Table of Contents
Context: Many Indians seek legal entry into countries like the U.S., while others may enter illegally due to limited opportunities for legal migration.
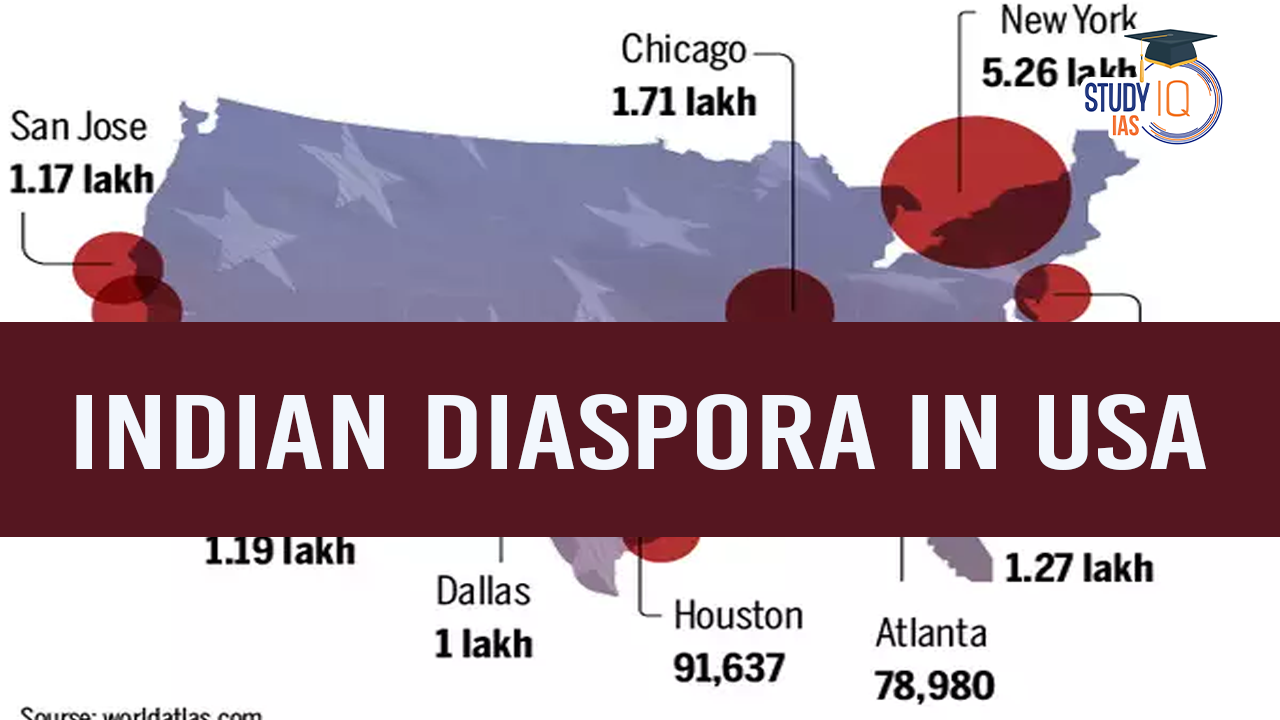
Impact of Indian Diaspora in the US
Positive Impacts
- Economic Contribution: Millions of Indians and Indian Americans have powered the US economy through skilled labor, entrepreneurship, and innovation.
- The rise of “global capability centers” in India has further strengthened US firms’ competitiveness by leveraging Indian talent.
- Innovation and Technological Advancement: Indian-origin scientists, engineers, and researchers contribute to cutting-edge innovations in fields like artificial intelligence, space research, and pharmaceuticals.
- Many startups founded by Indian-Americans have transformed industries globally.
- Cultural Influence and Soft Power: Bollywood, yoga, Indian cuisine, and festivals like Diwali have gained popularity in the US, fostering cultural exchange.
- Indian-Americans enhance India’s global image and diplomatic influence.
- Political and Strategic Influence: Increasing political representation (e.g., Kamala Harris, Nikki Haley, and several US Congress members of Indian origin) helps strengthen India-US relations.
- Lobbying efforts by Indian-American groups have influenced favourable US policies toward India.
- Remittances and Knowledge Transfer: The Indian diaspora sends billions of dollars in remittances back home, supporting families and economic growth.
- Professionals contribute through research collaborations, skill-sharing, and investments in India’s startup ecosystem.
Negative Impacts
- Brain Drain from India: Skilled professionals leaving India for better opportunities in the US weakens India’s workforce and slows domestic innovation.
- Sectors like healthcare and academia in India face shortages due to the migration of top talent.
- Struggles of Low-Skilled Migrants: Many Indian migrants working in low-wage jobs face exploitation, poor living conditions, and legal uncertainties.
- Illegal migrants risk deportation and social discrimination.
- Racial Discrimination and Xenophobia: Despite their success, Indian-Americans face racism, hate crimes, and workplace discrimination.
- Policies like visa restrictions (H-1B) have created uncertainty for Indian professionals.
- US-India Trade Imbalance and Policy Conflicts: Some Indian professionals contribute more to the US economy than they would in India, leading to economic imbalances.
- The US government’s changing immigration policies (e.g., “America First”) often impact Indian workers negatively.
- Divisions within the Indian-American Community: Political and ideological divisions within the Indian diaspora sometimes lead to friction in shaping a unified voice in US policymaking.
- Internal conflicts over religious, caste, and regional identities can affect collective representation.
Conclusion
While the Indian diaspora has played a vital role in strengthening US-India relations and boosting the American economy, challenges like brain drain, discrimination, and immigration restrictions persist. A balanced approach is needed to maximize benefits for both countries.

 India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corrid...
India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corrid...
 US-Iran Nuclear Talks: Key Developments ...
US-Iran Nuclear Talks: Key Developments ...
 EU Plans to Slash General Data Protectio...
EU Plans to Slash General Data Protectio...





















