Table of Contents
Context: The Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS) cleared a Rs 15,000 crore project to design and develop the Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA), India’s fifth-generation fighter multirole fighter jet.
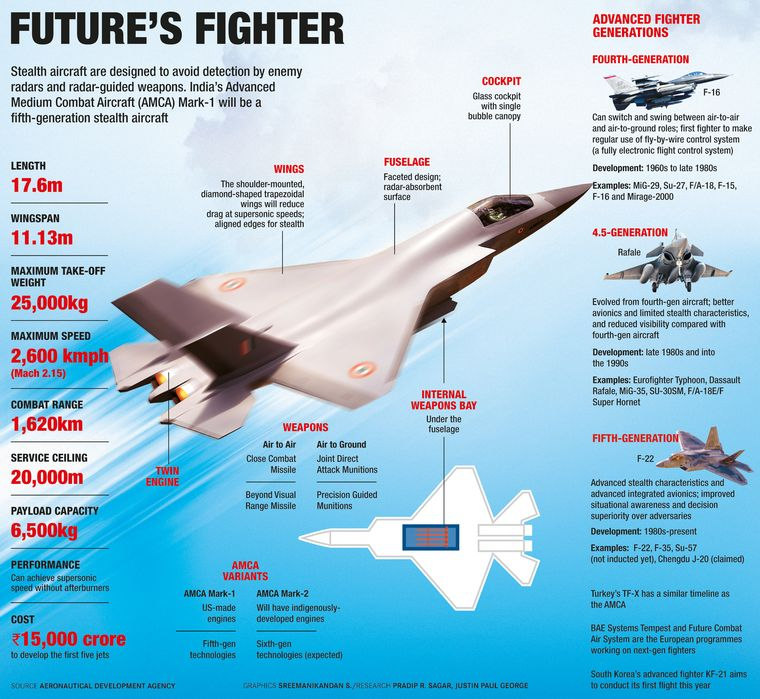
India’s Indigenous AMCA Fighter Jet: An Overview
- The AMCA (Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft) is India’s indigenous fifth-generation fighter jet project.
- Spearheaded by the Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA) and the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
- Indian Air Force’s (IAF) latest addition aimed to have stealth capabilities.
- Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) is a key manufacturing partner.
- Comparison with Other Fifth-Generation Fighters: Only a few countries have built fifth-generation stealth fighter aircraft.
- The list of aircraft currently in service includes the F-22 Raptor and F-35A Lightning II of the US, the Chinese J-20 Mighty Dragon, and the Russian Sukhoi Su-57.
We’re now on WhatsApp. Click to Join
Features of AMCA
- Stealth: AMCA, weighing 25 tons, is designed with stealth features making it less detectable by radar.
- Fuel and Weapons: Equipped with a larger fuel tank of 6.5 tons and an internal weapons bay for indigenous weapons.
- Engine: Two variants of engines are planned:
- The initial AMCA Mk1 with the existing GE414 engine and
- The subsequent Mk2 with the more powerful 110kN engine.
Importance of AMCA
- Strategic Edge: AMCA will enhance the IAF’s capabilities with modern stealth features, advanced weapons, and fuel capacity.
- Self-reliance: Part of India’s push towards self-reliance in defence technology.
- Innovation: Incorporates cutting-edge technology, like a multirole radar signature, making it a formidable asset in air combat.
- Advanced Systems: Outfitted with powerful sensors and advanced avionics to engage and counter threats effectively.
- Materials and Design: Utilises special materials and design features for a reduced radar signature.
- Significance in Military Strategy: AMCA will provide the IAF with advanced capabilities and contribute to India’s defence technology sector, representing a significant step towards indigenous military advancements and strategic autonomy.
IAF’s Winding Numbers
- The IAF is projected to have fewer fighter squadrons in the future due to the phasing out of older aircraft models like MiG-21s, MiG-29s, Jaguars, and Mirage 2000s.
- AMCA is part of the plan to bolster the IAF’s squadron strength but will not increase the total number of squadrons as it is set to replace current aircraft.


 National Technology Readiness Assessment...
National Technology Readiness Assessment...
 Justice Mission-2025: China’s Live-Fir...
Justice Mission-2025: China’s Live-Fir...
 Suryastra: First Made-in-India Long-Rang...
Suryastra: First Made-in-India Long-Rang...

























