians. The roots of the conflict trace back to the late 19th and early 20th centuries, with the rise of nationalist movements among Jews and Arabs in the Middle East.
History of the Israel-Palestine Conflict
The Israel-Palestine conflict is complex, involving historical, religious, and territorial dimensions. The quest for a two-state solution, with Israel and Palestine living side by side in peace, remains a central goal of international efforts to resolve the conflict. However, achieving a lasting and comprehensive resolution has proven to be challenging due to deep-seated grievances, conflicting narratives, and geopolitical complexities.
Historical Background
The Zionist movement, advocating for a Jewish homeland, gained momentum in the late 19th century. The Balfour Declaration in 1917 expressed British support for the establishment of a “national home for the Jewish people” in Palestine.
Partition and Establishment of Israel
The United Nations proposed a partition plan in 1947 to divide Palestine into separate Jewish and Arab states, with Jerusalem as an international city. While Jewish leaders accepted the plan, Arab leaders rejected it. Israel declared its independence in 1948, leading to the Arab-Israeli War.
Arab-Israeli Wars
The conflict has witnessed several wars, including the 1948 Arab-Israeli War, the Six-Day War in 1967, and the Yom Kippur War in 1973. These wars resulted in significant territorial changes and ongoing tensions.
Occupation and Settlements
Israel occupied the West Bank, East Jerusalem, and the Gaza Strip during the Six-Day War. The establishment of Israeli settlements in these territories has been a major point of contention.
Palestinian Resistance and Nationalism
Palestinians have engaged in various forms of resistance, including armed struggle, protests, and negotiations. The Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) has played a central role in representing Palestinian interests.
Peace Process
Numerous attempts have been made to broker peace between Israelis and Palestinians. The Oslo Accords in the 1990s aimed at establishing a framework for the eventual resolution of the conflict, but a final agreement has remained elusive.
Jerusalem
The status of Jerusalem is a critical issue. Israel claims the entire city as its capital, while Palestinians seek East Jerusalem as the capital of a future Palestinian state.
Gaza Strip
The Gaza Strip, controlled by the Palestinian group Hamas, has been a focal point of conflict. Israel has imposed blockades and conducted military operations in response to rocket attacks.
| Related Articles | |
| Israel-Iran Conflict | Israel-Hezbollah Conflict |
| Israel-Palestine Conflict |
World War |
Who are Hamas Group?
Hamas, or the Islamic Resistance Movement, is a Palestinian militant and political organization that emerged in the late 1980s during the First Intifada, which was a period of Palestinian uprising against Israeli rule. Hamas has both political and military wings and has played a significant role in Palestinian politics, particularly in the Gaza Strip.
Hamas’s role in Palestinian politics and its armed resistance against Israel has made it a highly controversial and influential actor in the broader context of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. The organization’s complex nature includes both political and militant dimensions, and its activities have had a profound impact on the dynamics of the region. Key points about Hamas Group include:
| Aspects | Details |
| Founding and Ideology | Hamas was founded in 1987 during the First Intifada, with the primary goal of resisting Israeli occupation and establishing an Islamic state in historic Palestine. |
| Political Wing | In addition to its military activities, Hamas has a political wing that engages in governance and operates social services. It participated in Palestinian elections and gained control of the Gaza Strip in 2007. |
| Military Wing | The military wing of Hamas is known as the Izz ad-Din al-Qassam Brigades. It has been involved in armed resistance against Israel, including the use of rockets, suicide bombings, and other tactics. |
| Charitable and Social Activities | Hamas operates schools, hospitals, and other social services in the areas it controls. This has contributed to its popularity among some Palestinians, particularly in the Gaza Strip. |
| Designation as a Terrorist Organization | Many countries, including the United States, European Union, and Israel, classify Hamas as a terrorist organization due to its use of violence against civilians and its stated goal of eliminating the state of Israel. |
| Role in Israeli-Palestinian Conflict | Hamas has been a central player in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. Its armed confrontations with Israel, particularly in the Gaza Strip, have led to periodic escalations of violence. |
| Ceasefires and Reconciliation Attempts | Over the years, there have been various attempts to broker ceasefires and reconcile differences between Hamas and other Palestinian factions. The situation remains complex, with periods of relative calm interspersed with episodes of violence. |
| Relationship with Fatah | Hamas has had a tense relationship with Fatah, another major Palestinian political party. Fatah controls the Palestinian Authority in the West Bank, and the division between the two factions has been a significant obstacle to Palestinian unity. |
What is the Yom Kippur War?
The Yom Kippur War, also known as the October War or the 1973 Arab-Israeli War, was a conflict fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab states led by Egypt and Syria. The war began on October 6, 1973, which coincided with the Jewish holy day of Yom Kippur, and lasted until October 25, 1973.
Key Features of the Yom Kippur War Include
The Yom Kippur War remains a pivotal event in the history of the Middle East, influencing subsequent diplomatic efforts and shaping the dynamics of the Arab-Israeli conflict.
- Background: The war was primarily a result of longstanding tensions and territorial disputes between Israel and its Arab neighbours, particularly regarding territories occupied by Israel in the Six-Day War of 1967.
- Surprise Attack: Egypt and Syria launched a coordinated surprise attack on Israel on Yom Kippur, the holiest day in the Jewish calendar. The attackers aimed to regain control of the Sinai Peninsula (Egypt) and the Golan Heights (Syria), territories lost in the 1967 war.
- Initial Arab Successes: The initial stages of the war saw Arab forces making significant territorial gains. Egyptian forces crossed the Suez Canal and penetrated the Bar Lev Line, while Syrian forces made advances in the Golan Heights.
- Israeli Counteroffensive: Israel, under the leadership of Prime Minister Golda Meir and Defense Minister Moshe Dayan, mounted a strong counteroffensive. Israeli forces crossed the Suez Canal and encircled the Egyptian Third Army, and they also pushed Syrian forces back on the Golan Heights.
- Ceasefire and Diplomacy: International pressure, particularly from the United States and the Soviet Union, led to a ceasefire on October 25, 1973. The war highlighted the need for diplomatic efforts, eventually leading to the Camp David Accords in 1978 between Israel and Egypt.
- Impacts and Consequences: The Yom Kippur War had significant geopolitical implications. It shattered the perception of Israeli invincibility established in the Six-Day War and led to a reassessment of defense strategies. The war also had economic consequences and prompted diplomatic efforts towards peace.
- Casualties and Losses: The war resulted in a substantial loss of life and equipment on both sides. Casualties were significant, and the conflict left a lasting impact on the region.


 EU Plans to Slash General Data Protectio...
EU Plans to Slash General Data Protectio...
 India-China Relations, Evolution, Areas ...
India-China Relations, Evolution, Areas ...
 India-Bangladesh Relation, Areas of Coop...
India-Bangladesh Relation, Areas of Coop...





















