Table of Contents
Heat Budget of Earth
The Earth’s heat budget is a way to balance heat, where incoming heat from the sun (Insolation or terrestrial radiation) is absorbed and outgoing heat escapes as radiation. The sun does not heat the Earth evenly it warms the equator more than the poles. The atmosphere and oceans help balance this uneven heating through processes like evaporation, convection, rainfall, winds, and ocean currents.
Earth would be getting either too warm or too cold if the balance between incoming and existing heat were off. These variables are properly balanced, which results in the perfect temperature of the earth. The equilibrium between insolation (short waves) and terrestrial radiation is known as the Earth’s Heat Budget (long waves).
Read More: Heat Transfer Methods
Heat Budget of Earth Atmosphere & Components
The Earth’s surface gets different amounts of solar radiation based on location, with some areas receiving more than others. Between 40°N and 40°S, there is a surplus of net radiation, while the poles experience a deficit. The extra heat from tropical regions is redistributed to the poles. This balance is crucial because it stops the tropics from getting too hot and prevents polar areas from becoming permanently frozen.
Insolation refers to the solar radiation received by the Earth’s surface. It helps maintain thermal balance through several processes:
- Reflection: Solar radiation can bounce off surfaces like land, water, or clouds without generating heat.
- Absorption: This is when solar radiation turns into heat energy.
- Scattering: When solar radiation hits small particles in the atmosphere, it spreads in all directions.
Terrestrial Radiation is the longwave radiation emitted by the Earth’s surface. It contributes to temperature balance through:
- Latent Heat Transfer: This is the energy absorbed or released during a substance’s phase change, like from solid to liquid or liquid to gas.
- Sensible Heat Transfer: This refers to energy that raises a substance’s temperature without changing its state.
- Emission by Vapour and Clouds: Clouds and water vapor also release significant amounts of terrestrial radiation.
Read More: Isotherms
Heat Budget of Earth in Detail
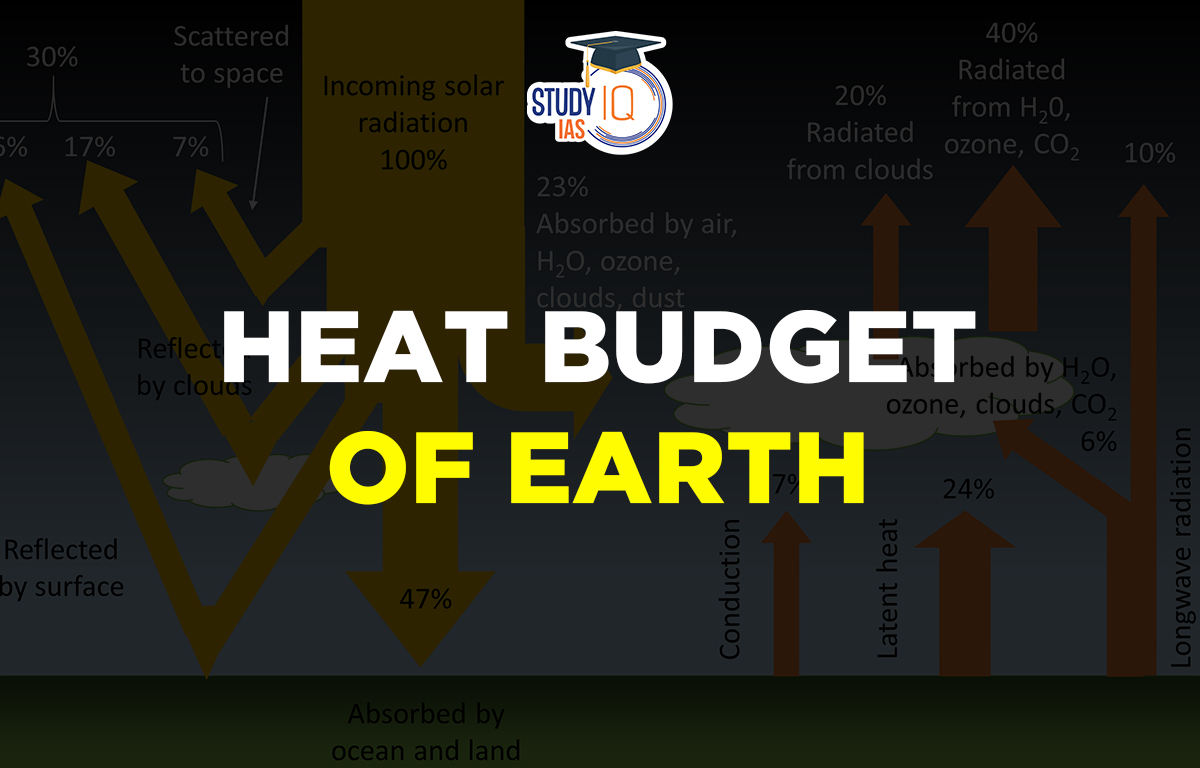
The heat budget refers to the amount of solar heat energy collected and used on Earth’s surface and in the atmosphere. The average temperature of the Earth stays stable because the energy from the sun is balanced by an equal amount of energy sent back into space. There is a balance or equilibrium between incoming solar radiation & outgoing terrestrial radiation. This balance is known as the Heat Budget of Earth.
