Table of Contents
Context: Indonesian President Prabowo Subianto arrived in India ahead of New Delhi’s 76th Republic Day celebrations, where he will serve as the chief guest.
India-Indonesia Ties Historical Context
- Deep-rooted Connections: India and Indonesia share commonalities in history, religion (Hinduism and Buddhism) and cultural exchange.
- Foundation of Diplomatic Relations: Formal diplomatic ties were established in 1950, followed by the Treaty of Friendship in 1951.
- Also, Both countries were founding members of the Non-Aligned Movement (NAM).
- Elevation to Strategic Partnership: The relationship was elevated to a Strategic Partnership in 2005, and further to a Comprehensive Strategic Partnership in 2018 with a focus on economic and security collaboration.
- Act East Policy: Indonesia has been part of the Act East policy since its inception in 2014.
Partnership Areas between India-Indonesia
Trade and Economic Relations
- Trade Volume: India and Indonesia have a trade volume of $30 billion, with significant untapped potential.
- Economic Strength of Indonesia: It has a GDP of $1.4 trillion. It is rich in natural resources, including palm oil, coal, and rubber which are vital for India.
- Indonesia is India’s second-largest trading partner in ASEAN.
- Indian businesses have invested over $1.56 billion in Indonesia in sectors like mining, textiles and infrastructure.
Maritime Security and Indo-Pacific Cooperation
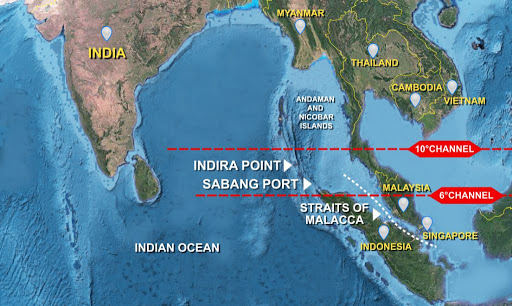
- Strategic Significance: Indonesia, as a large archipelagic state with thousands of islands, serves as a bridge between the Indian and Pacific Oceans.
- Sea Lines of Communication (SLOCs): Indonesian waters are crucial for global trade between East Asia, India, Africa, and Europe.
Indo-Pacific Collaboration
- Indonesia has aligned its ASEAN Outlook on the Indo-Pacific (AOIP) with India’s Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative (IPOI).
- Both nations are working together on maritime resources under the IPOI framework.
Defence and Strategic Cooperation
- Joint Military Exercises: Exercises like Garuda Shakti (Army), Samudra Shakti(Navy) and coordinated patrols (IND-INDO CORPAT).
- Defense Industry Collaboration: The inaugural India-Indonesia Defense Industry Exhibition in 2024.
Multilateral Engagement
- BRICS Membership: Indonesia joined BRICS in 2023. It provides a platform for India and Indonesia to collaborate on global issues.
- Regional Architecture: Both countries engage in ASEAN-related forums, such as the East Asia Summit (EAS) and the ASEAN Regional Forum (ARF).
Cultural & Educational Engagement
- India operates two cultural centres in Jakarta and Bali, promoting yoga, classical dance and music.
- India offers a significant number of scholarships to Indonesian students through the Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation (ITEC) program and the Indian Council for Cultural Relations (ICCR).
- Universities in India and Indonesia are collaborating on joint research projects, technology transfer and student exchange programs.
Challenges in Bilateral Relations
Divergent Perspectives on China
- Indonesia’s Balanced Policy: Indonesia maintains strong economic ties with China and has a tradition of balanced relations with major powers.
- Alignment Challenges: While India remains cautious of China’s strategic intentions, Indonesia’s approach to China is less adversarial.
Limited Trade and Investment
- Low Bilateral Trade: A trade volume of $30 billion is low considering the size and economic potential of both countries. Indonesia’s trade volume with China ($139 billion in 2023)
- Efforts to boost trade in sectors like technology, infrastructure and energy are limited.
Connectivity Issues
- Despite geographical proximity, physical and digital connectivity between India and Indonesia is underdeveloped, affecting trade and tourism.
Differing Views on Myanmar Issue
- India and Indonesia have different views on Myanmar, particularly regarding the political crisis and human rights issues.
Future Course of Action
Strengthening Economic Ties
- More focus on diversifying trade beyond commodities like palm oil and coal to include technology, infrastructure and renewable energy.
- Enhance connectivity between the two nations to facilitate trade and tourism.
Deepening Maritime and Defence Cooperation
- Expand cooperation in maritime security to secure sea lanes and combat piracy in the Indo-Pacific region.
Enhancing Regional Collaboration
- Strengthen trilateral partnerships with Australia and Japan under frameworks like IPOI and the Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA).
Promoting Multilateral Engagement
- Use BRICS as a platform to address shared concerns, such as economic reform and climate change.
- Advocate for Indonesia’s inclusion in BIMSTEC to strengthen regional cooperation.
Building Stronger Political Ties
- Develop strong relationships based on the goodwill generated by past visits and multilateral engagements.
- Promote stronger foreign ministerial consultations to ensure alignment on key regional and global issues.
Strengthen People-to-People Ties
- Increase educational exchanges through scholarships like ITEC and promote Indian diaspora contributions to bilateral cooperation.


 Iran Nuclear Crisis and India’s Role f...
Iran Nuclear Crisis and India’s Role f...
 H1B Visa Program, Beneficiaries, Eligibi...
H1B Visa Program, Beneficiaries, Eligibi...
 Comparison Between India & France's ...
Comparison Between India & France's ...

























