Table of Contents
Context: The Indian government is keen to provide necessary help to the nutraceuticals sector to reach its full potential.
- The global nutraceutical market is currently estimated at approximately $400 billion, integrating aspects of food, pharmaceuticals, and biotechnology.
- Despite this significant market size, India’s share remains under 2%.
- This limited participation is largely attributed to the absence of a clearly defined industry classification within Indian ministries, which hampers targeted support for the sector.
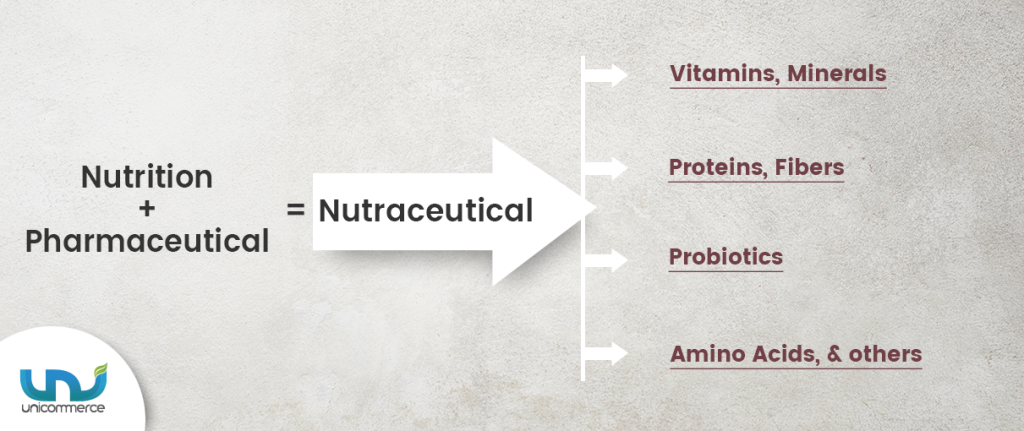
What are Nutraceuticals?
- It refers to food-based products with medicinal benefits, beyond basic nutritional value.
- These products are a blend of nutrition and pharmaceuticals, aimed at preventing diseases and improving health.
Types of Nutraceuticals
- Dietary Supplements: Vitamins, minerals, amino acids, probiotics, etc.
- Functional Foods: Fortified cereals, dairy products, energy drinks.
- Medicinal Foods: Products designed for specific dietary needs (e.g., diabetic-friendly foods).
- Herbal Products: Ayurvedic formulations, plant-based extracts.
| Fact |
| Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) is solely responsible for regulating the approvals, promotions, and labeling standards for health supplements and nutraceuticals. |
India’s Position in the Nutraceutical Sector
India is recognized as a key player in the nutraceutical industry due to several advantages:
- Traditional Knowledge: India boasts a rich heritage in health sciences, particularly through Ayurveda, which provides unique traditional knowledge applicable to nutraceuticals.
- Agro Climatic Diversity: The country has 52 agroclimatic zones, making it suitable for cultivating a wide range of medicinal plants.
- Medicinal Plant Resources: India is home to over 1,700 medicinal plants, including well-known varieties like curcumin, bacopa, and ashwagandha, which are awaiting modern scientific validation.
- Pharmaceutical Expertise: The Indian pharmaceutical sector has a strong foundation in formulation, which influences high-quality nutraceutical standards.
- Startup Ecosystem: A thriving startup environment has led to a growing number of successful nutraceutical companies that are driving sectoral growth.
Government and Institutional Initiatives Supporting Nutraceutical Growth
Nutraceutical Sector Task Force (TF)
Established in November 2021 by the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), this Task Force includes representatives from multiple ministries and industry stakeholders. such as:
- Department of Commerce
- Department of Pharmaceuticals
- Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI)
- Ministry of AYUSH
- Ministry of Food Processing
Chaired by India’s Principal Scientific Adviser, the TF focuses on regulatory frameworks and policies to boost the nutraceutical sector.
- It aims to create a “Harmonized System of Nomenclature” and align India with global standards.
- Introduction of Harmonized System of Nomenclature (HSN) Codes: India has developed its first-ever HSN codes for nutraceuticals to facilitate standardised trade practices and ease export procedures.
- Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme: For the first time, the nutraceutical industry is eligible for a PLI scheme. This incentive is designed to stimulate domestic production, making Indian nutraceuticals more competitive globally.