Imagine that 100% of solar energy reaches the top of the atmosphere. As this energy moves through the atmosphere, some of it is reflected, scattered, or absorbed. Only the rest make it to the Earth’s surface. Before reaching the ground, about 35 units of energy are reflected back into space. Here’s a breakdown of this reflected radiation:
- From the top of clouds, Reflected Radiations – 27 units
- By ice fields on earth, Reflected Radiations – 02 units
- Reflected by the atmosphere – 06 units
- Total – 35 units
Albedo of the Earth
The reflected amount of radiation has referred to the albedo of the Earth. Thus, this 35 per cent of radiation neither heats the atmosphere nor the Earth’s surface. The remaining 65 units are absorbed as:
- Absorbed by the atmosphere – 14 units
- Absorbed by the earth – 51 units (Scattered + direct radiation)
- Total – 65 units
Gas molecules and dust particles cause scattering. This occurs in all directions, with part of it moving towards the planet and some toward space. Overall, the earth receives 51 units of radiation, which radiates back in the form of terrestrial radiation. The details about this reflected radiation are as described in the following:
- Radiated to space directly – 17 units
- Radiated to the atmosphere – 34 units
The details of 34 units of radiation absorbed by the atmosphere from terrestrial radiation are:
- Absorbed directly – 06 units
- Absorbed through convection and turbulence – 09 units
- Absorbed through Latent heat of condensation5 – 19 units; (Latent heat refers to the energy released or absorbed by a body)
- Total – 34 units
The total units absorbed by the atmosphere are 48 (14 units of insolation + 34 units of Terrestrial radiation). These are radiated back into space. Thus, the total radiation returning from the earth and the atmosphere respectively are:
- Radiated back by earth – 17 units
- Radiated back by the atmosphere – 48 units
- Total – 65 units
These returning 65 units balance the total of 65 units received from the sun. This account of incoming and outgoing radiation always maintains the balance of heat on the earth’s surface. This is known as the heat budget of earth or heat balance of the earth.
Read More: Temperature Inversion
Latitudinal Heat Balance
While the Earth generally balances incoming and outgoing radiation, this balance varies by latitude. Areas around 40°N and 40°S have a surplus of radiation, while polar regions receive less. This could suggest that the tropics should get hotter and the poles colder, but that’s not what happens. The extra heat from the tropics is moved to the poles by ocean currents, winds, and air circulation. As a result, the tropics don’t keep getting hotter, and polar regions don’t stay covered in snow. About 75% of heat transfer happens through the atmosphere, while 25% comes from ocean currents, driven by thermal imbalances.
Read More: List of Major Local Winds
Heat Budget of Earth UPSC
The sun is the most powerful heat generator. And the primary cause of all climatic traits is the varied amounts of heat that different parts of the globe receive from the sun. In order to comprehend various climatic elements like wind systems, pressure systems, precipitation, etc., it is vital to understand the patterns of temperature distribution in different seasons. A crucial component of your UPSC preparation is geography. Both the UPSC Prelims and Mains General Studies Paper I include it. You may study everything about Heat Budget for the IAS Exam in this post.

 Important Lakes of India, State wise and...
Important Lakes of India, State wise and...
 Buddhism History, Origin, Sect, Councils...
Buddhism History, Origin, Sect, Councils...
 Andaman and Nicobar Islands, History, Cl...
Andaman and Nicobar Islands, History, Cl...





















