Table of Contents
Context: An expert committee constituted by the Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change recommended a proposal to rebuild the Teesta-3 dam on the Teesta river in Sikkim
Glacial Lakes
- Formation: Created by meltwater accumulating in depressions left by retreating glaciers.
- Types: ISRO categorised glacial lakes into four types: moraine-dammed, ice-dammed, erosion-based, and others.
- Moraine-dammed lakes are formed by water dammed by debris left by glaciers.
- Ice-dammed lakes are formed by water dammed by ice.
- Erosion-based lakes are formed by water trapped in depressions created by erosion.
- Importance: Source of freshwater for rivers.
Risks of Glacial Lakes
- Glacial lake outburst floods (GLOFs) can have devastating consequences downstream.
- GLOFs occur when large volumes of meltwater are released due to dam failures.
- Dam failures can be triggered by avalanches or other factors.
| Situation in Uttarakhand |
Uttarakhand has 13 glacial lakes that are susceptible to Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs).
|
Glacial lake outburst floods (GLOFs)
- Definition: A GLOF is a flood that occurs when water dammed by a Glacial Moraine is released suddenly.
- Features of GLOF: Glacier Lake Outburst flood has three main features
- Involves sudden (and sometimes cyclic) releases of water.
- These are rapid events, lasting hours to days.
- These result in large downstream river discharges, which often result in catastrophic flooding or disasters
Examples of GLOF-related disasters
- 1926 Jammu and Kashmir deluge
- 1981 Kinnaur valley floods in Himachal Pradesh
- 2013 Kedarnath outburst in Uttarakhand
- 2023 Sikkim GLOF event: A combination of excess rainfall + series of earthquakes in Nepal may have caused the Sikkim GLOF event.
Reasons for Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs)
- Melting of Glaciers: As global temperatures rise, glaciers are melting more quickly, causing glacial lakes to fill with water.
- The increased water level puts pressure on the lake’s natural boundaries, which are often made of unstable ice and debris.
- When these boundaries break, it can lead to a GLOF.
- Avalanches and Earthquakes: Landslides or ice avalanches near glacial lakes can push large amounts of water, causing the natural dams to burst and trigger a GLOF.
- Earthquakes can also destabilise the area, leading to a similar effect.
- Extreme Weather Conditions: Heavy rainfall, severe storms, or sudden changes in temperature can weaken the stability of glacial lakes, increasing the likelihood of a GLOF.
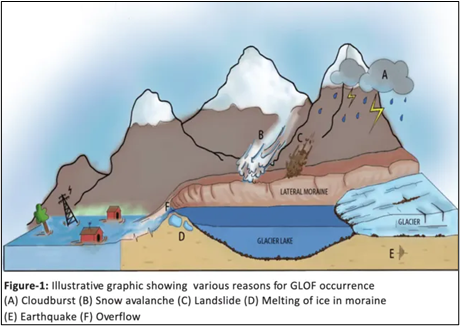
- Climate Change: The Himalayan-Hindukush region, which is highly affected by climate change, is seeing accelerated glacier melting.
- This leads to the formation of more glacial lakes, raising the risk of GLOFs.
- Climate change is also causing more frequent and intense cloudbursts, further contributing to GLOFs.
- Volcanic Activity: In regions near volcanoes, volcanic activity can heat glaciers and cause them to melt faster, increasing the risk of a GLOF.
- Weak Moraine Embankments: Moraines, which are piles of debris left by glaciers, often act as natural dams for glacial lakes.
- However, these moraines can be weak and prone to breaking, leading to GLOFs.
- Human Activities: Infrastructure projects like dams and roads in mountainous areas can add stress to the landscape, making GLOFs more likely.
- Example: 2021 Chamoli GLOF, which was linked to multiple hydroelectric projects in the area.
| Reason For Vulnerabilities of GLOF in Himalayan Region |
The Himalayan states of India, such as Uttarakhand, Sikkim, and Himachal Pradesh, are highly vulnerable to GLOFs due to several factors:
|
Impacts of Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs)
Loss of Life and Property
- GLOFs can lead to significant loss of life and destruction of property, including houses, bridges, roads, forests, and farmland, as well as livestock and crops.
- Example: GLOF in Sikkim, India, in October 2023 resulted in the deaths of at least 18 people and left over 150 missing.
- Similarly, a GLOF in Uttarakhand, India, in June 2013 claimed over 5,000 lives and caused extensive damage to hydropower projects.
Disruption of Livelihoods
- GLOFs can disrupt the livelihoods of local communities for extended periods by limiting their access to resources, markets, services, and opportunities.
- Additionally, GLOFs can harm the tourism industry, which is a critical source of income in many mountainous regions.
Damage to Infrastructure and Environment
- GLOFs can damage or destroy key infrastructure, such as hydropower plants, which are vital for electricity generation and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- GLOFs can also significantly alter the landscape, erode soil, increase sediment in rivers, and negatively impact water quality and availability.
