Table of Contents
Grasslands in the World
In many parts of the world, there are big areas covered in grass instead of trees or forests. These places are called grasslands. They are like nature’s open fields where different plants and animals live. This article explore these grasslands and discover the special world they hold.
Read about: Tropic of Cancer and Capricorn
What is Grassland?
A grassland, in geographical terms, is a type of ecosystem characterized by open spaces covered primarily with various types of grasses and other non-woody plants. Unlike forests, which are dominated by trees, grasslands have a more open landscape with scattered trees or no trees at all. The vegetation in grasslands is adapted to thrive in areas with moderate rainfall and seasonal variations. The soil in grasslands is usually fertile, which supports the growth of different types of grasses and plants.
Read More: Pressure Belt of Earth
Types of Grasslands in the World
Grasslands are broadly classified into two main types: temperate grasslands and tropical grasslands. Each type exhibits distinct characteristics shaped by its geographical location, climate, and ecosystem dynamics.
Temperate grasslands are found in regions with moderate climates, such as North America, Europe, and Asia. These grasslands are often characterized by vast expanses of grasses, with relatively few trees. The temperature in temperate grasslands can vary greatly, with hot summers and cold winters. These areas are crucial for agriculture and livestock grazing due to their fertile soil and relatively flat terrain.
Tropical grasslands, also known as savannas, are typically situated in tropical regions, including parts of Africa, South America, and Asia. These grasslands are a blend of grasses and scattered trees, creating a unique landscape. Tropical grasslands experience distinct wet and dry seasons, influencing the types of vegetation and wildlife that can thrive there. These areas are home to a diverse range of animals and have cultural significance for local communities.
Further, these two main types of grasslands are divided into a number of subtypes with different names in various regions, each reflecting unique characteristics and adaptations. Here is a comprehensive table that highlights different types of grasslands.
List of Types of Grasslands in the World
| Types of Grasslands in the World | ||||
| S.No | Name | Region | Characteristics | Economic Importance |
| 1 | Savannas | Africa, South America, Australia | Mix of grasses and scattered trees | Grazing, ecotourism, biodiversity preservation |
| 2 | Steppes | Eurasia | Large, flat expanses, semi-arid conditions | Grazing, agriculture |
| 3 | Pampas | South America | Rich soil, moderate rainfall | Cattle ranching, agriculture |
| 4 | Prairie | North America | Fertile soil, varying precipitation | Agriculture, grazing |
| 5 | Veld | Southern Africa | Diversity of grasses, variable rainfall | Grazing, agriculture |
| 6 | Downs | Australia, New Zealand | Rolling hills, grass-dominated | Grazing, agriculture |
| 7 | Campos | South America | Wet and dry seasons, shrubs and grasses | Grazing, agriculture |
| 8 | Pustaz Grasslands | Eurasia | Semi-arid, grasses and herbs | Grazing, biodiversity conservation |
| 9 | Manchuria Grasslands | China, Russia | Cold climate, mixed grass and shrubs | Grazing, traditional land use |
Read More: Rivers of India
Grasslands World Map
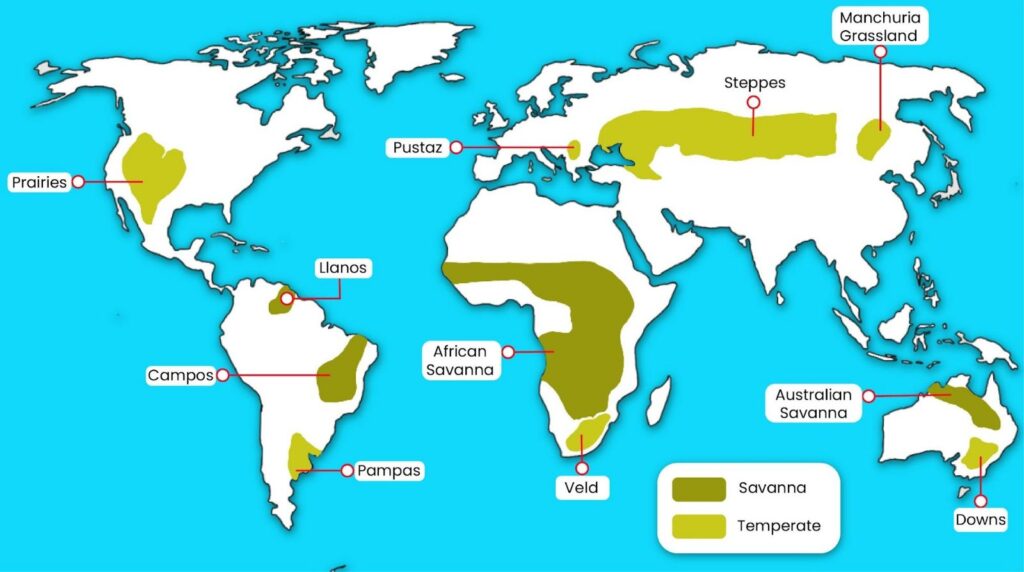
Read More: Northern Plains of India
Food Chain in the Grasslands
In the geographical context of a grassland ecosystem, a food chain illustrates how energy and nutrients flow from one living organism to another. In grasslands, the food chain typically starts with producers, organisms that create their own food through photosynthesis. These producers include various types of grasses and plants.
Herbivores, the animals that eat plants, form the next level of the food chain. In grasslands, herbivores can include animals like zebras, antelopes, and bison, which graze on the abundant grasses and plants.
Carnivores come next in the food chain. These are animals that eat other animals. In grasslands, carnivores include predators like lions, cheetahs, and wolves, which feed on the herbivores.
At the top of the food chain, there can be apex predators. These are carnivores that don’t have natural predators themselves. In some grassland ecosystems, apex predators can be animals like lions, which are at the highest level of the food chain.
The food chain in a grassland ecosystem demonstrates the interconnectedness of different organisms and how energy is transferred through the ecosystem. Producers capture energy from the sun, herbivores consume the producers, carnivores eat herbivores, and apex predators, if present, occupy the highest position in this chain. This complex interaction of organisms contributes to the balance and functioning of the grassland ecosystem on a geographical scale.
Read about: Plateaus in India
Grasslands in the World UPSC
The study of grasslands around the world holds significant importance within the UPSC (Union Public Service Commission) examination framework due to its relevance to the UPSC syllabus and the comprehensive preparation required for the exam.
Grasslands, a key topic covered in the UPSC Syllabus, align with environmental geography and biodiversity, making them essential for aspirants pursuing online coaching for the UPSC exam. Aspirants often encounter questions related to global ecosystems, conservation strategies, and sustainable land use, all of which grasslands encompass. Aspirant can master such topics by joining UPSC Online Coaching platforms and practicing UPSC Mock Test.
Read about: Types of Rocks

 Jallianwala Bagh Massacre, Date, History...
Jallianwala Bagh Massacre, Date, History...
 Important Lakes of India, State wise and...
Important Lakes of India, State wise and...
 Buddhism History, Origin, Sect, Councils...
Buddhism History, Origin, Sect, Councils...





















