Table of Contents
Context: The International Monetary Fund (IMF) recently revised India’s growth projection upwards to 6.8% for 2024, citing robust domestic demand conditions and a growing working-age population.
India’s Growth Projection as per IMF’s World Economic Outlook
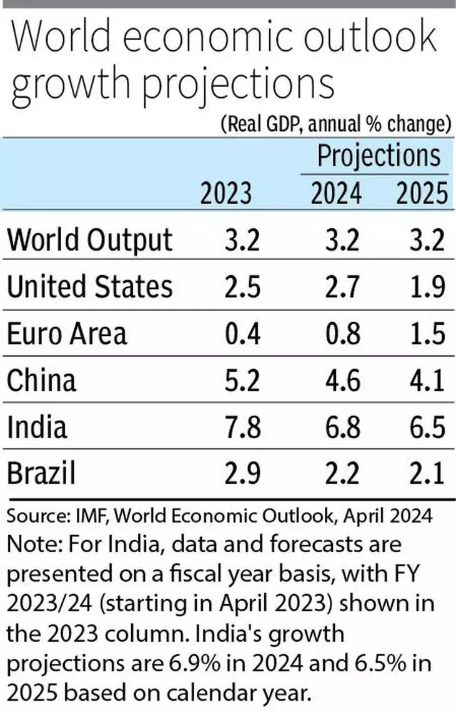
- IMF’s Revised Forecast: The IMF raised India’s growth projection to 6.8% for 2024, up from its previous estimate of 6.5% in January.
- Continued Growth Momentum: India’s growth trajectory remains strong, driven by robust domestic demand and a rising working-age population.
- Comparison with China: India outpaces China, with the latter’s growth projected at 4.6% for the same period.
- Inflation was projected to be 4.6% this year and 4.2% next year.
Global Economic Trends
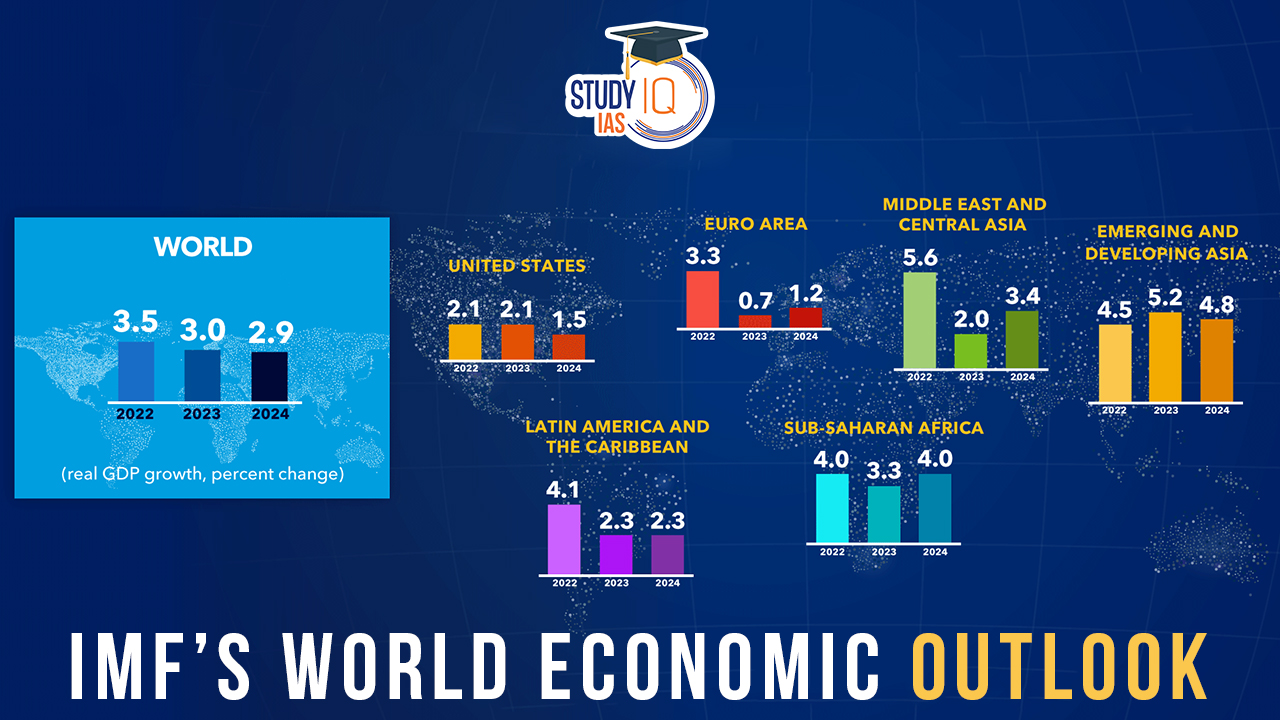
- Emerging and Developing Asia: Growth in this region is expected to decline slightly from 5.6% in 2023 to 5.2% in 2024 and 4.9% in 2025, with a modest upward revision compared to previous estimates.
