Table of Contents
Google’s First Corporate Nuclear Energy Deal
- Google has been an industry leader in clean energy, with its first 20-year wind farm power purchase agreement (PPA) dating back to 2010.
- The company is seeking alternative energy sources like nuclear due to challenges in renewable energy such as intermittency and storage limitations.
- The agreement involves purchasing energy from small modular reactors (SMRs) developed by Kairos Power, a California-based company.
- This initiative aims to power Google’s artificial intelligence (AI) data centres with clean & reliable nuclear energy.
| Did You Know |
|
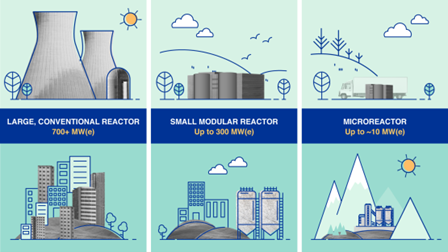
What are SMR’s?
- SMR’s are:
- Small: A fraction of the size of a conventional nuclear power reactor.
- Modular: Systems and components to be factory-assembled and transported as a unit to a location for installation.
- Reactors: Harnessing nuclear fission to generate heat to produce energy.
- Power capacity: Up to 300 MW(e) per unit, which is about one-third of the generating capacity of nuclear power reactor
- Key features and benefits of Small Modular Reactors (SMRs)
- Size and Portability: SMRs are smaller and more compact than conventional reactors, allowing for easier transport, installation and scalability.
- Enhanced Safety Features: SMRs incorporate advanced safety features to ensure the protection of the public and the environment. These features include passive cooling systems, advanced control mechanisms, and robust containment structures.
- Flexibility and Grid Resilience: Their smaller size and modular nature make them suitable for deployment in remote areas or as a supplement to existing power grids, enhancing grid resilience.
- Reduced Capital Costs: The modular design of SMRs allows for standardised manufacturing processes, potentially reducing construction costs.
- Potential for Decentralization: SMRs offer the potential for decentralised power generation, allowing communities or industries to have their own local sources of electricity.
- Integration with Renewable Energy: SMRs can complement renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, by providing baseload power and maintaining grid stability during periods of low renewable generation.
| International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) |
|


 New Ramsar Sites in India: Latest Additi...
New Ramsar Sites in India: Latest Additi...
 Lok Adalats in India: Meaning, Types, Ca...
Lok Adalats in India: Meaning, Types, Ca...
 New Insurance Bill, 2025: Key Provisions...
New Insurance Bill, 2025: Key Provisions...

























