Table of Contents
Over the past year, ISRO has made significant strides with several key missions. India has several space missions currently underway. Read this article to know the List of India’s Ongoing Space Missions in 2024. Union Cabinet has approved various space programmes including Chandrayaan 4, Venus Orbiter Mission etc.
List of ISRO’s Ongoing Space Missions
| Name of Space Missions | Details |
| Aditya L-1 |
|
| Gaganyaan |
|
| XPoSAT |
|
| INSAT-3DS |
|
| RLV-TD |
|
| Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV) |
|
| Private Space Missions |
|
List of India’s Upcoming Space Mission
Venus Orbiter Mission (VOM)
- It is a planned mission by the ISRO aimed at exploring Venus, Earth’s closest planetary neighbour. It is also known as ShukraYaan-1.
- Scheduled Launch: March 2028
- Objectives
- Surface and Atmospheric Study: To investigate the surface and subsurface characteristics of Venus, including geological composition and volcanic activity.
- Atmospheric Chemistry: To analyse the atmospheric dynamics and chemical processes, including studying solar irradiance and its effects on the Venusian atmosphere.
- Understanding Planetary Evolution: The mission aims to provide insights into why Venus evolved differently from Earth, despite their similar sizes and initial conditions.
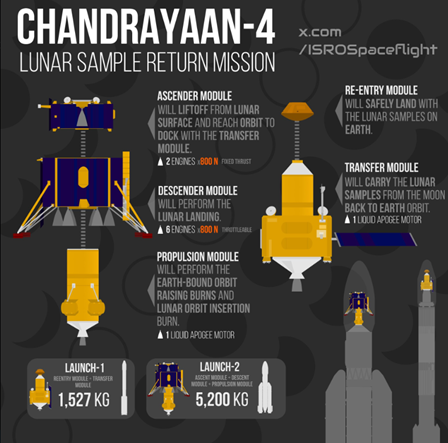
Chandrayaan 4 Mission
- Mission Objective: It aims to bring rock and soil samples back from the Moon.
- Modules: The Chandrayaan-4 spacecraft will consist of five modules, unlike Chandrayaan-3, which had three.
- Landing and Sample Collection: Two modules will detach from the main spacecraft, land on the Moon, and collect samples.
- One of these will then launch itself back to the main spacecraft in lunar orbit, where the samples will be transferred.
- Sample Return: The samples will be moved to an Earth re-entry vehicle, launched separately, which will return the samples to Earth.
- Docking Operations: The mission will involve docking space modules twice, introducing a new capability for ISRO that will be first tested in the upcoming Spadex mission.
TRISHNA
- It stands for Thermal Infra-Red Imaging Satellite for High-resolution Natural Resource Assessment (TRISHNA) mission.
- Agencies Involved: Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) and the French Space Agency (CNES).
- Features:
- The mission will use two primary payloads: a Thermal Infra-Red (TIR) payload and a Visible – Near Infra-Red – ShortWave Infra-Red (VNIR-SWIR) payload.
- It will operate in a Sun-synchronous (SSO) orbit for a period of five years.
- Scheduled Launch: In 2026 from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre on a PSLV rocket.
- Objectives:
- Understand water use and stress in ecosystems.
- To assess urban heat islands and provide heat alerts.
- To detect thermal anomalies linked to geothermal resources and volcanic activity.
- To Monitor climate through tracking droughts, measuring evapotranspiration rates, and monitoring permafrost changes.
Achievements of India’s Space Missions
India’s Space Research Organization (ISRO) has made significant achievements through its ongoing space missions, showcasing its growing capabilities and technological advancements.
- Chandrayaan-3 marked a historic achievement for India by successfully landing on the lunar surface on August 23, 2023. This made India the fourth country in the world, after the USA, the Soviet Union, and China, to achieve a soft landing on the Moon.
- Aditya-L1 is India’s first mission dedicated to studying the Sun. The successful initiation of this mission represents a major step forward in understanding solar activities and their impact on space weather.
- Gaganyaan mission, though still in progress, has achieved several milestones, including the development of indigenous crew modules, environmental control and life support systems, and astronaut training programs.
- While still in the planning stages, the Mangalyaan-2 mission builds on the success of Mangalyaan (Mars Orbiter Mission), which made India the first Asian nation to reach Martian orbit and the fourth space agency in the world to do so. The continuation of this mission underscores ISRO’s commitment to planetary exploration.
- NISAR represents a significant achievement in international collaboration, combining ISRO’s and NASA’s expertise to create a highly advanced Earth observation satellite.
- RISAT series has significantly enhanced India’s capabilities in all-weather, day-and-night surveillance, which is crucial for national security, disaster management, and agricultural monitoring.


 Advanced Air Defence Radars: Types, Comp...
Advanced Air Defence Radars: Types, Comp...
 Ion Chromatography, Working and Applicat...
Ion Chromatography, Working and Applicat...
 Broadly Neutralising Antibodies (bNAbs):...
Broadly Neutralising Antibodies (bNAbs):...

