- China’s Slowdown: China’s growth is projected to slow from 5.2% in 2023 to 4.6% in 2024 and 4.1% in 2025, attributed to factors such as easing post-pandemic consumption and weaknesses in the property sector.
About International Monetary Funds (IMF)
- Establishment: The IMF was created in 1944 following the Bretton Woods Agreement.
- Primary goal: To bring about international economic coordination to prevent competing currency devaluation by countries trying to promote their own exports.
- Eventually, it evolved to be a lender of last resort to governments of countries that had to deal with severe currency crises.
- Membership: It has 190 member countries.
- Headquarter: Washington, D.C., USA.
- Functions:
- International Cooperation: The IMF promotes global monetary stability and collaboration to prevent financial crises.
- Financial Aid: It offers loans and financial support to members facing economic challenges, often with conditions to improve economic health.
- Economic Surveillance: The IMF monitors economic developments and advises on policies for stability and growth.
- Technical Assistance: It provides expertise and training in fiscal and monetary policy, as well as financial regulation.
- Research and Analysis: The IMF researches various economic issues, including global economic trends and poverty reduction.
- Reports by IMF:
- Global Financial Stability Report.
- World Economic Outlook.
- It is usually published twice a year in April and October.
We’re now on WhatsApp. Click to Join
IMF World Economic Outlook Report
- Published biannually by the IMF.
- Publication Schedule: April and October for comprehensive reports, followed by less detailed updates in July and January.
- Data Provided: Includes information on member countries’ output, inflation, employment, fiscal balances, and debt statistics.
- It summarises the state of the world economy and significant recent developments.
Key Highlights of Recent World Economic Outlook Report
- Reserve Bank of India’s Estimate: The IMF’s estimate is lower than the Reserve Bank of India’s prediction of a 7% growth rate for FY24.
- FY25 Projection: The IMF also raised the growth projection for FY25 to 6.5% from the earlier 6.1%.
- IMF’s Medium-Term GDP Growth: The IMF has revised India’s medium-term (potential) GDP growth to 6.5% due to strong public investment, favourable labour market outcomes as seen in the latest PLFS report, and adjustments to the model.
- India’s economy is expected to reach the $5-trillion mark by 2027-28, and subsequently become the third-largest economy in the world.
- IMF Global Forecast: The IMF expects the global economy to grow by 3.1% in 2023, now projecting higher growth than its previous forecast, despite facing inflationary pressures, policy tightening, and turbulent markets.
- The IMF predicts the US economy to grow at 2.1% in 2024, which is higher than the earlier forecast.
IMF’s Outlook for Global Economy
- Steady Growth: Global growth, estimated at 3.2% in 2023, is projected to continue at the same pace in 2024 and 2025.
- Resilience Amid Challenges: Despite challenges such as supply chain disruptions and the Russia-Ukraine conflict, the global economy has shown resilience, with steady growth and declining inflation.
- Prioritizing Economic Resilience: Policymakers are urged to focus on strengthening government finances and revitalizing economic growth prospects to enhance economic resilience.
Chief Economist’s Insights
- Economic Resilience: Pierre-Olivier Gourinchas, the IMF’s chief economist, emphasizes the global economy’s resilience, with growth bottoming out in 2022 and inflation slowing.
- Reduced Economic Scarring: While the US economy has surpassed its pre-pandemic trend, low-income developing countries may experience more economic scarring.
- Challenges in China: China’s economy grapples with challenges in its property sector, necessitating measures to boost domestic demand and address trade imbalances.
|
Previous Year Prelims Question |
| Q. “Gold Tranche” (Reserve Tranche) refers to (2020)
(a) a loan system of the World Bank Ans: (d) Q. ‘Global Financial Stability Report’ is prepared by the (2016) (a) European Central Bank Ans: (b) |

 Unlocking the Potential of India–Afric...
Unlocking the Potential of India–Afric...
 Speedy Justice and the Crisis in Consume...
Speedy Justice and the Crisis in Consume...
 Kavachi Volcano: Location, Features, Eru...
Kavachi Volcano: Location, Features, Eru...

























