Table of Contents
Context: The India BioEconomy Report, released by the Department of Biotechnology, highlights the status of India’s bioeconomy.
India’s Biotechnology Sector Status
Current Value and Growth
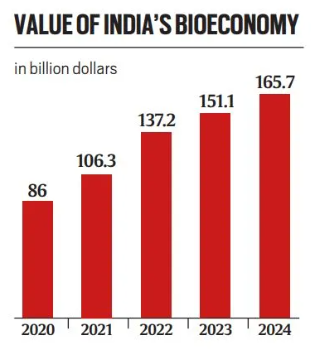
India’s bioeconomy was valued at $165 billion in 2024, contributing 2% to the GDP.
- The sector has nearly doubled from $86 billion in 2020.
- It is projected to grow to $300 billion by 2030 and reach $1 trillion by 2047.
Major Contributors
- Industrial Sector: Accounts for nearly half of the bioeconomy’s value ($78 billion) through biofuels, bioplastics, and bio-based chemicals.
- Pharmaceutical Sector: Contributes 35%, mainly from vaccine production.
- Research and IT: Fastest-growing segment in 2024, including biotech software development, clinical trials, and bioinformatics.
What is Bioeconomy?
- It refers to the economic activity derived from the use of biological resources (such as plants, animals, and microorganisms) and biological processes to produce goods and services.
- It involves the sustainable use of bioresources for industrial, agricultural, and healthcare applications, contributing to economic growth while reducing environmental impact.
Key Features
- Utilizes renewable biological resources.
- Focuses on sustainable and eco-friendly production processes.
- Encourages circular economy principles by minimizing waste and maximizing resource efficiency.
- Drives innovation in areas like biofuels, bioplastics, and biopharmaceuticals.
Components
- Industrial Bioeconomy: Involves the use of biological processes and bioresources for manufacturing and industrial applications.
- Examples: Biofuels, bioplastics, biodegradable chemicals, and industrial enzymes.
- Agricultural Bioeconomy: Focuses on enhancing agricultural productivity and sustainability using biotechnology and natural processes.
- Examples: Genetically modified (GM) crops, bio-fertilizers, and bio-pesticides.
- Healthcare and Pharmaceutical Bioeconomy: Utilizes biological resources for drug development, medical treatments, and healthcare innovations.
- Examples: Vaccines, biomedicines, gene therapy, and diagnostics.
- Marine and Aquatic Bioeconomy: Involves the use of marine and aquatic organisms for developing bio-based products.
- Examples: Marine-derived pharmaceuticals, biofuels from algae, and marine enzymes.
- Environmental Bioeconomy: Focuses on improving environmental sustainability using biological solutions.
- Examples: Bioremediation (using microbes to clean pollution), waste-to-energy conversion, and carbon capture.
- Research and Bioinformatics: Supports bioeconomy through research in biotechnology, synthetic biology, and data-driven biological solutions.
- Examples: Genetic engineering, synthetic biology, and clinical trials using bioinformatics.
Reasons for the Growth of Bioeconomy
- Rising Demand for Sustainable Solutions: Growing concerns over climate change, environmental degradation, and resource depletion have increased the need for eco-friendly alternatives.
- Bio-based products like bioplastics and biofuels offer sustainable replacements for fossil-based products.
- Technological Advancements in Biotechnology: Rapid progress in fields like genetic engineering, synthetic biology, and bioinformatics has expanded the scope of bio-based solutions.
- Innovations in CRISPR gene editing and microbial fermentation have improved the efficiency of bio-manufacturing.
- Increased Investment and Government Support: Governments are promoting bioeconomy through policies and financial incentives.
- India’s BioE3 policy (2024) aims to establish India as a global bio-manufacturing hub.
- Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC) provides funding and infrastructure support.
- Expansion of Bio-based Industries: Growth in industries like biofuels, bioplastics, and biopharmaceuticals has boosted bioeconomy value.
- Example: India’s ethanol production for biofuel has increased due to the Ethanol Blending Programme.
- Increased production of vaccines and biomedicines has also driven growth.
- Cost-effectiveness and Local Availability of Bioresources: Bioresources such as plants and microorganisms are renewable, relatively cheap, and locally available.
- Bio-based production processes are often more energy-efficient and less polluting than conventional methods.
- Global Shift Toward a Circular Economy: Focus on reducing waste and reusing resources has aligned with the principles of bioeconomy.
- Bio-based industries contribute to circular economy goals by converting waste into valuable products (e.g., waste-to-energy projects).
Challenges Facing India’s Bioeconomy
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Lack of a clear and consistent regulatory framework for biotechnology innovations.
- Continued reluctance to approve genetically modified (GM) crops limits agricultural productivity.
- Complex approval processes and delays hinder the commercialization of biotech products.
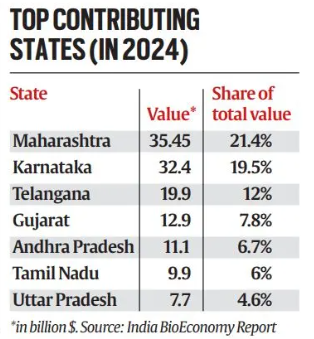
- Regional Imbalance: Bioeconomy growth is concentrated in a few states like Maharashtra, Karnataka, Telangana, Gujarat, and Andhra Pradesh — contributing over two-thirds of the sector’s value.
- Eastern and Northeastern India generate less than 6% of the total bioeconomy value.
- Limited R&D Investment: Inadequate funding for biotech research and innovation compared to global leaders like the US, China, and the EU.
- Shortage of Skilled Workforce: Lack of trained professionals in bioinformatics, synthetic biology, and biomanufacturing.
Way Ahead
By addressing policy gaps (e.g., establishing a National BioEconomy Mission, creating a single-window clearance system for biotech products) , improving infrastructure, promoting R&D, and reducing regional imbalance, India can sustain high growth rates in the bioeconomy sector.


 Comprehensive Remote Sensing Observation...
Comprehensive Remote Sensing Observation...
 Perovskite Solar Cells, Objective and Ch...
Perovskite Solar Cells, Objective and Ch...
 Navy-Marine Expeditionary Ship Interdict...
Navy-Marine Expeditionary Ship Interdict...





