Nutraceutical Industry Panel under SHEFEXIL
- A dedicated industry panel was established under SHEFEXIL (Shellac & Forest Products Export Promotion Council), aiming to strengthen regulatory and export support for the sector.
Compliance and Export Incentives
- SHEFEXIL has recommended that nutraceuticals be classified as food products under FSSAI (Food Safety and Standards Authority of India) for regulatory clarity.
- Additionally, nutraceutical exports now qualify for the Remission of Duties and Taxes on Export Products (RoDTEP) Scheme, which offsets export costs to boost competitiveness in the European market and beyond.
Infrastructure and Research Support
India has prioritised infrastructure for innovation in nutraceuticals:
- NIFTEM-Kundli, Centurion University, and AIC-CSIR-CCMB have set up hubs focused on nutraceutical R&D.
- In 2024, the Kerala government launched the first government-backed Nutraceutical Centre of Excellence, fostering cutting-edge research and development.
Global Engagement and Trade Promotion
Through the Department of Commerce, India has showcased its nutraceutical products at global trade fairs, raising international awareness and building partnerships with foreign stakeholders.
Advantages for India
- Rich Traditional Knowledge: India has a deep-rooted history in health sciences, particularly Ayurveda, providing a unique edge in nutraceutical formulations.
- Diverse Agroclimatic Conditions: With 52 agroclimatic zones, India is well-suited for the cultivation of medicinal plants, ensuring a steady supply of raw materials.
- Abundance of Medicinal Plants: Home to over 1,700 medicinal plants, including curcumin, bacopa, and ashwagandha, many of which are globally recognized and await further scientific validation.
- Pharmaceutical Expertise: India’s strong foundation in pharmaceutical formulation contributes to the development of high-quality nutraceutical products.
- Growing Startup Ecosystem; A thriving nutraceutical startup landscape and the emergence of successful companies are driving innovation and sectoral expansion.
- Rising Health Consciousness: Post-pandemic, people are prioritizing immunity, wellness, and preventive healthcare.
- Demand for immunity boosters like Vitamin C, Zinc, and herbal supplements has surged.
- Growing Lifestyle Diseases: Increased cases of diabetes, obesity, hypertension, and heart diseases have led to higher demand for functional foods and supplements.
- Eg., India is home to 315 million people with hypertension, and 101 million with diabetes (According to a study by ICMR).
- Growing Market Potential: The global nutrition market is valued at $520 billion.
- India’s share is estimated at $8 billion, indicating vast growth potential, especially in Ayurveda-based nutraceuticals.
What are the Challenges Associated
- Overlapping Jurisdictions: The potential shift of regulatory oversight from the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) to the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) has raised concerns.
- Industry experts fear that such a move could stifle innovation and lead to economic downturns within the sector.
- Standardization Issues: Ensuring consistent quality across products remains a challenge due to variability in raw materials and manufacturing processes.
- Supply Chain Management: Raw material shortages and supply chain disruptions due to geopolitical tensions, natural disasters, or limited geographic availability of ingredients.
- Global Players: International companies are expanding their presence in India, intensifying competition for domestic nutraceutical firms.
- Innovation Barriers: Limited investment in R&D hampers the development of new and effective nutraceutical products, affecting the industry’s ability to meet evolving consumer demands.
- Educational Gaps: Despite growing health consciousness, there is still a lack of comprehensive understanding among consumers about the benefits and proper use of nutraceuticals, leading to scepticism and underutilization.
Solutions
- Quality Control and Standardization: Implement robust quality assurance protocols including raw material testing, active ingredient specification, and collaboration with reputable suppliers.
- Regulatory Compliance: Stay updated with global regulations, partner with regulatory consultants, and invest in Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) for adherence to safety standards.
- Ingredient Sourcing and Supply Chain Management: Diversify suppliers, establish long-term partnerships, invest in vertical integration, and maintain buffer stocks for uninterrupted supply.
- Product Stability and Shelf Life: Use advanced packaging technologies, conduct stability studies, and invest in R&D for stable formulations to extend shelf life.
- Consumer Education and Safety Concerns: Provide clear labelling, offer educational resources on websites, and collaborate with healthcare professionals for consumer awareness.


 Minors Bank Account above 10 Years: Chan...
Minors Bank Account above 10 Years: Chan...
 Creative Economy in India, Current Situa...
Creative Economy in India, Current Situa...
 Indus Water Treaty 1960 Suspended by Ind...
Indus Water Treaty 1960 Suspended by Ind...





















