Table of Contents
Context: According to a recent discovery, the Indian Plate is splitting into two, with a portion of it sinking into the mantle.
Indian Continental Plate and Himalayan Formation
- The Indian Plate has been colliding with the Eurasian Plate for the last ~60 million years.
- This ongoing collision is the primary cause of the uplift of the Himalayas and the formation of the Tibetan Plateau.
- Traditionally, tectonic plates were thought to be rigid, but this view is now being challenged.
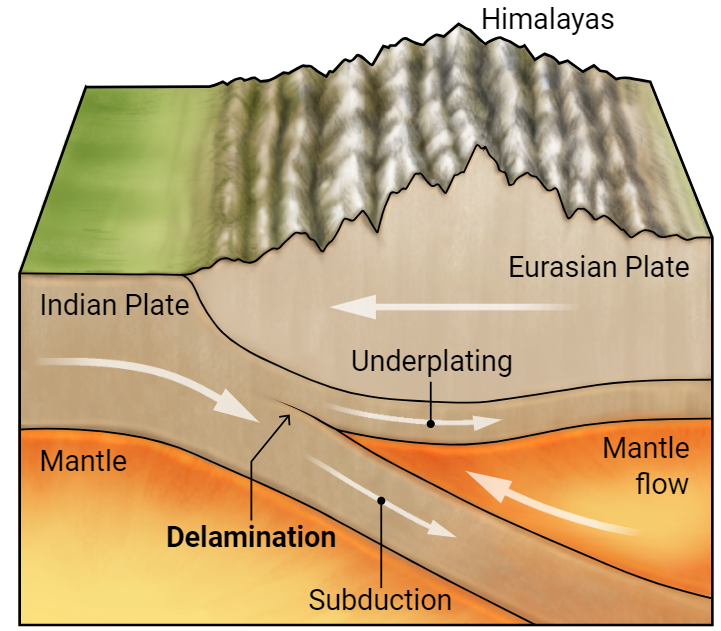
Delamination of the Indian Plate
- Delamination refers to a vertical tearing and peeling away of the dense lower layer of a tectonic plate.
- The lower part detaches and sinks into the Earth’s mantle, while the upper part may remain in place or move differently.
- Scientists discovered that a portion of the Indian Plate is undergoing delamination.
- This means the plate is splitting into two, and one part is sinking into the mantle.
- Delamination increases earthquake risks by changing how stress builds up in the Earth’s crust.
Areas at Risk
- Tibetan Plateau – already prone to earthquakes.
- Cona-Sangri Rift – a deep geological fracture possibly caused by this ongoing tear, may become a new seismic hotspot.


 Harnessing Spiritual Aastha for River Re...
Harnessing Spiritual Aastha for River Re...
 Rare Earth Elements, Metals, Magnets, Ap...
Rare Earth Elements, Metals, Magnets, Ap...
 Places in News for UPSC 2025 for Prelims...
Places in News for UPSC 2025 for Prelims...





