Mitigating the Risks of Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs)
Identifying Potentially Dangerous Lakes
Identifying lakes that pose a high risk requires a multidisciplinary approach.
- This includes field observations, studying historical records, and analysing the geomorphological and geotechnical features of the area.
- Such information is crucial for prioritising monitoring efforts and implementing risk-reduction strategies.
Use of Technology
Leveraging technology like synthetic-perture radar (SAR) imagery can significantly improve early warning systems.
- Satellite remote sensing is a valuable tool due to:
- Wide coverage
- Revisit capability
- Satellite data helps understand glacial lake dynamics for:
- Environmental impact assessment
- Developing strategies for:
- GLOF risk management
- Climate change adaptation
|
Fact |
|
Channelling Potential Floods
Structural management of lakes is key to reducing GLOF risks.
- Techniques such as controlled breaching, pumping out excess water, and constructing tunnels can help lower the water levels in lakes, thereby minimising the threat of a GLOF.
- These interventions must be carefully planned and executed to avoid adverse effects downstream.
Uniform Codes for Construction Activity
- Establishing uniform construction codes for infrastructure and land use in GLOF-prone areas is vital.
- These codes should account for geological and hydrological risks and incorporate mitigation measures into construction projects to ensure safety.
| GLOF Risk Mitigation |
|
Enhancing Early Warning Systems (EWS)
Early warning systems are essential for disaster preparedness.
- Implementing sensor-based and monitoring-based technical systems for GLOF early warnings can provide timely alerts to vulnerable communities.
- Expanding the reach of these systems is particularly important in areas prone to GLOFs.
Training Local Manpower
Local communities are crucial in disaster response and preparedness.
- Training local personnel in GLOF response can enhance their ability to act swiftly and effectively.
- These trained individuals can lead search and rescue operations, help set up emergency shelters, and manage relief distribution, forming the first line of defence during disasters.
Comprehensive Alarm Systems
- Modern communication technologies, such as cell phones and smartphones, can complement or replace traditional alarm systems.
- Using these technologies for mass notification can ensure that timely warnings reach a broader audience, improving disaster response and preparedness.
Tragedy at South Lhonak Lake
In October 2023, a glacial lake outburst flood (GLOF) from South Lhonak Lake in Sikkim caused the catastrophic destruction of the Teesta-3 dam and its hydroelectric facility. The flood, triggered by a slope failure in a moraine (glacial debris) on the lake’s flank, released nearly 50 billion litres of water into the valley, leading to landslides and severe downstream damage. The disaster resulted in over 100 deaths and affected more than 80,000 people across four districts.
Factors Increasing Vulnerability
- Climate Change & Glacier Melt – Rising temperatures and black carbon (soot) accelerate Himalayan glacier melting, leading to larger and more unstable glacial lakes.
- Geological Instability – Glacier retreat weakens surrounding landforms, increasing risks of landslides and moraine collapses.
- Deficiencies in Risk Modelling – Current GLOF assessment models fail to fully account for erosion, sediment transport, and riverbank collapses, making predictions unreliable.
- Hydropower Infrastructure Risks – Large dams in seismically active and landslide-prone regions add to vulnerabilities, as infrastructure failure can amplify disaster impacts.
- Inadequate Early-Warning Systems – The region lacked robust monitoring and alert mechanisms, delaying evacuation and disaster response.
Improvements in the New Construction (Teesta-3 2.0)
- Concrete-only Structure – Unlike the original rock-and-concrete design, the new dam will be built entirely of reinforced concrete for better resilience.
- Larger Spillway – The spillway capacity has been tripled to handle extreme flooding scenarios.
- Early-Warning System – A real-time monitoring and flood alert system is planned to improve response times.
- Climate Adaptation Modelling – The design is based on “worst-case scenario” rainfall predictions over the next century.
What Needs to be Done?
- Holistic Risk Assessment – Factor in climate change-driven uncertainties, including sediment dynamics, moraine stability, and extreme weather patterns.
- Stronger Environmental Regulations – Conduct independent impact assessments before rebuilding, considering downstream risks.
- Community Resilience – Strengthen disaster preparedness, evacuation plans, and compensation mechanisms for local populations.
- Alternative Energy Solutions – Reduce dependence on large hydro projects in high-risk areas and explore solar, wind, and smaller hydro alternatives.
- Sustainable Development Framework – Ensure hydropower viability without externalizing social and environmental costs, integrating local concerns into decision-making.


 Rare Earth Elements, Metals, Magnets, Ap...
Rare Earth Elements, Metals, Magnets, Ap...
 Places in News for UPSC 2025 for Prelims...
Places in News for UPSC 2025 for Prelims...
 Indian Continental Plate is Splitting Ap...
Indian Continental Plate is Splitting Ap...





















