Table of Contents
What is Global Warming?
Global Warming is a long-term increase in average global temperature. It is considered a natural phenomenon but anthropogenic activities on earth, particularly post Industrial Revolution, have led to an increase in the rate of this temperature increase. Reports from the International Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) show that human activities have raised the average global temperature by about 1 degree Celsius since 1850, with most of this warming occurring in the latter half of the 20th century. The fact that 5 of the hottest years ever recorded happened since 2015 shows us how much human activities are hurting the planet.
Global Warming Causes
Green House Gases also known as GHGs in the atmosphere trap the solar radiations that are reflected by the earth’s surface.
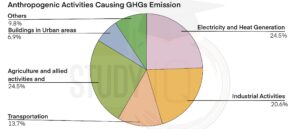
Normally, most of the Earth’s radiation escapes into space. But human activities have increased greenhouse gases (GHGs) in the atmosphere, causing the planet to heat up. Common GHGs include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and water vapor. Each gas has a different warming effect; for instance, methane is 25 times more powerful than carbon dioxide, and nitrous oxide is over 250 times stronger. The top anthropogenic activities that are responsible for the release of GHGs are shown below.
Global Warming and Green House Effect
Both phenomena are related to each other. Green House Gases also known as GHGs in the atmosphere trap the solar radiations that are reflected by the earth’s surface. Under normal circumstances, most of these radiations escape into outer space. However, the release of GHGs by anthropogenic activities has increased their concentration in the atmosphere. This is the primary cause of Global Warming.
Global Warming Effects
Increase in the Average Temperature of the Earth
According to IPCC reports, human-induced global warming is responsible for nearly 1 degree Celsius temperature rise vis a vis pre-industrial level. Data from NASA suggest that 2016 has been the hottest year on record.
Frequency of Extreme Weather Events is Increasing
Extreme weather events are happening more often around the world. For example, forest fires in California are now a yearly occurrence and are getting more frequent. We’ve also seen heat waves in Antarctica recently, and cyclones in the Bay of Bengal are becoming stronger. Similarly, the frequency of occurrence of El Niño and La Niña has reduced from once in 8–10 years to once in 3–4 years now. More frequent episodes of floods and drought are being recorded every year across the world.
Melting of Ice
According to IPCC, there is 10% less permafrost in North Hemisphere at present compared to the 1900s. Remote sensing data suggest Arctic ice is melting fast. Experts suggest that not only will the sea level rise with the melting of glaciers, but there is also a danger of new bacteria and viruses being released into the environment which has so far been trapped in ice sheets. This may lead to outbreaks of disease and pandemics which are beyond the control of human medical sciences.
Sea Level Rise and Acidification of Ocean
A report published by WMO, suggests that the rate of sea level rise has doubled for the period between 2013 and 2021 compared to the rate for the period between 1993 and 2002. Earth scientists warn that if this continues, many coastal areas where people live could be underwater in the coming years. Rising carbon dioxide levels are also causing oceans to absorb more CO2, leading to ocean acidification. This can be harmful to ocean life, especially coral reefs.
Adverse Impact on Terrestrial Ecosystems of the Earth
It has been recorded that many flora and fauna species are heading northwards in Northern Hemisphere, changes have been observed in the migratory movements of birds across the world. Animals are arriving early at their summer feeding and breeding grounds. Experts say rising temperatures in tropical and subtropical areas could cause new diseases, putting many plants and animals at risk of extinction.
Social and Economic Impact
A rising number of extreme weather events will have an adverse impact on agriculture and fisheries. Rising global temperatures will have a negative impact on the productivity of human beings, particularly in tropical and subtropical regions of the earth. The impact on life and livelihoods of indigenous people across the world will be even more pronounced.
Global Warming Solutions
Global Cooperation for Reduction of Emissions
We need to take the goal of keeping the global temperature rise within 1.5 degrees Celsius seriously. Global efforts should recognize that all countries have different responsibilities. This means acknowledging past injustices faced by developing countries and giving them a fair chance to grow. Countries must work quickly to reach Net Zero Emissions as soon as possible.
Transition to Cleaner and Greener Forms of Energy
Coal-based power plants should be made more efficient, and the inefficient ones should be closed down. We should promote the use of renewable energy like solar power and explore hydrogen as a fuel. Also, we need to look into nuclear fusion for energy and make nuclear fission safer.
Changes in Agricultural Practices and Land Use
Agriculture based on the use of nitrogenous fertilizers must be replaced with organic farming techniques. We should capture methane gas from farms and animal waste to use as biogas at home. There should be large tree-planting efforts, and city governments need to make sure to include green spaces in their plans.
Improving Transportation System
The rise of electric vehicles is great, but we need better batteries for them. City planners should focus on improving public transportation and design cities to encourage more walking and cycling.
Behavioural Changes
All the above discussions will have no meaning if we as individuals are not sensitive enough. We need to make reducing, reusing and recycling a mantra of our living. It should be our civic duty to save water, and wildlife and raise awareness among others.
Solar Geoengineering
Solar geoengineering, a proposed climate intervention method focus to counteract global warming by reflecting a portion of the sun’s rays back into space. One method involves injecting sulfur dioxide into the upper atmosphere to create reflective particles that can scatter sunlight and cool the Earth. However, solar geoengineering is controversial because it may disrupt weather patterns and create geopolitical risks. Research in this field is ongoing, but it remains a theoretical concept with limited practical implementation.
Can Solar Geoengineering Halt Global Warming?
Solar geoengineering is also called solar radiation management (SRM) is being studied as a way to reduce global warming by reflecting sunlight away from Earth. This could involve injecting substances like sulfur dioxide into the atmosphere to create reflective aerosols. However, its effectiveness and potential side effects raise concerns, and it is still mostly theoretical with little practical use so far.
Global Warming Conclusion
It’s often said that “charity begins at home,” and this idea applies to climate action too. Each person can start by ensuring their home and nearby areas are eco-friendly. When individuals do this it helps make local, national, and global policies more effective.
Global Warming UPSC
Each year, we read about rising global temperatures. Also, catching the headlines is the news related to disasters caused by events like cyclones, forest fires, floods and drought. All these phenomena can be attributed to one single cause which is global warming.
Global Warming is a long-term increase in average global temperature. It is considered a natural phenomenon, but anthropogenic activities on earth, particularly post-Industrial Revolution, have led to an increase in the rate of this temperature increase.


 Goods and Services Tax (GST), Objectives...
Goods and Services Tax (GST), Objectives...
 World Oceans Day 2025, History, Theme, S...
World Oceans Day 2025, History, Theme, S...
 World Environment Day 2025, Theme, Histo...
World Environment Day 2025, Theme, Histo...





















