Context: The Indian government is expected to file a complaint against the International Labour Organization’s (ILO) employment report for India.
Findings of the ILO’s India Employment Report
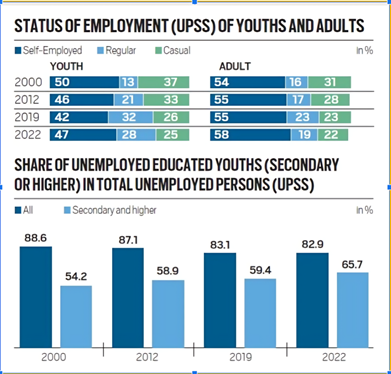
Unemployment Among Youth
- High Proportion of Youth Unemployment: India’s youth make up about 83% of the unemployed workforce.
- Rising Unemployment Among Educated Youth: The share of young people with secondary or higher education in the total unemployed youth nearly doubled, from 2% in 2000 to 65.7% in 2022.
Employment Trends
- Change in Employment Patterns: Youth employment and underemployment increased from 2000 to 2019 but saw a decline during the pandemic.
- Labour Market Deterioration and Subsequent Improvement: There was a long-term deterioration in key labour market indicators like the Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR), Worker Population Ratio (WPR), and Unemployment Rate (UR) until 2018, followed by improvement post-2019.
Paradoxical Improvements
- Complex Improvements in Employment: Despite some improvements in labour market indicators, the fundamental issue remains the inadequate growth of non-farm sectors and their capacity to absorb agricultural workers.
- Informal Work Prevalence: Around 90% of workers are engaged in informal work, with a notable decline in regular work after 2018.
Livelihood Insecurities
- Social Protection Measures: A minor portion of the workforce, primarily in the non-agriculture organised sector, is covered by social protection measures.
- Rise in Contractualisation: There has been an increase in the contractualisation of labour, affecting the security of regular workers.
Skill Gap
- Significant Skill Deficiencies: A large portion of the youth lacks basic digital literacy, such as sending emails with attachments (75%), copying and pasting files (60%), and using mathematical formulas in spreadsheets (90%).
Gender Gap in Employment
- High Joblessness Among Educated Young Women: The report highlights a substantial gender gap in the labour market, with women accounting for a larger share (76.7%) than men (62.2%).
- Low Female Labour Force Participation: There are low rates of participation by females in the labour force, exacerbating gender disparities.
Social Inequalities
- Disparities Among Social Groups: Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes face significant barriers in accessing better employment opportunities, often finding themselves in low-paid, temporary, casual wage work and informal employment.
- Persistence of Social Hierarchies: Despite educational improvements, the hierarchical divide within social groups remains pronounced.
| About International Labour Organisation (ILO) |
|


 Securities Markets Code Bill 2025: Towar...
Securities Markets Code Bill 2025: Towar...
 Weakly Interacting Massive Particles (WI...
Weakly Interacting Massive Particles (WI...
 India–Oman Trade Deal: CEPA Signed to ...
India–Oman Trade Deal: CEPA Signed to ...

























